powerpoint

Overview of the Solar System
Its gross features and theories of how it formed.
At the heart of science is an essential tension between two seemingly contradictory attitudes – an openness to new ideas, no matter how bizarre or counterintuitive they may be, and the most ruthless skeptical scrutiny of all ideas, old and new.
- Carl Sagan
Final Exam: Dec. 13, 11AM-1PM
HW due Friday.
Topic of Essay II due Friday.
There will be only the 1 st Sky Journal, worth 5% of the final grade. The HW is adjusted to 35% of the final grade.
Reconnaissance of the
Solar System so far
Sun, planets, moons, asteroids, comets, dust, gas.
Overview of the Planets
Orbital Characteristic Review
Eccentricity measures the flattening of the ellipse
The Orbits of some Planets are
Slightly Inclined to the Ecliptic
Plane
Orbits of the Planets
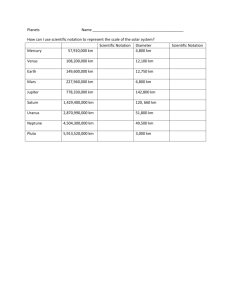
Planet
Mercury
Venus
Earth
Mars
Jupiter
Saturn
Uranus
Neptune
Pluto
Semi-major Axis Eccentricity
(A.U.) (degrees)
0.387
0.723
1
1.523
5.203
9.537
19.191
30.069
39.481
0.205
0.007
0.017
0.093
0.048
0.054
0.047
0.008
0.248
Inclination
(degrees)
7.005
3.395
0
1.851
1.305
2.484
0.77
1.769
17.141
Graph of Semi-major axes
Planetary Orbits
45
40
35
30
25
20
15
10
5
0
M er cu ry
V en us
E ar th
M ar s
Ju pi te r
Planets
S at ur n
U ra nu s
N pe tu ne
P lu to
Rotation of the Planets
Planet
Mercury
Venus
Earth
Mars
Jupiter
Saturn
Uranus
Neptune
Pluto
Rotation Period
(days)
58.646
-243.0187
0.997
1.026
0.413
0.444
-0.718
0.671
-6.387
Axis Tilt
(degrees)
0
177.3
23.45
25.19
3.12
26.73
97.86
29.58
119.61
Summary of Orbital Characteristics
• Planets orbit in nearly the same plane (the ecliptic plane), inclinations are small.
• Planets orbit in the same direction with small eccentricities. The direction is that which the sun rotates.
• Most of the planets spin in the same direction that they orbit. Venus, Uranus and Pluto are exceptions.
Sizes and Densities of the Planets
Sun
Mercury
Venus
Earth
Mars
Jupiter
Saturn
Uranus
Neptune
Pluto
Radius
(kilometers)
695508
2440
6052
6378
3397
71492
60268
25559
24764
1195
Mass
(kilograms)
1.99E+30
3.30E+23
4.87E+24
5.97E+24
6.42E+23
1.90E+27
5.69E+26
8.68E+25
1.02E+26
1.30E+22
Density
(grams/cc)
1.409
5.43
5.24
5.5
3.94
1.33
0.7
1.3
1.76
2.1
H
2
O has a density of 1 gram/cc
Silicate rocks ~ 3-4 grams/cc
Metals ~5-7 grams/cc
Composition of the Solar System
C
O
N
Some Nomenclature
Astronomers classify materials according to their tendency to exist as gases, ices, or rocks at
Earth-like temperatures and pressures.
• Gases: Elements - H, He, Ar, Ne, other noble gas. Molecules - H
2
, He, Ar, Ne, …
• Ices: Elements – O, C, N. Molecules – H
2
CH
4
, NH
3
, CO, CO
2
, …
O,
• Rocks: Elements, Fe, Si, O, Mg, Ni, …
Minerals – Silicates, Sulfides, Metals, …
Classification of Planets
Terrestrial Planets: Mercury, Venus, Earth, Mars
Mostly rock, radii of several thousand kilometers, densities of
~5 grams/cc. These are the first 4 planets out from the Sun.
Jovian Planets: Jupiter, Saturn, Uranus, Neptune
Radii of tens of thousands of kilometers, densities of
0.7-1.76 grams/cc composition similar to the Sun but with extra “heavy” elements (carbon, oxygen, nitrogen, etc.).
Flotsom and Jetsom of the Solar System:
Comets, Asteroids, Kuiper Belt Objects, Pluto.
Radii from tens (or smaller) to hundreds of kilometers.
Density ~ 0.5-2 grams/cc (with exceptions). Composed of ice and rock.
Inner vs Outer
Planets
Mars
Jupiter
Composition Trends
Sun
Body
Terrestrial
Planets
Jupiter
Saturn
Uranus
Neptune
Rocky(%) Icy(%) Gaseous(%)
0.3
1.2
98.5
70 30 0
2
6
25
27
5
14
58
62
93
80
17
11
Zelik, P 358
The Nebula Hypothesis
The solar system (planets, satellites, asteroids, comets, etc.) formed along with the Sun 4.5 Byr ago from the gravitational collapse of an interstellar cloud of gas and dust. The planets and Sun formed from the same reservoir of interstellar matter and are therefore composed of primarily the same elements.
As the cloud collapsed under the force of gravity it began to spin rapidly and then flattened into a plane. This explains why the solar system is a relatively flat plane and why the planets orbit in the same direction and tend to rotate in the direction that they orbit.
The collapsing cloud of gas and dust was hottest near the Sun and coolest far from the
Sun. The local temperature determined which compounds solidified from the gas phase as a function of distance from the Sun. This explains why the inner planets are composed mostly of rock and the outer planets have large complements of ice. Ice forming elements are more abundant than rock forming elements so planets in the outer solar system are larger. In fact they are so large that their gravitational fields were able to capture the
H and He in the cloud. The gravity of the inner planets is too weak to hold on H and He. This explains why the outer planets are gaseous and the inner planets are rocky .
Accretion of the Planets
Why Planets Spin the Way That
They Do
Click here to see movie
Condensation in the Solar Nebula
High Density
Low Density