Digital Citizenship Project
advertisement

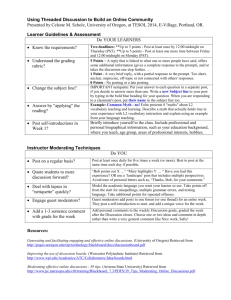
DIGITAL CITIZENSHIP PROJECT Kelley Hopkins ED 505 WHAT IS DIGITAL CITIZENSHIP Digital citizenship includes rules and guidelines to help technology users understand how to use technology appropriately Categories of Digital Citizenship Netiquette Copyright and Fair Use Plagiarism Safety on the Internet Safety on the Computer NETIQUETTE ON SOCIAL MEDIA SITES NETIQUETTE ON SOCIAL SITES What is netiquette? Netiquette is network etiquette, or a set of rules for behaving properly online Guidelines exist for understanding how to behave when in cyberspace A complete list of guidelines can be found at http://www.albion.com/netiquette/corerules.html NETIQUETTE ON SOCIAL SITES Do’s and Don’ts of Social Netiquettes DO… Behave ethically Take time to research places you go online Put your best foot forward (others can see what you put online, even your boss!) Share knowledge Be forgiving of others mistakes (Shea, 2011) NETIQUETTE ON SOCIAL SITES DON’T… Participate in “flaming,” which is when people express strong opinions without holding back emotion (Shea, 2011) Invade other’s privacy Forget you are interacting with humans Abuse your power Send SPAM or chain e-mails (Shea, 2011) COPYRIGHT AND FAIR USE COPYRIGHT AND FAIR USE Copyright is defined by Merriam Webster as… “the exclusive legal right to reproduce, publish, sell or redistribute the matter and form of something (as a literary, musical, or artistic work)” (Merriam Webster, 2012) COPYRIGHT AND FAIR USE Copyright Categories Include: Literary works Musical works Dramatic works Choreographic works Pictorial, graphic, and sculptural works Motion pictures and AV works Sound recordings Architectural works (Parness, 2012) COPYRIGHT AND FAIR USE Fair Use is defined by Merriam Webster as… “a legal doctrine that portions of copyrighted materials may be used without permission of the copyright owner provided the use is fair and reasonable, does not substantially impair the value of the materials, and does not curtail the profits reasonably expected by the owner” (Merriam-Webster, 2012) COPYRIGHT AND FAIR USE Fair use allows for copyrighted materials to be used for educational purposes without needing permission from the owners of the material Fair use depends on four factors: The purpose of the used material The nature of the used material The amount of material used The affect on the market of the original owner (Crews, 2011) COPYRIGHT AND FAIR USE Fair Use Rules for Media Teachers can make copies of… A chapter from a book (the lesser of 10% or 1000 words) An article from a periodical A short story, essay, or poem (poem of 250 words of less) Copies of an article, essay, or story (2500 words or less or less than 10 %) Copies of charts, graphs, diagrams, or pictures (no more than 10% or 5 images/artist Music (up to 10% but no longer than 30 seconds) (UMUC, 2011) PLAGIARISM PLAGIARISM Plagiarize is defined by Merriam Webster as… “to steal and pass off (the ideas or words of another) as one's own : use (another's production) without crediting the source “ Or “to commit literary theft : present as new and original an idea or product derived from an existing source” (Merriam-Webster, 2012) PLAGIARISM How to Avoid Plagiarism Learn: How to cite sources and give credit where credit is due In-text citations as well as a reference page How to paraphrase correctly To use your own ideas (The College Board, 2012) PLAGIARISM Ways to Check For Plagiarism There are many websites that will check for plagiarism. These include: Turnitin.com Plagiarismchecker.com Academicplagiarism.com Checkforplagiarism.net SAFETY ON THE INTERNET SAFETY ON THE INTERNET Safety Issues on the Internet Include… Identity Theft Reputation Management Password Safety Cyberbullying Cyberstalking SAFETY ON THE INTERNET Identity theft occurs when someone steals your identify information, such as your name, social security number, or financial information As many as 9 million Americans have their identity stolen each year Identity theft happens by: Dumpster diving Skimming Phishing (SPAM e-mail) Changing your address (FTC, 2012) SAFETY ON THE INTERNET Ways to Protect Yourself from Identity Theft Monitor all accounts on a monthly basis Be aware of what is happening to your accounts Check your credit reports regularly BE AWARE! SAFETY ON THE INTERNET Steps to Managing Your Online Reputation Register your username on websites Manage privacy settings carefully Set up monitor alerts to catch every mention of your name Get involved in the online conversation Build credibility (Outspoken Media, 2011) SAFETY ON THE INTERNET Choosing Passwords Your password authenticates who you are to your computer Computer users should choose strong passwords that are difficult to decipher Computer users should also take every caution to safeguard their passwords SAFETY ON THE INTERNET How to Choose a Good Password Choose a password with at least six characters Mix upper and lower case with other punctuation Use uncommon phrases Use misspelled words Use a password that would be random to anyone but yourself (Wells, 2012) SAFETY ON THE INTERNET Tips for Safeguarding a Password Do NOT share your password with anyone Make your password something easy to remember Make your password difficult for others to guess Do NOT fall victim to an e-mail scam asking for you to change your password (Wells, 2012) SAFETY ON THE INTERNET Cyberbullying is defined as… “when a child, preteen or teen is tormented, threatened, harassed, humiliated, embarrassed or otherwise targeted by another child, preteen or teen using the Internet, interactive and digital technologies or mobile phones. It has to have a minor on both sides, or at least have been instigated by a minor against another minor.” (Wired Kids, 2012) SAFETY ON THE INTERNET There are two types of cyberbullying Direct attacks: those sent directly to the child Direct attacks may be perpetrated through text, e-mail, on blogs, websites, or other social media Cyberbullying by