File
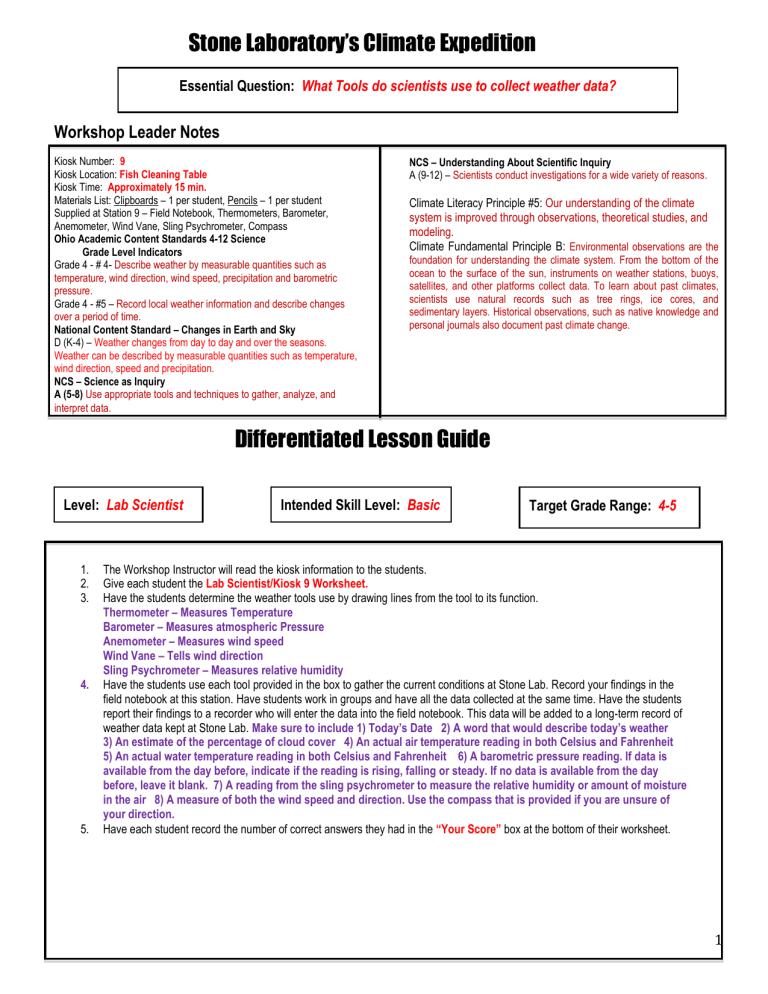
Stone Laboratory’s Climate Expedition
Essential Question:
What Tools do scientists use to collect weather data?
Workshop Leader Notes
Kiosk Number: 9
Kiosk Location: Fish Cleaning Table
Kiosk Time: Approximately 15 min.
Materials List: Clipboards – 1 per student, Pencils – 1 per student
Supplied at Station 9 – Field Notebook, Thermometers, Barometer,
Anemometer, Wind Vane, Sling Psychrometer, Compass
Ohio Academic Content Standards 4-12 Science
Grade Level Indicators
Grade 4 - # 4- Describe weather by measurable quantities such as temperature, wind direction, wind speed, precipitation and barometric pressure.
Grade 4 - #5 – Record local weather information and describe changes over a period of time.
National Content Standard – Changes in Earth and Sky
D (K-4) – Weather changes from day to day and over the seasons.
Weather can be described by measurable quantities such as temperature, wind direction, speed and precipitation.
NCS – Science as Inquiry
A (5-8) Use appropriate tools and techniques to gather, analyze, and interpret data.
Level:
Lab Scientist
Differentiated Lesson Guide
Intended Skill Level:
NCS – Understanding About Scientific Inquiry
A (9-12) – Scientists conduct investigations for a wide variety of reasons.
Climate Literacy Principle #5: Our understanding of the climate system is improved through observations, theoretical studies, and modeling.
Climate Fundamental Principle B: Environmental observations are the foundation for understanding the climate system. From the bottom of the ocean to the surface of the sun, instruments on weather stations, buoys, satellites, and other platforms collect data. To learn about past climates, scientists use natural records such as tree rings, ice cores, and sedimentary layers. Historical observations, such as native knowledge and personal journals also document past climate change.
Basic
Target Grade Range:
4-5
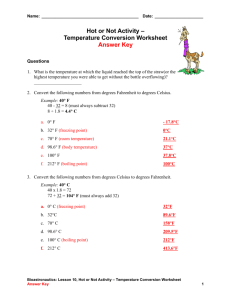
1.
