GPRS
advertisement

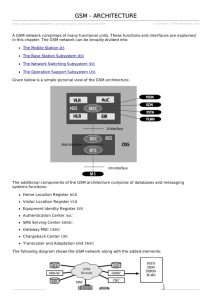
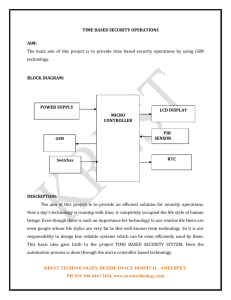
GSM Systems Division Andrew J Wilton Director of Applied Research GSM Systems Division GSM Systems Division Agenda AGENDA Why Packet? GSM/GPRS Architecture What is EDGE? Deployment Issues Standards Terminal Classes GPRS Applications GSM Systems Division AGENDA Why Packet? GSM/GPRS Architecture What is EDGE? Deployment Issues Terminal Classes Standards GPRS Applications Why Packet? Why Packet GSM Systems Division Bursty Services Circuit Data Utilisation bit/s Circuit Capacity 33.6k Capacity (Mbytes) WWW pages USED AVAILABLE* % USED Email (Download) 0.99 9.7 10.2 Email 0.06 3.0 2.0 0.23 4.2 5.5 t Mean WWW browsing example (Browsing) • Many user actions are bursty e.g. browsing WWW pages • Internet has variable delays • PSTN channel not used 100% Web (browsing) * 56.6 Kbits/s Why Permanent Virtual Permanent Virtual Circuits Circuits? GSM Systems Division Email via GSM User Modem GSM Modem PSTN Auth. Server Email Server Internet Email via GPRS User GPRS Virtual GPRS Data Tunnel INITIAL CALL PROCESS • • • • GSM Call TrainModem Login and Authenticate Download mail Total Internet Authenticated path to Email server TIME (s) INITIAL CALL PROCESS TIME (s) 4 30 11 180 • GPRS Call • Login and Authenticate • Download mail 4 11 180 3 min 45s SUBSEQUENT CALL • Repeat Above Auth. Server Email Server Total 3 min 15s SUBSEQUENT CALL 3 min 45s Mail Only When Connected • Not applicable - Virtual Cct 0min 0s Mail Continuously Downloaded GSM Systems Division GPRS - the Low Cost Data Upgrade Upgrade to Data Saturated Voice Cell - 1 Carrier - 150 subscribers Saturated Voice Cell + 15% Subs are Data Users @ 56kbit/s New Timeslots Required 1 Penetration GPRS HSCSD 3% 0 5*-12 15% 0 14*-21 1 Conditions: Voice - 20mE - 1% blocking Data - 1:10 duty cycle - 15 minute sessions * lower figure is data only - 1 session/ 4 hours ~ 10 mins worst case delay GSM Systems Division Agenda AGENDA Why Packet? GSM/GPRS Architecture What is EDGE? Deployment Issues Standards Terminal Classes GPRS Applications GSM Architecture GSM Systems Division GMSC PSTN A-bis BTS ‘A’ BSC MSC MAP GPRS Register H/VLR HLR/AUC GPRS Register GSM Systems Division Architecture - GSM with GPRS GMSC PSTN Circuit Switched Traffic A-bis BTS ‘A’ MSC MAP Peer Elements BSC GPRS Register H/VLR PCU Gb Packet Traffic HLR/AUC GPRS Register MAP SGSN Public Switched Packet Network Gn GGSN Gi What IS an SGSN/GGSN GSM Systems Division Mobililty Management Session Management - QoS - Security - Attach/Detach HLR MAP Signalling (GGSN) External Data Domain MAP Signalling (SGSN) BSS PCU BSS PCU SGSN Routeing info Client BSS PCU Internet Intranet GGSN SGSN BSS PCU Client BSS PCU - Routing - Signalling - Resource Mgt. Servers GSM Systems Division The Packet Control Unit (PCU) BTS BSC GSN Abis Gb PCU GPRS Function CCU MAC RLC Packet Switching RLC MAC –Segmentation/Re-assembly –ARQ –Multiplexing (different mobiles) –Contention resolution (u/l) - QOS related –Scheduling/queueing (d/l) - QOS related GSM Systems Division Agenda AGENDA Why Packet? GSM/GPRS Architecture What is EDGE? Deployment Issues Standards Terminal Classes GPRS Applications GSM Systems Division Coding Rates for GPRS & EDGE GPRS Rate Code Rate 9.05kb/s 0.5 13.4kb/s 0.66 15.6kb/s 0.75 21.4kb/s 1.0 CS1 CS2 CS3 CS4 GMSK (1 bit/s/symbol) EDGE MCS1 MCS2 MCS3 MCS4 Rate 8.8 kb/s 11.2 kb/s 14.8 kb/s 17.6 kb/s Code Rate 0.53 0.66 0.80 1.00 GMSK (1 bit/s/symbol) EDGE - Key Aspects • A new modulation Scheme - 8PSK • 200 KHz Channel spacing - unchanged EDGE = GMSK + PSK MCS5 MCS6 MCS7 MCS8 8-PSK (3 bit/s/symbol) Rate 22.4 kb/s 29.6 kb/s 44.8 kb/s 59.2 kb/s Code Rate 0.37 0.49 0.76 1.00 • Symbol rate unchanged - 270k symbol/s BUT - 3 bits/symbol EDGE - Coverage vs Data Rate GSM Systems Division Shannon’s Law EDGE Coverage Relative to Speech 1,2 ( ) C log S 1+ = 2 I B % Cell Area Covered 100 80 60 • Higher Date Rate Requires - More RF Bandwidth 40 20 0 8.8 11.2 - More C/I • For EDGE additional C/I - 7 - 10 dB 14.8 17.6 22.4 29.6 44.8 Data Rate / Time Slot 1 Interference Limited Case 2 Conditions: • • • • Speech Coverage 12dB C/I 4/12 Re-use No SFH 10 % Block Erasure Rate 59.2 GSM Systems Division Path Standards GSM Now Evolution Paths for GSM Delay Equipment Spectrum B/W Now x4 Q1 ‘99 x4 EDGE 1 Q1 ‘00 x20 UMTS* Q1 ‘00 x40 HSCSD 1 GPRS 1 * Whole Carrier 1 4 time Slots Coverage 2 Interference Ltd 2 GSM Systems Division Agenda AGENDA Why Packet? GSM/GPRS Architecture