mammals
advertisement

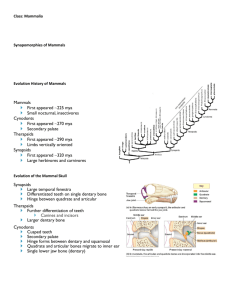
Mammalogy (Spring 2015 Althoff - reference FDVM Chapter 4) Mammals Origins Bill Horn LEC 02 Mammals are… space-age reptiles. THEY _______ & _______ FASTER!!!! Origins of Mammals • Have to think “synapsids” first…. • Synapsids thought to have originated at the end of the Paleozoic ~300-290 MYA • Three major radiations: 1) 1 pelycosaurs (~300-250 MYA…now extinct) 2) 2 therapsids (~250-140 MYA…now extinct) 3) 3 mammals (~_____ MYA to today) • 1 and 2 considered “mammal-like reptiles • Mammal major radiations peaked in the Cenozoic (starting ~ _______ MYA) Mammal-like 2 1 reptilest 3 Mammals Dominance of Mammals • Dominance by mammals occurred during late Cretaceous period…after decline of ruling reptiles…90-65 MYA • Why did Synapid reptiles decline…and mammals flourish? Two explanations have been offered…. Reptiles “out”, Mammals “in”?? • Competition from other reptile groups • Changing climatic conditions Which is most likely??? Back to Mammalian Dominance • Specifically, late Cretaceous period to Paleocene epoch • Adaptative _________ led to dominance during Cenozoic era Periods of Extinction & Radiation • MASS Extinction: dinosaurs & reptiles 60-144 mya • Significant extinctions for mammals: 37-58 mya 24-37 mya 100,000 – 2 mya • Significant radiations associated with break-up of Pangaea & continental drift as well as increased faunal and floral diversity…most pronounced during Paleocene (next slide) 225 MYA Present 135 MYA 65 MYA “Modern” mammals • Geologic time division when most modern families (aka family diversity) appeared is the Oligocene (37-24 MYA) & Miocene (24-5 MYA) • Oligocene and Miocene may have also represented the period of greatest species diversity as well Skull Characteristics • Differ from reptiles with development of perforations of temporal portion • Anapsid = no temporal opening vs. • Diapsid = 2 temporal openings, separated by post orbital process vs. • _______ = 1 opening MAMMALS MAMMALS arose from… Lizards & snake arose from.. SYNAPSID DIAPSID ANAPSID Lineage lead to turtles “Better” skull design…advantages • Mammalian skull design (originating from reptilian lineage subclass Synapsida) a) increased freedom for expansion of ______________________ or b) selective advantage gained by ________________________ (i.e., less bone, less wt. = bone replaced by opening) Anapsid Synapsid (primitive amniotes & turtles) (mammals) Lateral view Adductor muscle Adductor muscle Cross-sectional view More room for “bulging” muscles Evolutionary Trends in Synapsids • Key change from during evolution of synapsid lineage was crossing of physiological boundary from ectothermy to _______________ • “Changes” from a physiological perspective— which would influence metabolic rate—obviously not fossilized. But changes in skulls and skeletons can offer clues how higher metabolic rates could have been achieved: 1) greater food intake or rate of feeding (FR = food-related) 2) greater respiration rate (AR = activity-related) Pelycosaur Noncynodont therapsid Cynodont therapsid Early Mammal Megazostrodon “Mods” SIZE OF THE TEMPORAL FENESTRA—larger fenestra indicates a greater volume of jaw musculature…also larger temporal fossa CONDITION OF THE LOWER TEMPORAL BAR— bar of bone owed out from skull behind the orbit indicates presence of masseter muscle. For mammals, zygomatic arch “bows” out LOWER JAW AND JAW JOINT—change from only about half of lower jaw with teeth to greatly expanded dentary. For mammals, dentary now forms a new jaw joint with skull—coronoid process prominent “Mods” …con’t TEETH—specialization of the dentition. Went from homodont to ____________ condition (i.e., differentiated teeth) resulting in change in size, form, and function. Impacts chewing motion as well in combo with #2 DEVELOPMENT OF SECONDARY PALATE— separates nasal passage from mouth allowing animal to eat and breath at the same time POSITION OF THE LIMBS—placed more underneath the body “Mods” …con’t SHAPE OF THE LIMB GIRDLES—more lightly built girdles than the “mammal-like” reptiles. Mammals have reduced pubis and a rod-shaped ilium….allows more dorsoventral flexion (see 10, too) SHAPE OF FEET—Shorter toes. Calcaneal heal provides a lever arm for a greater degree of pushoff from the gastrocnemius (calf) muscle) FORM OF VERTEBRAL COLUMN— loss of lumbar ribs , reduction of cervical ribs suggest presence of _____________________ Classification & Diversity of Mammals Mammalia CLASS 29 ORDERS FAMILIES 153 GENERA SPECIES ~ 1,200 > ?? EXTANT… mammals Mammal-like reptilest 1 Fig. 18-2, p489 PJH 2 3 1 • MONOTREMATA order (3 species) “egg-laying” mammals) 2 • MARSUPIALIA infraclass (242 species) (7 orders within “pouched mammals”) • All others-“placental mammals” 3 Infraclass EUTHERIA (eutherians) (4,500-plus species) (21 orders within “placentals”) Early Mammal groups TIME