The Workshop Instructor will read the kiosk information to the students.
2.
Give each student the Lab Scientist/Kiosk 9 Worksheet.
3.
Have the students determine the weather tools use by drawing lines from the tool to its function.
Thermometer – Measures Temperature
Barometer – Measures atmospheric Pressure
Anemometer – Measures wind speed
Wind Vane – Tells wind direction
Sling Psychrometer – Measures relative humidity
4.
Have the students use each tool provided in the box to gather the current conditions at Stone Lab. Record your findings in the field notebook at this station. Have students work in groups and have all the data collected at the same time. Have the students report their findings to a recorder who will enter the data into the field notebook. This data will be added to a long-term record of weather data kept at Stone Lab. Make sure to include 1) Today’s Date 2) A word that would describe today’s weather
3) An estimate of the percentage of cloud cover 4) An actual air temperature reading in both Celsius and Fahrenheit
5) An actual water temperature reading in both Celsius and Fahrenheit 6) A barometric pressure reading. If data is available from the day before, indicate if the reading is rising, falling or steady. If no data is available from the day before, leave it blank. 7) A reading from the sling psychrometer to measure the relative humidity or amount of moisture in the air 8) A measure of both the wind speed and direction. Use the compass that is provided if you are unsure of your direction.
5.
Have each student record the number of correct answers they had in the “Your Score” box at the bottom of their worksheet.
1
Level:
Lab Scientist
Level:
Field Scientist
Intended Sill Level:
Average
Target Grade Range:
6-8
1. The Workshop Instructor will read the kiosk information to the students.
2. Give each student the Field Scientist/Kiosk 9 Worksheet. Have the “Climatologists add their name to their worksheet.
3. Have the students determine the weather tools use by drawing lines from the tool to its function.
Thermometer – Measures Temperature
Barometer – Measures atmospheric Pressure
Anemometer – Measures wind speed
Wind Vane – Tells wind direction
Sling Psychrometer – Measures relative humidity
4. Have the students use each tool provided in the box to gather the current conditions at Stone Lab. Record your findings in the field notebook at this station. Have students work in groups and have all the data collected at the same time. Have the students report their findings to a recorder who will enter the data into the field notebook. This data will be added to a long-term record of weather data kept at Stone Lab. Make sure to include 1) Today’s Date 2) A word that would describe today’s weather
3) An estimate of the percentage of cloud cover 4) An actual air temperature reading in both Celsius and Fahrenheit
5) An actual water temperature reading in both Celsius and Fahrenheit 6) A barometric pressure reading. If data is available from the day before, indicate if the reading is rising, falling or steady. If no data is available from the day before, leave it
blank. 7) A reading from the sling psychrometer to measure the relative humidity or amount of moisture in the air
8) A measure of both the wind speed and direction. Use the compass that is provided.
5. Have each student record the number of correct answers they had in the “Your Score” box at the bottom of their worksheet.
Level:
Research Scientist
Intended Sill Level:
Advanced
Target Grade Range:
9-12
5.
The Workshop Instructor will read the kiosk information to the students.
6.
Give each student the Research Scientist/Kiosk 9 Worksheet. Have the “Climatologists add their name to their worksheet.
7.
Have the students determine the weather tools use by drawing lines from the tool to its function.
Thermometer – Measures Temperature
Barometer – Measures atmospheric Pressure
Anemometer – Measures wind speed
Wind Vane – Tells wind direction
Sling Psychrometer – Measures relative humidity
8.
Have the students use each tool provided in the box to gather the current conditions at Stone Lab. Record your findings in the field notebook at this station. Have students work in groups and have all the data collected at the same time. Have the students report their findings to a recorder who will enter the data into the field notebook. This data will be added to a long-term record of weather data kept at Stone Lab. Make sure to include 1) Today’s Date 2) A word that would describe today’s weather
3) An estimate of the percentage of cloud cover 4) An actual air temperature reading in both Celsius and Fahrenheit
5) An actual water temperature reading in both Celsius and Fahrenheit 6) A barometric pressure reading. If data is available from the day before, indicate if the reading is rising, falling or steady. If no data is available from the day before, leave it blank. 7) A reading from the sling psychrometer to measure the relative humidity or amount of moisture in the air 8) A measure of both the wind speed and direction. Use the compass that is provided if you are unsure of your direction.
2