File - Adolescent Psychology

Moral Development, Values, and Religion
Moral Development
Thoughts, feelings and behaviors regarding standards of right and wrong
Both interpersonal and intrapersonal
When being social and when not engaged with others
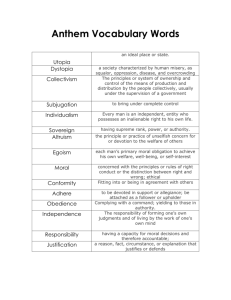
Values: beliefs and attitudes about the way things should be .
Moral Thought
Piaget – children’s moral development
Lawrence Kohlberg – Moral development based on moral reasoning
Studied using vignettes (11 moral dilemmas)
3 levels of moral development
Each level has 2 stages
Go from values being external and superficial to more internal and mature as one progresses through levels and stages
Lets look at Kohlberg’s model of moral development…
Kohlberg – Level 1:
Preconventional Reasoning
Lowest level, focused on reward and punishment
Before age 9
Stage 1: punishment & obedience orientation
Stage 2: Individualism, instrumental purpose, and exchange
What is right involves an equal exchange
Nice to you so you will be nice to me
“What’s in it for me?”
Kohlberg – Level 2:
Conventional Reasoning
Second, intermediate level – abide by internal standards, but there are external standards of others
Most adolescents are reasoning in conventional ways; stage 3 with some stage 2 and stage 4
Stage 3: Mutual interpersonal expectations, relationships, and interpersonal conformity
Value trust, caring, and loyalty as basis of what is “right”
Often adopt parent’s values at this stage
Seek to be seen as “good”
Stage 4: Social systems morality
Moral judgment based on social order, law and justice
Understanding that for community to work we need laws
Kohlberg – Level 3:
Postconventional Reasoning
Highest level, morality becomes more internal
Sees alternative moral courses
Explores the moral options
Decides on personal moral code
Stage 5 – early 20s and Stage 6 is questionable for various reasons
Stage 5: Social contract or utility and individual rights
Values, rights, and principles are basis of moral reasoning
Evaluate laws and social systems based on how they uphold and protect fundamental rights
Stage 6: Universal ethical principles
Moral reasoning based on universal human rights
When law and conscience conflict, individual will follow conscience
Individual takes personal risks to stand by their morality
Kohlberg’s Theory
Stage 6 has been removed from scoring manual
Moral reasoning changes very slowly and gradually
(2009)
Moral orientation – cognitive development and exposure to appropriate social experiences
Some believe that morality develops in similar ways to cognitive development (equilibrium and conflict)
So…moral thought can be moved to higher level through exposure to models or discussion that is more advanced than the adolescent’s level
Emphasized importance of peer give-and-take interactions in development of higher moral reasoning (including role taking and challenging conversations)
Parent-child interactions: allow & encourage conversations about value-laden topics
Critics: not enough focus on behavior
May be able to reason, but what do they DO…
Moral Reasoning
Justice vs. care perspectives (Carol Gilligan)
Care perspective not addressed adequately in Kohlberg’s theory
Emphasizes relationships and concern for others
Gender
Social Conventional Reasoning : thoughts about social consensus and convention
Moral Behavior & Feeling
Processes of reward, punishment, and imitation
Social Cognitive Theory – difference between moral competence (ability to produce moral bxs) and moral performance (enactment of bxs in specific situations)
Self-control, self-regulation
Prosocial Behavior: altruism, forgiveness, gratitude
Moral Feelings: empathy develops around 10-12 years of age
Sympathy, empathy, admiration and self-esteem
Anger, outrage, shame and guilt
Contexts of Moral Development:
Parenting
Supportive parenting
Encouraging to question and expand moral reasoning
Opportunity to learn about other’s perspectives
Included in family decision making process
Higher level of moral reasoning in adolescence
Child-rearing Techniques (discipline)
Love withdrawal anxiety
Power assertion hostility
Induction
– use of reason and explanation of consequences for others from adolescent’s behavior