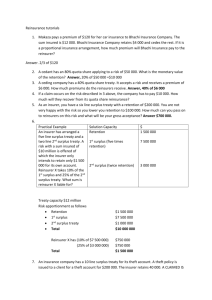
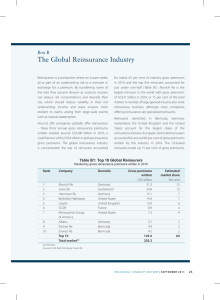
Stuart_Shepley - Insurance Market Conferences
advertisement

Non-traditional solutions for Liability Exposures Stuart Shepley Chief Operating Officer Ace Tempest Re (Europe) Themes • Will non-traditional business grow significantly? • Is there ‘real’ value in buying a non-traditional deal? • Should actuaries be underwriters? Contents • • • • • Introduction to non-traditional solutions Products available The current marketplace Choosing a product and provider Checklist Introduction to non-traditional solutions Spectrum of products Risk financing Financial Reinsurance Alternative Risk Transfer Products Risk transfer Traditional reinsurance Reinsurers Equity & Debt Contingent capital Securitisation Futures Options Capital Market Key characteristics of traditional R/I • • • • • • Single year deals Guaranteed cost for single year with full risk transfer, however …. Highly volatile renewal pricing In hard market may not even be capacity available Likely to be demand for payback following a loss Limited profit sharing (although may be able to use “bank” in negotiations) • Generic “off the shelf” products Key characteristics of ART • • • • • • Emphasis on financing as well as transferring risk Risk spread over time and possibly product lines Risk shared between insurer and reinsurer Low finite limits Premiums adjusted according to own experience Concepts such as “payback” and “bank” as well as effect of investment income made explicit • Solutions tailored to specific client issues ART • So called alternative products concentrate on the most basic aims of reinsurance • …. as a risk management partnership between insurer and reinsurer • … as an efficient form of capital for the insurance industry • …. as a driver of shareholder value • …. as a solution to specific industry issues (shortage of traditional capacity, uninsurable risks, asbestos and environmental reserve increases) Needs met by ART • • • • • • Smoothing of fluctuations in reserve levels, catastrophic or large losses Smoothing of reinsurance prices Optimisation of balance sheet structure Protection of security rating Facilitation of mergers and acquisitions Additional underwriting capacity precisely when it is required Products available Main Types of cover • • • • • • • Loss portfolio transfer (LPT) Adverse development cover (ADC) Spread loss Finite quota share (FQS) Multi-year, multi-line products (MMP) Multi-trigger products Options to buy cover/multi-year deals LPT/ADC • Basic idea is to transfer outstanding claims reserves to reinsurer • Reinsurer agrees to pay claims from a retention level (lower than existing reserves) up to a pre-set limit (at or a little above existing reserves) • Reinsurer assesses likely pay-out of claims and charges premium equal to discounted value of expected payment • Adverse development cover protects against deterioration of claim levels beyond current levels • Reinsurer takes timing and investment risk and may take reserving risk • Often crucial element of M&As or of putting lines of business into run-off • Particularly suitable for liability portfolios due to long settlement periods and scope for volatile reserve development LPT/ADC - Example Balance sheet (before) Reserves $75M Current Investment income $20M Best Estimate Best Reserves Estimate $75M Discounted Reserves $55M Deterioration cover Limit +$25M Decrease in reserves Premium $60M Balance sheet (after) Reserves $0M Premium ceded $60M Improvement $15M Spread loss treaties • Cover prospective claims • In simplest form, an excess of loss type contract but for a multi-year term and with the concepts of bank and payback made explicit within the contract • A single limit applies over the period of the contract • An experience account is used to track the results of the contract • Adjustable and return premiums used to adjust balance towards zero • Party cancelling contract while “ahead” pays profit commission (if reinsurer) or cancellation premium (if insured) Experience Account Balance bought forward (5,000,000) In quarter Basic reinsurance premium (Reinsurers' margin) Additional reinsurance premium 15% of basic 25% of balance b/f Claims paid Notional interest on balance b/f Balance carried forward 1,250,000 (187,500) 1,250,000 500,000 