5' primer - Biology Department
advertisement

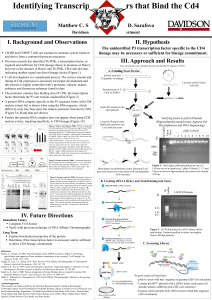
A Potential Second Promoter in the Cd4 Gene that Functions at the Double Positive Stage of Development Walker Shaw and Sophia Sarafova Biology Department, Davidson College, Davidson, NC 28036 QuickTime™ and a TIFF (Uncompressed) decompressor are needed to see this picture. Abstract Methods Cd4 gene expression is regulated by several different known transcriptional elements, including a silencer, a promoter, an immature enhancer, a distal enhancer, and a proximal enhancer. Different combinations of these elements are employed to regulate Cd4 expression in mature CD4 cells versus immature double positive (DP) cells. In humans an additional transcriptional control element has been described that serves as a second promoter for Cd4 and is proposed to be responsible for Cd4 expression in macrophages and some dendritic cells. Since mice do not have cell surface expression of CD4 in the macrophage, the presence of a second promoter and its potential function during T cell development has not been investigated so far. To determine if a second promoter is present in the first intron of the Cd4 gene and utilized during the DP stage of T cell development, we looked for new transcription start sites in RNA from murine DP cells by 5’RACE. In addition to the expected 320bp band that indicates transcription from the known promoter, we observed a strong 500bp band, indicating that there is another transcription start site in the Cd4 gene. We are in the process of cloning and sequencing all the Cd4 transcription products and identifying the second promoter. Whether the putative second promoter is used in mature CD4 cells remains to be determined. Results Our FACS stain data showed that PNA panning of thymocytes decreased the CD4 cell contamination by 78% (compare A and B) yielding a 95% pure DP cell population (B), which was used for RNA isolation and 5’ RACE. Thymus cells PNA Cell Panning Reserve for FACS staining Cells Stick to Plate Immunostaining of Cells CD8 antibody Tagged with FITC CD4 Locus … ? P Ex1 Sil TATA ATG Ex2 Ex3 Ex4 Ex5 DPe … Known mRNA Product ATG Ex1 Ex2 Ex3 Ex4 Ex5 Potential DP mRNA Product ATG Ex2 Ex3 Ex4 Ex5 … … CD4 antibody Tagged with PE Check purity By FACS CD4 Two color immunostaining and flowcytometry of PNA-panned B10.A thymocytes 95.58% 1.52% 500bp 320bp 1 2 3 4 Primer dimers We identified a second transcription start site for the murine Cd4 gene, located in the first intron, that functions at the DP stage of T cell development . We think it may represent a second promoter in the Cd4 gene, similar to the one described in humans. To confirm the presence, identify, and understand the function of this transcriptional control element we will BEADS Avidin-coated beads Bind mRNA to BEADS 5’-primer TTTTTTT biotin mRNA bound 5’ primer TTTTTTT-3’ 3’-AAAAAAA-----5’ mRNA in solution 5’ RACE In Solution 5’-primerTTTT 3’AAAA------5’ Reverse transcription of the first strand; Cs added on 3’ end by the reverse transcriptase. (same products, not attached to beads) 5’-primer TTTT------------CCC-3’ 3’-GGG-capfinder CD4 Cd4 gene transcription products were visualized by RT followed by Rapid Amplification of cDNA 5’ Ends (5’ RACE) and agarose gel electrophoresis (C). Normally, a 320bp product is expected if the known Cd4 promoter is used in the DP cells. Products of larger size are unexpected and can be explained only if Cd4 transcription is initiated from a different promoter in DP cells (occurring in intron 1). We observed 1000 900 800 both the 320bp and a larger product 700 600 500 (lanes 3 and 4 gray and black 400 arrows), indicating that an additional 300 transcription initiation site exists in 200 DP cells. The bands in lanes 1 and 100 2 represent DNA contamination. Conclusions and Future Work Isolate Panned Cells’ RNA with Trizol® 5’ RACE on Beads 6.91% C Background Information CD4 is a transmembrane glycoprotein expressed on the cell surface of thymocytes and mature T- lymphocytes with helper function. T-cells develop in the thymus and their stages of development are defined by the level of CD4 and CD8 expression. Briefly, T-cell progenitors enter the thymus as DN cells, expressing no CD4 or CD8 on their cell surface. Upon successful rearrangement of TCR they develop into DP thymocytes, which express both CD4 and CD8. Finally, positively selected DP thymocytes differentiate into CD4 or CD8 single positive cells. The DP enhancer is necessary for the expression of CD4 protein in DP cells. We speculate that there could be a different, unknown promoter region that is “turned on” by this DP enhancer instead of or in addition to the promoter used for CD4 expression in mature T-helper cells. The diagram below shows the Cd4 gene and the transcriptional elements that regulate CD4 expression. It also shows how a potential secondary promoter could express the same protein. 84.37% B PNA Cells Float A Two color immunostaining and flowcytometry of fresh B10.A thymocytes • Repeat current work with a FACS sorted pure population of DP cells. • Repeat the analysis using CD4 SP cells to determine if the alternate transcription start site is unique to DP cells. • Purify and sequence the DNA segments from the 5’ RACE to determine the potential alternate transcription start site(s) and help look for a potential promoter. •Identify the putative second promoter of the Cd4 gene by transient transfection into AKR1G1 double positive cell line of constructs containing DNA from upstream of the newly identified transcription start site. Reverse transcription of the second strand using capfinder 5’-primer TTTT------------------CCC-3’ 3’-primer AAAA -----------------GGG-capfinder-5’ cDNA products PCR using Cd4 specific exon3 primer exon3 5’-primer TTTT--------------------------------CCC-3’ 3’-primer AAAA -------------------------------GGG-capfinder-5’ GGG-capfinder exon3----capfinder exon3----capfinder Analyze PCR products on agarose gel (see Results) Acknowledgements We would like to thank Amy Becton for maintaining our mouse colony, Susan Sharrow (NCI, EIB) for antibodies and FACS advice, and Terry Guinter (NCI, EIB) for help with the PNA panning protocol.