Ethnographic Techniques
advertisement

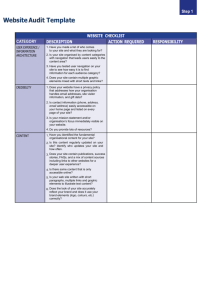
An Investigation into Web Site Design Practice Mark Newman March 16, 1999 U. C. Berkeley InfoSys 213 http://guir.berkeley.edu Outline • • • • Motivation Methodology Overview of Investigation Design process – Artifacts • Sketching • Implications for Design Tool Motivation • Interested in informal interfaces – allow natural modes of input • speaking, writing, sketching, gesturing – allow preservation of intended ambiguity • Web design is a good testbed – “creative” activity – relatively new area of design – many designers sketch on paper Learning About Web Design • Read published literature? – mostly prescriptive, not descriptive – little focus on process or early design • mostly tricks-of-the-trade, rules-of-thumb • Go to the source – interact directly with professional designers, to learn what they do – take an ethnographic approach An “Ethnographic Approach”? • Ethnography originated in anthropology to study “exotic” cultures – Over time, applied to cultures “closer to home” • Not a method, but an approach based on – – – – natural settings holism representing members’ point of view descriptiveness (Blomberg, 1993) “Classic” Ethnography Ethnography and HCI • More recently, growing interest in applying ethnography to system design – e.g. Hughes, et al. air traffic controllers study Ethnography and HCI • Not easy to merge ethnography with design – time & market pressures – engineers & qualitative data? • Various techniques have emerged – “Quick-and-dirty” Ethnography – Contextual Inquiry – Video Re-presentation ... inspired by ethnography Overview of Investigation • Field visits to four companies – three design firms – one design department of web “portal” – in addition: two independent consultants • In situ interviews with designers – placed focus on specific projects • Collection of artifacts – used artifacts to frame discussion Who They Were • 11 interviews total • Training & Education – 7 graphic design, 2 computer science, 1 cognitive science, 1 other • Current responsibilities – 4 graphic design, 3 UI design, 4 hybrid • Professional experience – 7 had < 5 years experience – others 8, 10, 20+ “Results” (Observations) • Design specialties – different dimensions of “web design” – how they are related • Design process – focus on artifacts and activities performed at different stages Design Specialties • Information design – structure, categories of information • Navigation design – interaction with information structure • Graphic design – visual presentation of information and navigation (color, typography, etc.) Design Specialties • Information Architecture – includes management and more responsibility for content • User Interface Design – includes testing and evaluation Relationship of Design Specialties in Organizations • Specialists vs. Generalists – UI design & info arch vs. graphic design – no specialization at smaller firms • Information & navigation design often done before graphic design – (with one exception) The Design Process • Several published accounts exist – But little agreed upon terminology • “Official” process structures work and communication – Defines a set of deliverables (artifacts) – However, “everything is custom” • Process is malleable • I will use design process as a framework for presentation Web Site Development Process (from Fleming, J. Web Navigation: Designing the User Experience. O’ Reilly. 1998) Web Site Design Process Web Site Design Process Discovery Conceptualization Preliminary Design Design Implementation Design Process: Discovery Discovery Conceptualization Preliminary Design Design Implementation Assess needs – understand client’s expectations – determine scope of project – characteristics of users Design Process: Discovery • Activities – Review materials provided by client • Existing versions of products/sites • Other documents – Competitive analysis – Collect data from users: interviewing, task analysis, etc. • Deliverables – Written reports – Presentations Design Process: Discovery (information design) Design Process: Conceptualization Discovery Conceptualization Preliminary Design Design Implementation Begin defining site – Take results from discovery and visualize solutions – Early information design Design Process: Conceptualization • Activities – Brainstorming (collaborative & solo) – Sketching ideas (collaborative & solo) – Defining site structure • Deliverables – Site maps – Written reports – Presentations Design Process: Conceptualization (information design: site map) (information design: site map + navigation) Design Process: Conceptualization (information design: site map) Design Process: Conceptualization (information design: site map) Design Process: Preliminary Design Discovery Conceptualization Preliminary Design Design Implementation Generate multiple (35) designs – one will be selected for development – navigation design – early graphic design Design Process: Preliminary Design • Activities – Sketching designs – Creating mock-ups – Quick and rough • Deliverables – – – – Schematics (a.k.a. templates) Site maps Mock-ups Presentations Design Process: Preliminary Design (information/navigation design: schematic) Design Process: Preliminary Design (information/navigation design: schematic) Design Process: Preliminary Design (navigation design: storyboard) Design Process: Design Discovery Conceptualization Preliminary Design Design Implementation Develop the design – Design is selected in previous stage – Increasing level of detail – Iterate on design Design Process: Design Discovery Conceptualization Iteration Design Evaluate Preliminary Design Design Implementation Prototype • iteration at the level of development process • And within design stage Design Process: Design • Activities – Creating and refining mock-ups – Graphic design very active – Prototyping • Deliverables – Mock-ups – Prototypes (HTML, Director) – Presentations Design Process: Design (graphic design: mock-up) Design Process: Implementation Discovery Conceptualization Preliminary Design Design Implementation • Prepare design for handoff – Create final deliverable – Specifications and prototypes – As much detail as possible Design Process: Implementation • Activities – Create final deliverables – Prepare specifications and guidelines – Prepare prototypes • Deliverables – Specifications/Guidelines • written or interactive – Prototypes (HTML, Director) – Presentations Design Process: Implementation (interactive specification) Design Process: Hand off • Project is handed off to engineers/programmers who will implement the site • There may or may not be direct communication between the designers and programmers Duration of design phases Discovery 1-2 weeks Conceptualization Preliminary Design 1-2 weeks Design 6-8 weeks Implementation 2-3 weeks (this varies wildly) Dimensions of Communication Designer Designer Client Team Member Designer Designer Implementor Self How Sketching Is Used • All designers interviewed sketch – Most of them downplay their sketches – Not inclined to show sketches to outsiders • Early conversion to electronic form – Most of them “used to do it more” – Once electronic, never go back • Collaborative sketching – Paper is portable and easy to share Sketching: Information / Navigation Navigation Design Graphic Design Another Use for Paper (print-outs are shared and annotated ) Implications for Design • Confirmation of informal approach • Better understanding of context – support preliminary design phase – support information/navigation design • Less emphasis on transformation and specification, more on expression Implications for Design • Support creation of specific artifacts – – – – schematics site maps prototypes walkthroughs/presentations? • Integration with other media, input modes (i.e. paper, existing tools) ... and more: still exploring the data Questions and Feedback http://guir.berkeley.edu