5% of balance b/f (250,000) (2,437,500) Financial quota share • Quota share with high profit commission, sliding scale ceding commission and loss-caps • May be multi-year deals with terms for subsequent years adjusted by experience of earlier years • Main aim is to increase underwriting capacity of insurer while allowing them to retaining more of profitability of underlying business than with conventional quota share • One variation is an anti-cyclical quota share – ceding commission increases as loss ratios increases, result is to smooth results of cedant Coverage Multi-year multi-line products Year 3 Years 1-3 Year 2 Year 1 Traditional single line approach • Yearly renewals • Separate lines • Large number of reinsurers • Risk transfer All lines Integrated approach • Multi-year • Multi-line (including financial or non-insurable risks) • One provider • Funded concept – spread loss mechanism Multi-trigger products • Claims are paid only if, in addition to a conventional insurance event (the first “trigger”) a pre-defined non-correlated event has also occurred (the second “trigger”) • More efficient cover as paid only when required • E.g Catastrophe cover that is only paid if the FTSE has fallen in the calendar year • E.g. A bottom layer casualty excess of loss which only comes into force if there has been a PCS natural event of pre-agreed magnitude Multi-trigger products Catastrophic Loss (Insurance Event) Multi Trigger Responds Stock Market Fall (Financial Event) The current market US P&C Industry Combined Ratio 120 115 110 105 100 Source: AM Best, 2002 estimate 02** 00 98 96 94 92 90 88 86 84 82 80 78 76 74 72 70 95 Insurers balance sheets hit TOXIC MOLD LADDERING STX FALLS Current convergence market Our own industry Current issues – ART products • "(The FSA) has been investigating financial reinsurance with some care and I have to say that we have found some more examples of arrangements where it is wholly unclear whether any risk has in fact been transferred and where the motivation seems purely presentational” Howard Davies post Equitable Life failure • FSA and Bank of England concerned at insurance of credit risks • Interest rates environment makes discounting challenging • High rates of traditional insurance makes demand for non-traditional products high but supply low as reinsurers concentrate on “bread and butter” products Aside - Regulation • FASB 113 (USA) requires transfer of underwriting and timing risk as well as “significant” risk of loss for reinsurers • EITF 93-96 (USA) – cedants must show balances of experience accounts in balance sheet if obligation to ultimately repay • FRAG 35/94 (UK) – more pragmatic, relies on economic substance of transaction, timing risk only is allowable • Post Enron - Executives required to sign-off on accuracy of accounts • Move away from fixed accounting rules to true and fair view Choosing a product and provider Choice of provider • Dictated by nature of product and current accounting/financial environment • Need provider that will offer partnership in product design, and in pricing • Absolute transparency with all parties is key – auditors, regulators, management, investors • Need reinsurer that can price and provide traditional risk transfer as part of product Choice and evaluation of product • Work in partnership with reinsurer • Start with insurers problem not reinsurers “off the shelf” solution • Identify key financial measures which wish to protect or key financial aims • E.g. Balance sheet protection, maintain security rating, stabilise combined ratio, tax efficiency • Need to perform stochastic analysis of key financial ratios before and after deal • Look at accounting and economic effect Assessment of risk 14.0% Probability Mode 12.0% 10.0% 8.0% 6.0% 5% probability of losing more than 10% of premiums 4.0% 2.0% 0.0% -35% -10% 0% +25% (Average) Profit as % of premium +75% Checklist Informed Purchase Reason for Buying Transparency of inner workings Credit and Operational Risk in addition to Insurance Risk Treat as a banking transaction Tax and Regulatory arbitrage not drivers of deal Consider pro-forma impact Discuss with supervisors / agencies in advance Agree up front early termination process Sign and issue policy before commencement Non-traditional solutions for Liability Exposures Discussion / Questions