File - Marketing (D)
advertisement

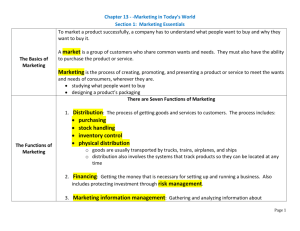
Defining Marketing for 21st century What is Marketing? “ marketing is about identifying and meeting human and social needs with profit” “marketing includes all the activities from the product manufacturing till it been used” Core Marketing Concepts • Needs, wants and demands: – Needs are the basic human requirements – These needs become want when they are directed to specific objects that might satisfy the need. – Demands are wants for specific products backed by an ability to pay. Marketers do not develop needs they influence wants. • Target markets,Positioning, and segmentation. – Marketers start by dividing the market into segments. They identify and profile distinct groups of buyer who might prefer distinct groups. – After identifying segment the marketer then decides which present the greatest opportunity-which are its target market. – The firm develops a market offering that it positions in the minds of the target buyers as delivering some central benefit. • Offerings and brands: – Value proposition, a set of tangible and intangible benefits that they offer to customer to satisfy their needs. – A brand is an offering from a known source. • Value and satisfaction: – Value reflects the sum of the perceived tangible and intangible benefits and costs to customers. It’s primarily a combination of quality, service and price called the “customer value triad”. – Satisfaction reflects a person’s judgment of a product’s perceived performance in relationship to expectations. • Marketing channels: – The marketer uses three kinds of marketing channels. • Communication channels deliver and receive messages from target buyers and include newspaper, magazines, radio, television, mail, telephone, billboards, posters. • Distribution channels to display, sell, or deliver the physical product or services to the buyer or user. Like distributor, wholesalers, retailers and agents. • Service channels are used to carry out the transaction with potential buyers. Service channels include warehouses, transportation companies, banks and insurance companies. • Supply chain: – It’s a longer channel stretching from raw materials to components to final products that are carried to final buyers. • Competition: – Includes all the actual and potential rival offerings and substitutes a buyer might consider. – Close competitors: the product have almost same features as your product has. – Distant competitors: the product which has same basic function as your has. • Marketing Environment: the marketing environment consist of the task environment and board environment. • The micro environment includes the actors that affect the company’s ability to serve its customers. The company suppliers, marketing intermediaries, customer markets, competitors and publics. • The board environment consist of six components – – – – – – Demographic environment Economic environment Physical environment Technological environment Political - legal environment Social-cultural environment Company Orientation towards market place Evolution of marketing ideas. • The production concept: – One of the oldest concepts in business – It holds that consumer will prefer products that are widely available and inexpensive. – Managers of production-oriented businesses concentrate on achieving high production efficiency, low cost and mass distribution. • The product concept: – The product concept proposes that consumers favor products that offer the most quality performance, or innovative features. – Managers in these organizations focus on making superior products and improving them over time. • The selling concept: – The purpose of marketing is to sell more stuff to more people more often for more money in order to make more profit. – Their aim is to sell what they make rather than make what the market wants. – This concept is practiced most aggressively with unsought goods. • The marketing concept: – Instead of “make and sale” product centered philosophy, business shifted to customer centered “sense and respond” philosophy. – The job is not to find the right customer for your product but to find the right product for your customer. – The marketing concept holds that the key to achieving organizational goal is more effective than competitors in creating, delivering and communicating superior customer value to your chosen target market. • The marketing concept: (continued) – Reactive market orientation: understanding and meeting expressed customers’ needs. – Proactive marketing orientation: respond to the customers’ latent needs. – Total market orientation: companies that practice both a reactive and a proactive marketing orientation. • The Holistic Market concept: – It recognize that every thing matters in marketing. – There are four broad components characterizing holistic marketing: • Relationship marketing • Integrated marketing • Internal marketing • Performance marketing – Successful companies are those that can keep their marketing changing with the change in their marketplace and market space “breakthrough marketing” • Relationship Marketing: it aims to build mutually satisfying long-term relationships with key constituents in order to earn and retain business. The four key constituents for relationship marketing are – – – – Customers Employees Marketing partners (channels, suppliers, distributors, dealers, agencies) Member of financial community (shareholder, investors, analysts) The ultimate outcome of relationship marketing is a unique company asset called marketing network. Consist of company and its supporting stakeholders, customers, employees, suppliers, distributors, retailers, ad agencies and others. • Integrated Marketing: the marketer’s task is to device marketing activities and assemble fully integrated marketing programs to create, communicate, and deliver value to customers. these marketing activities are classified as marketing mix which consist of four Ps of marketing. – – – – Product Price (psychological, cost plus, premium pricing, economy) Promotion Place • Internal marketing: management philosophy is to promoting the firm and its policies to employees as if they are the internal customers of the firm. If a company can operate in a coordinated and standardized way that company can provide a more consistent experience to the customers. • Performance Marketing: holistic marketing incorporates performance marketing and understanding the return to the business from marketing activities and programs, as well as addressing broader concerns and their legal, ethical, social and environmental effect. – Financial Accountability: marketers are asked to justify their investments to senior management in financial and profitability terms. – Social Responsibility Marketing: marketers must carefully consider their role in broader terms, and the ethical, environmental, legal and social context of their activities.