Law of Reflection and Mirrors
advertisement

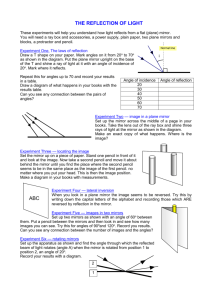
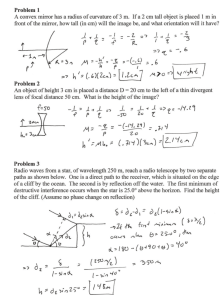
Law of Reflection and Mirrors How Light can be Redirected The Law of Reflection • When an object is smooth, the light that reflects off of the surface of that object will form an image – An image is a reproduction of an object produced by an optical device • An optical device is anything that uses light • Light rays bounce off of a mirror in a similar way that a pool ball bounces off the bumpers of a pool table Law of Reflection (cont’d) • When an incoming ray of light, called the incident ray, hits a mirror at a specific angle, called the angle of incidence, it will reflect that ray off at precisely the same angle, called angle of reflection. • The diagram on the next slide will give you a better idea of what this looks like Law of Reflection (cont’d) Notice how the angle of incident, labelled i, and the angle of reflection, labelled r , are measured from a line drawn perpendicular to the plane of the mirror, called the normal. i r The Law of Reflection • The law of reflection can be written using the Greek letter theta, θ. – This symbol is commonly used to represent an angle • Putting subscripts next to theta helps to identify what angle the symbol represents θi = θr • Once again remember that θ is measured from the normal line. Plane Mirrors • The law of reflection applies to both flat mirrors and curved mirrors. • Any mirror that has a flat reflective surface is called a plane mirror. • Images in a plane mirror appear as far behind the mirror as the object being imaged is in front of the mirror • The image appears to be behind the mirror, but it would not be possible to catch this image on a piece of paper if it were put behind the mirror because no light form the object reaches this point. • When no light comes from where an image appears to be, we call this a virtual image. Mirror Plane Mirror (cont’d) Object do di Reflected Virtual Image For a plane mirror, the distance of the object from the mirror is equal to the distance the image appears to be in the mirror. In other words, do = di. Plane Mirrors Exercise • Take a Post-It note and put the initial of your first name on in dots on the far left, as shown: • Then draw a line down the middle using a ruler as shown • Finally measure the distances the dots are from the line and make a dot an equal distance from line on the other side of the line as seen above Plane Mirrors Exercise(cont’d) • What did you notice about your letters? • Were the two letters exactly the same? • If they were exactly the same try the same exercise with the letter R. • This shows why letters appear backwards in images in mirrors. • You’ll see examples of how we try to correct for such problems on the front of ambulances (see above). Questions • Do Plane Mirror Reflection Quick Lab on page 428 of the textbook. – Answer questions 7 and 8 a & b for the lab. • Do questions 1, 2 and 9 from page 433 in the textbook. Put your answers to these questions in the title page document that coincides with this PowerPoint presentation.