Autonomic Nervous System Visceral control! - 34

Diencephalon
& Autonomic
Nervous System
Objectives
Identify all of the subcortical fasciculi and tracts
Define projection, commissural, and association fibers
For each fasciculus or tract, identify the type of fibers it consists of and the regions it connects.
Compare and contrast the changes that occur to the different regions of the cortex throughout a lifespan.
Describe the Anatomy, Blood supply and Functions of Diencephalon structures:
Thalamus
Hypothalamus & Pituitary Gland
Epithalamus & Pineal Gland
Subthalamus
Thalamus
Thalamus
3 types of nuclei (by function)
Relay nuclei – relays information not involved in a loop
Example: sensory information from face VPM somatosensory cortex
Association nuclei – nuclei involved in executive functioning loops
Example: mediodorsal nucleus is involved in the limbic loop (pg
421 LE)
Nonspecific nuclei – receive info from several regions, send info to entire cortex, involved with alertness and arousal
Example: intralaminar nuclei
Thalamus Blood Supply
Hypothalamus
Hypothalamus
3 zones:
Periventricular zone
oxytocin - intimacy vasopressin - water retention
Medial zone (3 regions):
Supraoptic region
satiety center – body composition
Suprachiasmatic n. - circadian rhythm
Tuberal region
satiety center – body composition behavioral center – aggression, rage
Mammillary region
converts short term memory to long term memory (by connections with hippocampus through fornix)
Lateral zone
involved with satiety
Hypothalamus and Pituitary
It’s Complicated!!
Do NOT need to know
Full list of functions of hypothalamus and pituitary
Growth
Blood pressure
Some aspects of pregnancy and childbirth including stimulation of uterine contractions during childbirth
Breast milk production
Sex organ functions in both males and females
Thyroid gland function
The conversion of food into energy ( metabolism )
Water and osmolarity regulation in the body
Water balance via the control of reabsorption of water by the kidneys
Temperature regulation
Pain relief
Source: Wikipedia
Hypothalamus Blood Supply
Same as Thalamus!
Epithalamus
Pineal Gland
Releases melatonin
Collects mineral deposits
Calcium, flouride, phosphorous
Blood supply – no BBB!
Posterior Choroidal A.
Subthalamus
Involved in motor control
Associated with the Basal Ganglia (striatum, lentiform, PPN, substantia nigra)
Objectives
Compare and contrast the sympathetic and parasympathetic nervous systems
(neurotransmitters, receptors and effects)
Describe how afferent information enters the CNS
Describe the difference between pre-ganglionic and post-ganglionic
Describe or draw the structure of the sympathetic trunk
Identify and locate the centers that control respiration, cardiac regulation, and vasomotor regulation
Organization
Efferents
Neurotransmitters
Symp.
Para.
Receptors
Symp.
Para.
Afferents
Anatomy
Symp.
Para.
Control Centers
Effects
Symp.
Para.
Neurotransmitters
Cholinergic – all preganglionic, & postganglionic parasympathetic
Adrenergic – postganglionic sympathetic only
Adrenal glands have no postganglionic neuron – they receive acetylcholine and release adrenaline to bloodstream to stimulate sympathetic activity of all organs
Receptor types vary
SC Ganglia
Target
Organ
Discuss
With a partner, 2 minutes
What is the significance of pre-ganglionic vs. post-ganglionic? How is this different from the somatic NS?
What systems are adrenaline and noradrenaline used in?
What systems are acetylcholine used in?
Answers
Pre-ganglionic is the neuron from the CNS that ends in a peripheral ganglia
Post-ganglionic is the neuron from the peripheral ganglia that ends in a target organ
The somatic NS has no synapses outside the CNS
Adrenaline & Noradrenaline are only in the
Sympathetic NS
Acetylcholine is used in parasympathetic, sympathetic, and somatic systems
Receptors (sympathetic)
Adrenergic receptors
(sympathetic on target organs)
α1, a2, b1, b2, b3 a1 & a2 receptors constrict blood vessels to skin, viscera, brain, reproductive system, constrict bronchioles
B1 controls pacemaker potential
B2 dilates coronary arteries, arteries to skeletal muscles, dilates bronchioles
Functions (sympathetic)
Receptors (parasympathetic)
Muscarinic & Nicotinic receptors
(parasympathetic)
No parasympathetic receptors in uterus
a1 cause contraction & b2 cause relaxation
No parasympathetic receptors in sweat glands, liver, most blood vessels, ventricular muscle
Functions (parasympathetic)
Dilate blood vessels to reproductive system & salivary glands
Decreases cardiac output
Contracts bronchioles
Constricts pupils
Organization
Efferents
Neurotransmitters
Symp.
Para.
Receptors
Symp.
Para.
Afferents
Anatomy
Symp.
Para.
Control Centers
Effects
Symp.
Para.
Visceral Afferents
Organ splanchnic nerves
dorsal root ganglion spinal cord solitary nucleus
Collaterals synapse in laminae 5-6 of the spinal cord
Autonomic reflexes
Parasympathetic Anatomy
“Craniosacral outflow”
Preganglionic somas located in solitary n., ambiguus, dorsal motor n. of X (medulla), and sacral spinal cord
Vagus nerve and splanchnic nerves contain preganglionic axons
Ganglia are located near target organs
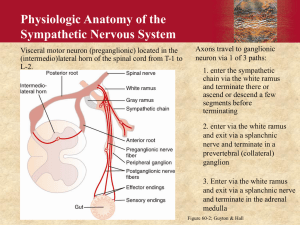
Sympathetic Anatomy
“Thoracolumbar outflow”
Preganglionic somas located in the lateral horn
Postganglionic somas located in either the sympathetic trunk/chain or near the target organs
Cervical cardiac and thoracic visceral nerves contain postganglionic axons
Thoracic, lumbar and sacral splanchnic nerves contain preganglionic axons
Sympathetic trunk
Venn Diagram
Conclusion
Hypothalamus & Pituitary
ANS – parasympathetic vs sympathetic
Sensory info from special regulatory centers directly to Solitary nuc.
Receptor types and neurotransmitter types
Presentations
If time – meet with groups