(Dichotomous) Key
advertisement
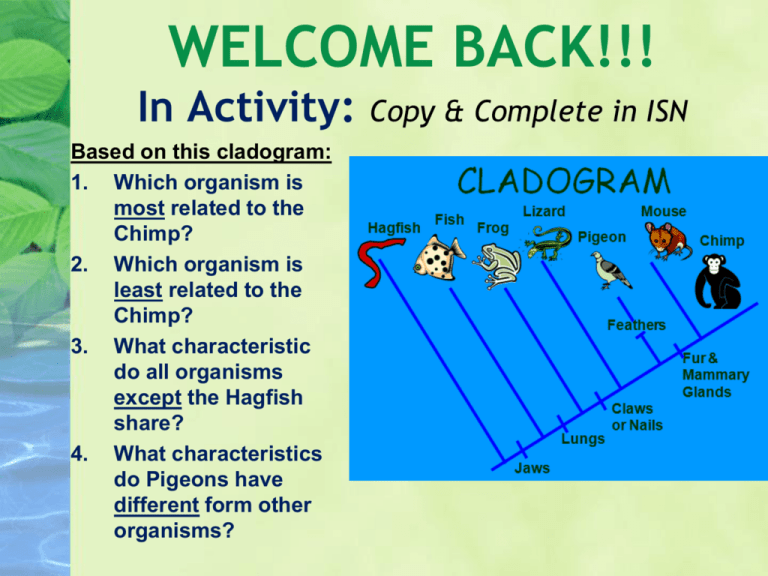
WELCOME BACK!!! In Activity: Based on this cladogram: 1. Which organism is most related to the Chimp? 2. Which organism is least related to the Chimp? 3. What characteristic do all organisms except the Hagfish share? 4. What characteristics do Pigeons have different form other organisms? Copy & Complete in ISN Classification/Taxonomy 8A define taxonomy and recognize the importance of a standardized taxonomic system to the scientific community. 8B categorize organisms using a hierarchical classification system based on similarities and differences shared among groups. Cladograms Clade – group of related organisms Cladogram – branching diagram showing evolutionary descent C B A Properties of cladogram • Each split represents appearance of new trait(s) • Related organisms are closer together new trait(s) new trait(s) Evolutionary Classification (Phylogeny) • Grouping organisms based on evolutionary history PHYLOGENY • Very useful because organisms are placed in groups that show how things may have evolved. Cladistic Analysis… • Traces evolution in a group by focusing on derived characteristics that appear in some organisms but not in others. • Derived Character appears in recent parts of a lineage, but not in its older members • Ex: jaws, lungs, hair Possible Cladograms How should we classify these organisms? BARNACLE CRAB LIMPET CLASSIFICATION BASED ON VISIBLE SIMILARITIES CLASSIFICATIN BASED ON GENETIC SIMILARITIES Cladagram – diagram that shows evolutionary relationships Cladograms Cladogram – branching diagram showing evolutionary descent What can be determined from this cladogram? Lemurs Lorises Tarsiers New world Old world Apes • Primates share Monkeys Monkeys common ancestor • Humans more closely related to apes than to monkeys • Lemurs lack traits common to monkeys Humans Cladograms Cladogram of a group of animals Tuataras Lizards Snakes Crocodiles Birds What can be determined from this cladogram? • Tuataras are not lizards • Birds share common ancestor with reptiles • Snakes are more closely related to lizards than crocodiles Image modified from Benchill [GNU] VENN DIAGRAMS 1. Venn Diagrams can be used to make models of hierarchical classification schemes. A Venn diagram is shown below: A. B. C. D. A. B. C. D. • Four groups are represented by circular regions • Each region represents different taxonomic levels. • Regions that overlap, share common members. • Regions that do not overlap do not have common members. A. B. C. D. Matching: Mammals C Animals with backbones B Insects D All animals A LAB: SURVEY OF LIFE Follow directions on the handout to complete Pre-Lab, All Charts, & Questions at the end. (Return station materials NEATLY BEFORE leaving that one) How can you identify an organism you find? Taxonomic (Dichotomous) Key = series of paired statements describing characteristics of organisms Dichotomous Key Dichotomous key – tool used to identify organisms • Also called classification key • Helps user observe similarities and differences among organisms • Each step presents a level of identification – Only one of the statements in a step can be true about a single organism Dichotomous Key Example • 1A Object has curved lines……go to 2 • 1B Object has straight lines……go to 3 • 2A Object is one continuous curved line…go to 4 • 2B Object has parallel curved lines….Shape A • 3A Object has 3 straight lines….Shape B • 3B Object has 4 straight lines….go to 4 • 4A Object is colored green……Shape C • 4B Object is colored red……Shape D Dichotomous Key What is the scientific name of this seashell? Seashell Dichotomous Key Image by Shellnut (Own work) [CC-BY-SA-3.0] 1a Cone-shaped 1b Not cone-shaped Go to 2 Go to 5 2a Outside surface smooth 2b Outside surface rigid Go to 3 Go to 4 3a Surface solid color 3b Surface spotted Conus californicus Conus spurius 4a Surface one color 4b Surface has contrasting stripe Calliostoma supragranulosa Calliostoma annulatum 5a Holes along shell margin 5b No holes along shell margin Haliotis refuscens Go to 6 6a Purple in color 6b Not purple in color Janthina janthina Littorina obtusata LAB: SURVEY OF LIFE Follow directions on the handout to complete Pre-Lab, All Charts, & Questions at the end. (Return station materials NEATLY BEFORE leaving that one) WELCOME BACK! • Part 1: In Activity: • Part 2: WELCOME BACK! • Part 1: In Activity: WELCOME BACK! • Part 2: In Activity: Taxonomic Groups Group (Kingdom) Archaea Bacteria Protista Fungi Plantae Animalia Major Characteristics Examples Prokaryotes, cell wall, may live in extreme environments, unicellular, autotrophs or heterotrophs Prokaryotes, cell wall made of peptidoglycan, unicellular, autotrophs or heterotrophs Methane-producing archaea, thermophiles E. coli, salmonella Eukaryotes, unicellular or multicellular, Algae, paramecia, euglena, autotrophs or heterotrophs, some have cell wall, diatoms many are microscopic Eukaryotes, most are multicellular, cell walls, Mushrooms, molds, yeasts absorbs nutrients through cell wall, sessile Eukaryotes, most are multicellular, cell walls composed of cellulose, photosynthetic, autotrophs Eukaryotes, multicellular, heterotrophs, most are motile Ferns, mosses, conifers, flowering plants Mammals, birds, insects, worms, sponges Classification Mnemonic • • • • • • • • Donkey Kong Puts Coconuts On Funky Gorilla Salads! 