The Renaissance
advertisement

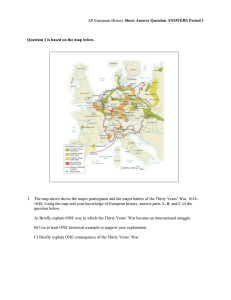
RELIGIOUS WARS Late 16th to early 17th centuries BIG IDEA Religious pluralism challenged the concept of a unified Europe The struggle for sovereignty within the among states resulted in varying degrees of political centralization THE MODERN STATE Tax collection Military force Dispensing justice Right to determine religion for subjects FRENCH WARS OF RELIGION 1562-1598 Growing monarchical power Taille military Power of nobility diminishing urbanization Calvinism (Huguenots) (Bourbon) v. Catholics (Guise) Henry IV (Bourbon) Politique – sacrifice religion for peace Converts to Catholicism Edict of Nantes religious rights to Huguenots Freedom of public worship Right to assembly Admission to public offices and universities Permission to main fortified towns ENGLISH CIVIL WAR Elizabeth I – kept peace between the Anglicans and the Puritans (Calvinists) English Parliament challenged the authority of the king Sympathetic to the Puritans James I – divine right of kings Charles I – Long Parliament cut off revenue for wars English Civil War (1642-1649) Cavaliers v. Roundheads Cromwell abolished the monarchy HABSBURGS Holy Roman Emperors controlled Austria, Spain, Italy, Netherland, Hungary Treaty of Augsburg (1555) Fight between Catholic Charles V and Protestant German princes Recognized Lutheran Church Secularization of Church lands All princes could choose the religion of their lands and subjects Charles V abdicates Phillip II of Spain militant Catholicism Revolts in Netherlands unsuccessful England defeated Spanish Armanda decline in Spanish power and rise of England THIRTY YEARS WAR Causes Growth of Calvinism Peace of Augsburg only allowed Lutheran worship Resurgence of Catholicism Four Phases Bohemian (1618-1625) wiped out Protestantism Danish (1625-1629) Edict of Restitution (forbade all Protestants except Lutherans from worship Swedish (1630-1635) turns tide towards Protestants, France enters war on side of Protestants French (1635-1648) complete destruction of German states (international) PEACE OF WESTPHALIA (1648) Turning point (end of the first period of APEH 1450-1648) 1. Recognized the sovereignty of the German princes Declare war and make peace Destruction of the Holy Roman Empire emperor left with no centralize rule 2. Change in terriotory Netherlands and Swiss recognized as sovereign (Habsburg) France and Sweden take German lands France allowed to intervene in German affairs 3. Augsburg upheld Calvinism now included North German states – Protestant South German states – Catholic PEACE OF WESTPHALIA (1648) Long term impacts Decrease in the Habsburg power Germany remained fragmented no real role in European affairs France, England and Netherland rise in power Fragmented Europe constantly rebalancing power