EOC differentiation cubing
advertisement

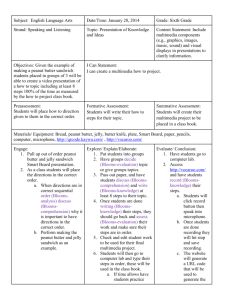
Econ EOC Cubing This activity requires students to look at a topic from six different angles. You can either make the cubes with the questions on it or you can use a die to correspond to the numbers on each activity. Introducing Cubing to your class: Use a Reese’s peanut butter cup to explain the concept. 1) Hand out Peanut butter cups to students 2) assign groups to look (or study) the candy from several angles. 3) Using the candy as the topic, ask students to: • Describe It: What does the candy look like? • Compare It: Compare the peanut butter cup to something else. What is it similar to or different from? • Associate It: What do you associate peanut butter cups with? What does it make you think about? • Analyze It: Describe what the peanut butter cup is made of. What are its parts? What are the ingredients? • Apply It: What can you do with a peanut butter cup other than just eat it from the bag? • Argue For or Against It: Present an argument for why the peanut butter cup is or is not the best candy. Differentiated Lesson Plan Grade:ECONOMICS Unit: End Of Course Review Key Concept: EOC preparation Standard: All standards based on individualized needs Vocabulary for Concept: dependent on unit of need Formative Assessment for DI: Thinkgate results over the course of the year showing areas of concern Mini-Lesson (s): Day 1-3: Review lectures on the 5 units of Economics Differentiated Lesson or Task: CUBING Start in group that is greatest concern (based on test scores). o For each student write 1-5 (weakest to strongest) to show which order the student should rotate in groups. Aim to keep groups at a maximum of 4 Have each student roll the die. Start with the youngest person in the group. o Each student will answer the question corresponding to the number rolled on the die. o Have other 3 members of table check the answer. If same number is rolled again, have the student say something additional that wasn’t initially stated. Once all members have rolled (or all numbers are answered) have students move to the next group – based on each person’s area of weakness. ----- you can also put a time limit on this so students can get to all groups and there is no lag time. Group 1: (Fundamental) • 1 - What does scarcity mean? • 2 - Compare a nation’s decision on whether to make cookies or candy bars based on opportunity cost and the production possibilities curve. • 3 - What can you associate with each of the factors of production? - What roles do each play in the production of goods? • 4 - Analyze why a nation would implement government regulations and why, in some cases, a nation would deregulate. • 5 - What ways can a nation use the factors of production based on their Economic system? - Which concepts do these nations believe in – freedom, security, growth, efficiency, and/or stability? • 6 - Present an argument for or against the use of specialization in a business or nation. Group 2: (Microeconomics) • 1 - How do businesses and individuals interact in the circular flow? - What role does money play? • 2 - Compare and contrast the 3 forms of business organizations. • 3 - What do you associate with the different types of market structures in terms of number of firms, types of products, and varying prices? • 4 - Describe the factors that shift supply and demand. - Analyze what occurs to equilibrium when supply and demand shift. • 5 - What is the purpose of a price floor and price ceiling? - What is the impact of these government regulations? • 6 - Present an argument on why some goods are elastic in their supply and demand and why other goods are inelastic in their supply and demand. (Give examples of each). Tier 3: (Macroeconomics) 1- Describe the ways that we measure the economy. (GDP, Business Cycle, Inflation, AS/AD, unemployment) 2 - Compare Tight Monetary Policy to Easy Monetary Policy. - Compare Expansionary Fiscal Policy to Contractionary/Restrictive Fiscal Policy. 3 - What do you associate the four types of unemployment with (examples)? - What do the four types of unemployment make you think about? 4 - Describe the components of GDP. - What are its parts? How is it calculated? 5 - Where on the Business cycle do the following occur (expansion or contraction): GDP increasing, unemployment decreasing, inflation, decrease aggregate supply/demand, decrease in required reserve, increase in interest rate, decrease in taxes, increase in government spending. 6 - Present an argument for and against using deficit spending, based on the three Fiscal policy theories (supply side, demand side, classic). Tier 4: (International) 1- What is the difference between absolute advantage and comparative advantage? - Which would a nation rather have? 2- How are “balance of trade” and “balance of payments similar?” - How are they different? 3- Give a definition of each trade barrier (quota, embargo, standard.) - Provide an example of one. 4- Describe NAFTA, EU, and ASEAN. - Why were they created? - How do they help/hurt the participating nations? 5 - Why is it important to know about exchange rates? - If 1(one) Mexican Peso is equal to 0.065 U.S. Dollars, how many Pesos could you get for $100? 6 - Present an argument for why a nation would want a strong U.S. dollar over a weak U.S. dollar. Tier 5: (Personal Finance) 1- What is insurance? - Why do people purchase it? - What types of insurance are there? 2- Compare the different types of taxes. - How are progressive, regressive, and proportional taxes similar? How are they different? 3 - What do you associate with the functions of financial institutions? - How does this association change based on what type of financial institution it is? 4 - Describe credit. - Why is having “good” credit better than having “bad” credit? - How do people use credit? 5 - What is the difference between interest charged and interest earned? - When would it be good to have a high interest rate? When would it be bad to have a high interest rate? 6 - Present an argument for why saving your money is important. - Present an argument for spending your money instead of saving.