15 min. to Finish… LAB: SURVEY OF LIFE Follow directions on the handout to complete Pre-Lab, All Charts, & Questions at the end. (Return station materials NEATLY BEFORE leaving that one) Classifying Organisms Learning Objectives • Categorize organisms using a hierarchical classification system based on similarities and differences shared among groups – Using characteristics of major groups – Using dichotomous keys Dichotomous Key What is the scientific name of this seashell? Seashell Dichotomous Key Image by Hans Hillewaert (Own work) [CC-BY-SA-3.0] 1a Cone-shaped 1b Not cone-shaped Go to 2 Go to 5 2a Outside surface smooth 2b Outside surface rigid Go to 3 Go to 4 3a Surface solid color 3b Surface spotted Conus californicus Conus spurius 4a Surface one color 4b Surface has contrasting stripe Calliostoma supragranulosa Calliostoma annulatum 5a Holes along shell margin 5b No holes along shell margin Haliotis refuscens Go to 6 6a Purple in color 6b Not purple in color Janthina janthina Littorina obtusata Dichotomous Key What is the scientific name of this seashell? Seashell Dichotomous Key 1a Cone-shaped 1b Not cone-shaped Go to 2 Go to 5 2a Outside surface smooth 2b Outside surface rigid Go to 3 Go to 4 3a Surface solid color 3b Surface spotted Conus californicus Conus spurius 4a Surface one color 4b Surface has contrasting stripe Calliostoma supragranulosa Calliostoma annulatum 5a Holes along shell margin 5b No holes along shell margin Haliotis refuscens Go to 6 6a Purple in color 6b Not purple in color Janthina janthina Littorina obtusata Dichotomous Key Is this animal a vertebrate or invertebrate? If it is a vertebrate, what class does it belong in? Vertebrate Animal Dichotomous Key Image by Dario Sanches (Own Work) [CC-BY-SA-2.0] 1a Spinal column present 1b Spinal column absent Go to 2 Invertebrate 2a Fins and gills present 2b Fins and gills absent Fish Go to 3 3a Scales present 3b Scales absent Reptile Go to 4 4a Feathers present 4b Feathers absent Bird Go to 5 5a Hair or fur present 5b Hair or fur absent Mammal Amphibian Dichotomous Key Is this animal a vertebrate or invertebrate? If it is a vertebrate, what class does it belong in? Vertebrate Animal Dichotomous Key 1a Spinal column present 1b Spinal column absent Go to 2 Invertebrate 2a Fins and gills present 2b Fins and gills absent Fish Go to 3 3a Scales present 3b Scales absent Reptile Go to 4 4a Feathers present 4b Feathers absent Bird Go to 5 5a Hair or fur present 5b Hair or fur absent Mammal Amphibian Dichotomous Key Is this animal a vertebrate or invertebrate? If it is a vertebrate, what class does it belong in? Vertebrate Animal Dichotomous Key 1a Spinal column present 1b Spinal column absent Go to 2 Invertebrate 2a Fins and gills present 2b Fins and gills absent Fish Go to 3 3a Scales present 3b Scales absent Reptile Go to 4 4a Feathers present 4b Feathers absent Bird Go to 5 5a Hair or fur present 5b Hair or fur absent Mammal Amphibian 15 min. to Finish… LAB: SURVEY OF LIFE Follow directions on the handout to complete Pre-Lab, All Charts, & Questions at the end. (Return station materials NEATLY BEFORE leaving that one) Taxonomic Groups Group (Kingdom) Archaea Bacteria Protista Fungi Plantae Animalia Major Characteristics Examples Prokaryotes, cell wall, may live in extreme environments, unicellular, autotrophs or heterotrophs Prokaryotes, cell wall made of peptidoglycan, unicellular, autotrophs or heterotrophs Methane-producing archaea, thermophiles E. coli, salmonella Eukaryotes, unicellular or multicellular, Algae, paramecia, euglena, autotrophs or heterotrophs, some have cell wall, diatoms many are microscopic Eukaryotes, most are multicellular, cell walls, Mushrooms, molds, yeasts absorbs nutrients through cell wall, sessile Eukaryotes, most are multicellular, cell walls composed of cellulose, photosynthetic, autotrophs Eukaryotes, multicellular, heterotrophs, most are motile Ferns, mosses, conifers, flowering plants Mammals, birds, insects, worms, sponges Activity: Wild Cats Dichotomous Key Follow directions on the handout to complete Part 1 & 2. Turn-in for grade & Study for your QUIZ: TAXONOMY Exit Ticket (CLOZE) Exit Ticket (CLOZE)