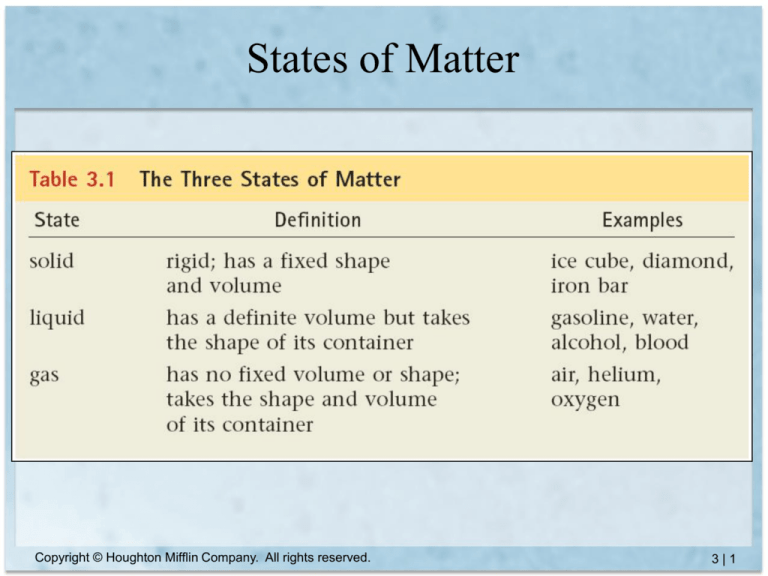
States of Matter
Copyright © Houghton Mifflin Company. All rights reserved.
3|1
Some definitions
• Matter: has mass and volume
• Chemistry is the study of matter
– The properties of different types of matter
– The way matter changes and behaves when
influenced by other matter and/or energy
Copyright © Houghton Mifflin Company. All rights reserved.
3|2
Properties of Matter
• Physical Properties: the inherent characteristics of
matter that are directly observable.
– Color
– Melting point
– Boiling point
• Chemical Properties: the characteristics of matter
that allow it to form new substances
Alcohol ignites in a flame.
Wood is burned in a fireplace.
Copyright © Houghton Mifflin Company. All rights reserved.
3|3
Classify each of the following
as a physical or chemical property:
• Ethyl alcohol boiling at 78°C.
• Hardness of a diamond.
• Sugar fermenting to form ethyl alcohol.
Copyright © Houghton Mifflin Company. All rights reserved.
3|4
Changes in Matter
• Physical changes: changes to matter that do not
result in a change the inherent make-up of the
substance
– State changes: boiling, melting, condensing
• Chemical changes: changes that involve a change
in the fundamental components of the substance
– Chemical reactions: Reactants Products
e.g. propane + oxygen → carbon dioxide + water
Copyright © Houghton Mifflin Company. All rights reserved.
3|5
Classify each of the following
as a physical or chemical change:
• Iron metal melting
• Iron combining with oxygen to form rust
• Sugar fermenting to form ethyl alcohol
Copyright © Houghton Mifflin Company. All rights reserved.
3|6
Elements and Compounds
• Elements: substances that cannot be
broken down into simpler substances by
chemical reactions
• Most substances are chemical combinations
of elements. These combinations are called
compounds.
– Compounds are made of elements.
– Compounds can be broken down into elements.
Copyright © Houghton Mifflin Company. All rights reserved.
3|7
Classification of Matter
Matter
Pure Substance
Constant Composition
Homogeneous
Mixture
Variable Composition
• Homogeneous: uniform composition throughout
– Pure substances
– Solutions (homogeneous mixtures)
• Heterogeneous: non-uniform; contains regions with different
properties than other regions
Copyright © Houghton Mifflin Company. All rights reserved.
3|8
Pure Substances
• Pure substances
– All samples have the same physical and chemical
properties.
– Constant composition: All samples have the same
composition.
– Homogeneous
Copyright © Houghton Mifflin Company. All rights reserved.
3|9
Mixtures
• Mixtures
– Different samples may show different
properties.
– Variable composition.
– Homogeneous or heterogeneous.
– Separate into components based on physical
properties
• All mixtures are made of pure substances.
Copyright © Houghton Mifflin Company. All rights reserved.
3 | 10
Solutions
• A solution is a homogeneous mixture.
• Phase can be gaseous, liquid, or solid.
Copyright © Houghton Mifflin Company. All rights reserved.
3 | 11
Identity each of the following as a pure substance,
homogeneous mixture, or heterogeneous mixture.
• Gasoline
• A stream with gravel on the bottom
• Copper metal
Copyright © Houghton Mifflin Company. All rights reserved.
3 | 12
Gas Chromatogram of Unleaded Gasoline
Copyright © Houghton Mifflin Company. All rights reserved.
3 | 13
Separation of a Mixture
Copyright © Houghton Mifflin Company. All rights reserved.
3 | 14
The organization of matter (Figure 3.10)
Matter
Homogeneous
mixtures
Heterogeneous
mixtures
Physical methods
Pure substances
Elements
Chemical
methods
Copyright © Houghton Mifflin Company. All rights reserved.
Compounds
3 | 15