proxy: where the bullying is done using the help of another person, either knowingly or unknowingly Cyberbullying by proxy can sometimes become even more dangerous if adults become involved (Wired Kids, 2012) SAFETY ON THE INTERNET Preventing cyberbullying can be done by: Educating children about the consequences Teaching children how to respect each other and take a stand Explaining cyberbullying laws to children Great information about cyberbullying can be found at www.stopcyberbullying.org (Wired Kids, 2012) SAFETY ON THE INTERNET Cyberstalking is “threatening behavior or unwanted advances directed at another using the Internet and other forms of online and computer communications” Cyberstalkers stalk their victims through online media, such as chat rooms, forums, and e-mail Some cyberstalking situations advance to off-line stalking, which can result in excessive phone calls, threats, vandalism, and even assault (National Center for Victims of Crime, 2011) SAFETY ON THE INTERNET Help for victims of cyberstalking Victims under age 18 should tell an adult Send the stalker a clear warning in written form that the communication is not wanted File a complaint with Internet providers Collect evidence and documentation Keep a log of communication Contact local authorities Change personal information, such as e-mail addresses and phone numbers (National Center for Victims of Crime, 2011) SAFETY ON YOUR COMPUTER SAFETY ON YOUR COMPUTER Safety on your computer can be compromised by: Viruses Phishing Trojan Horses Worms SAFETY ON YOUR COMPUTER According to Merriam Webster, a virus is… “a computer program usually hidden within another seemingly innocuous program that produces copies of itself and inserts them into other programs or files, and that usually performs a malicious action (such as destroying data)” There are two categories of viruses Macro virus Worms Viruses are always man-made, but they can’t always be controlled once they are started (Merriam Webster, 2012; UITS, 2010) SAFETY ON YOUR COMPUTER Facts about computer viruses A virus is the result of a program someone has written and placed inside a computer program Some viruses can erase all the information on the place it is found inside your computer Once in your computer, a virus hides in a computer’s memory and starts duplicating itself when the program it is attached to is run Viruses can affect RAM and computer discs Programs have been developed to detect and fix viruses found on a computer (Beal, 2011) SAFETY ON YOUR COMPUTER Phishing is a method of online identity theft Phishers can steal your personal and financial data Phishers can also infect your computer with viruses Phishing involves: Planning Setup Attack Collection Identity theft / fraud (How Stuff Works, 2011) SAFETY ON YOUR COMPUTER A trojan horse is a program that does something that the installer is unaware of but the programmer planned A trojan horse appears to be useful software but does damage to your computer once it is installed Trojan horses can cause serious damage to your computer by deleting important files or destroying system information Trojan horses to not reproduce to infect other files or self-replicate (Beal, 2011) SAFETY ON YOUR COMPUTER Worms Are a sub-class of a computer virus Can spread from computer to computer without human help Can replicate itself on your system, thus sending out thousands of copies rather than just one virus Can travel across networks, causing individual, server, and network problems (Beal, 2011) SAFETY ON YOUR COMPUTER Preventing Computer Attacks Keep your Operating System up to date Install an anti-virus software, such as Norton Anti-Virus Download updates frequently Use a firewall to prevent unauthorized use of your system (Beal, 2011) REFERENCES Beal, V. (2011, March 29). The difference between a computer virus, worm, and trojan horse. Retrieved from http://www.webopedia.com/DidYouKnow/Internet/2004/virus.asp Copyright. 2012. In Merriam-Webster.com. Retrieved February 8, 2012, from http://www.merriam-webster.com/dictionary/copyright Crews, K. (2011, December 22). Copyright quick guide. Retrieved from http://copyright.columbia.edu/copyright/copyright-in-general/copyright-quickguide Fair Use. 2012. In Merriam-Webster.com. Retrieved February 9, 2012, from http://www.merriam-webster.com/dictionary/fairuse FTC. (2012). Fighting back against identity theft. Retrieved from http://www.ftc.gov/bcp/edu/microsites/idtheft/consumers/about-identity-theft.html How Stuff Works. (2011). How phishing works. Retrieved from http://computer.howstuffworks.com/phishing.htm National Center for Victims of Crime. (2011). Cyberstalking. Retrieved from http://www.ncvc.org/ncvc/main.aspx?dbName=DocumentViewer&DocumentID=32458 Outspoken Media. (2011). The online reputation management guide. Retrieved from http://outspokenmedia.com/guides/orm-guide/ Parness, A. (2012). Copyright basics. Retrieved from http://www.copyrightkids.org/cbasicsframes.htm Plagiarize. 2012. In Merriam-Webster.com. Retrieved February 9, 2012, from http://www.merriam-webster.com/dictionary/plagiarize REFERENCES Shea, V. (2011). The core rules of netiquette. Retrieved from http://www.albion.com/netiquette/corerules.html The College Board. (2012). How to avoid plagiarism: Give credit where credit's due. Retrieved from http://www.collegeboard.com/student/plan/college-success/10314.html UITS. (2010). What are viruses, worms, & trojan horses. Retrieved from http://kb.iu.edu/data/aehm.html University of Maryland College. (2011, January 28). Copyright and fair use in the umuc online or face-to-face classroom . Retrieved from http://www.umuc.edu/library/libhow/copyright.cfm Viruses. 2012. In Merriam-Webster.com. Retrieved February 9, 2012, from http://www.merriam-webster.com/dictionary/viruses Wells, S. (2012, January 16). Choosing a good password. Retrieved from http://www.ghostnetinc.com/index.php/2012/01/16/choosing-a-good-password/ Wired Kids. (2012). Stop cyberbullying. Retrieved from http://www.stopcyberbullying.org/what_is_cyberbullying_exactly.html