What is EDGE? Deployment Issues Standards Terminal Classes GPRS Applications Effect of ARQ GSM Systems Division 100 No Retransmission 80 60 One Retransmission 40 Two Retransmissions 20 0 8.8 11.2 14.8 17.6 22.4 (kb/s) 29.6 44.8 • Assumes 4/12 reuse and speech coverage at 12 dB C/I (no SFH) 59.2 Voice Over IP GSM Systems Division PSTN Cost PPDN GMSC Bandwidth vs Delay GGSN Voice packets lost Data in spare voice B/W bit/s Capacity SGSN MSC Average Voice XCDR t Voice over Packet 20 ms* Voice over Circuit BSC PC U x1 2 ms* BTS ? • Transmission • MSC Costs • Transcoders Packet Switch ? • Transmission • IP Routers • Media Gateways x10 • Over Dimension Transmission - delay budget • QoS Management GSM Systems Division The Service provider IP Address PSTN PPDN GMSC GGSN MSC SGSN Server GPRS SERVICE IMPLEMENTATION XCDR GSM SERVICE IMPLEMENTATION - MSC based Slow rollout (regression testing) Service lost on roaming New Service introduction - potentially corrupts all services - Tied to MSC vendor - Client Server based BSC PC U BTS - Very fast rollout - Multiple sources for Application development - Each service is stand alone - cannot corrupt others - Matched to Web implementation Phone (Client) GSM Systems Division GPRS- Opportunities for Competition PPDN PSTN 4 Server Single MSC/ + BSS Supplier GMSC 1 4th Supplier - Service Framework GGSN 3 SGSN MSC 3rd Supplier - GPRS Core Network ‘A’ XCDR XCDR BSC BSC BTS BTS 2 2nd Supplier - BSS Gb Iu PCU RNC 5 NODE B NODE B UMTS RAN 5th Supplier - UMTS RAN GSM Systems Division Islands of Coverage UMTS GSM Server Data UMTS UMTS GPRS/EDGE UMTS Data UMTS Service CELLULAR COVERAGE • Islands of UMTS coverage - small cell size - demand driven • Wide area coverage - GPRS or EDGE • Dual mode UMTS/GSM handsets CELLULAR SERVICE • Services at edge of network - transport via GSM or UMTS • Service Transparent to Transport - between operators - between media (copper, mobile etc.,) - A few services - will run less well on GPRS/EDGE GSM Systems Division GPRS Threats and Opportunities • Client/Server will be the Service Solution - Speed of service deployment - UMTS will require for cost effective deployment - No disruption to speech service • Opportunities for Competition - No longer ‘tied’ to switch vendor • UMTS Ready - Re-use of GPRS core network • Large number of Application Developers - Competition - Speed • Service Re-use on UMTS • Sell Service on Value not Cost GSM Systems Division Agenda AGENDA Why Packet? GSM/GPRS Architecture What is EDGE? Deployment Issues Standards Terminal Classes GPRS Applications Standards Issues GSM Systems Division PPDN PSTN GMSC GGSN MSC SGSN Upgraded MSC Network Server GPRS Core Network Gb XCDR Iu Interface RNC To GSM BSS Iu - One Logical Interface - Two Physical Interfaces NODE B NODE B UMTS RAN GSM Systems Division Agenda AGENDA Why Packet? GSM/GPRS Architecture What is EDGE? Deployment Issues Standards Terminal Classes GPRS Applications GSM Systems Division GPRS Terminal Types Type A: Can support circuit and packet calls concurrently. Type B:This type of phone can support circuit or packet (not both together) and can be registered for both…i.e. an IP address and a PSTN number. Type C:This type of phone can only be registered for packet OR circuit but not both. GSM Systems Division GPRS Terminal - Multi-Slot Classes Multislot class COMPLEXITY FACTOR Low Medium High 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 Maximum number of slots Rx 1 2 2 3 2 3 3 4 3 4 4 4 3 4 5 6 7 8 6 6 6 6 6 8 8 8 8 8 8 Tx 1 1 2 1 2 2 3 1 2 2 3 4 3 4 5 6 7 8 2 3 4 4 6 2 3 4 4 6 8 Type 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 2 2 2 2 2 2 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 Tx and Rx not concurrent Tx and Rx Duplex Tx and Rx separate frames GSM Systems Division Agenda AGENDA Why Packet? GSM/GPRS Architecture What is EDGE? Deployment Issues Standards Terminal Classes GPRS Applications GSM Systems Division E-Commerce -Key Enablers • Dual Slot Phones • SIM Toolkit - some services now • WAP,MExE - full network interaction - in the future GSM Systems Division E-commerce E- Commerce Over GPRS Financial / Banking Finance Banking On-line transactions Clearing House Application Providers Retailers Content News Weather Sport Loyalty Cards Banking Shopping Promotions Certificate Authority Corporate / Operator Applications VPN e-mail Cost control Intranet Mobile Transactions Merchant Transactions Dual-slot mobile phones (SIM Toolkit) GSM Systems Division GSM Systems Division The End