ArtHistoryCheatSheet1
advertisement
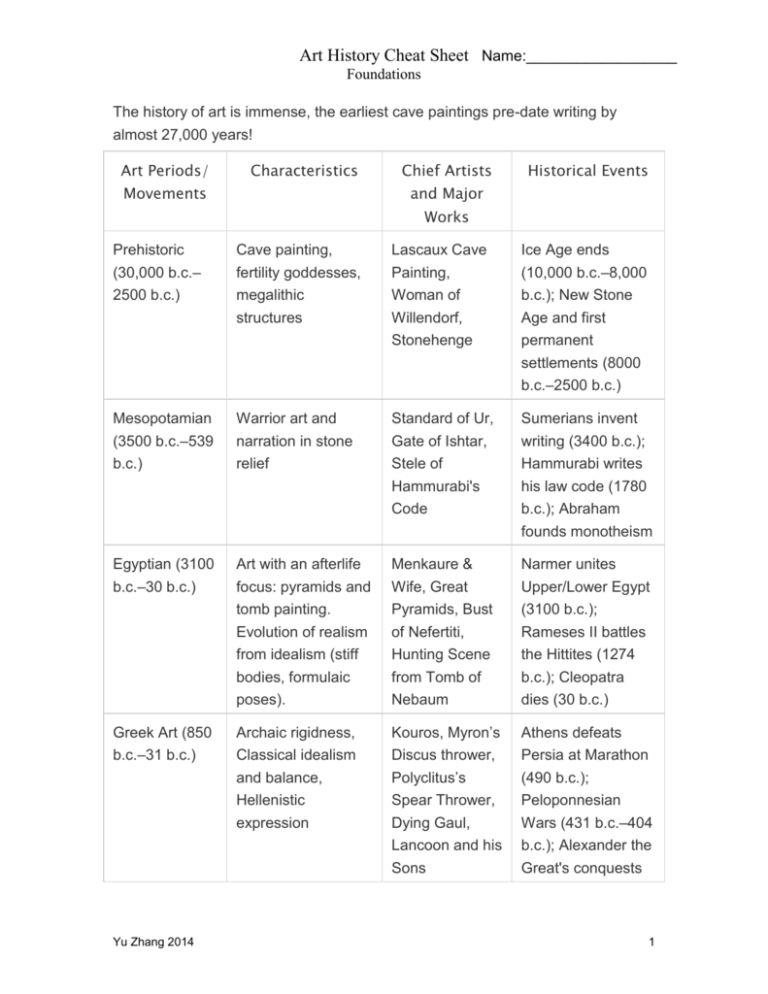
Art History Cheat Sheet Name:__________________ Foundations The history of art is immense, the earliest cave paintings pre-date writing by almost 27,000 years! Art Periods/ Characteristics Movements Chief Artists Historical Events and Major Works Prehistoric (30,000 b.c.– 2500 b.c.) Mesopotamian (3500 b.c.–539 b.c.) Cave painting, fertility goddesses, megalithic Lascaux Cave Painting, Woman of Ice Age ends (10,000 b.c.–8,000 b.c.); New Stone structures Willendorf, Stonehenge Age and first permanent settlements (8000 b.c.–2500 b.c.) Warrior art and narration in stone relief Standard of Ur, Gate of Ishtar, Stele of Hammurabi's Code Sumerians invent writing (3400 b.c.); Hammurabi writes his law code (1780 b.c.); Abraham founds monotheism Egyptian (3100 b.c.–30 b.c.) Art with an afterlife focus: pyramids and tomb painting. Evolution of realism from idealism (stiff bodies, formulaic poses). Menkaure & Wife, Great Pyramids, Bust of Nefertiti, Hunting Scene from Tomb of Nebaum Narmer unites Upper/Lower Egypt (3100 b.c.); Rameses II battles the Hittites (1274 b.c.); Cleopatra dies (30 b.c.) Greek Art (850 b.c.–31 b.c.) Archaic rigidness, Classical idealism and balance, Hellenistic expression Kouros, Myron’s Discus thrower, Polyclitus’s Spear Thrower, Dying Gaul, Lancoon and his Sons Athens defeats Persia at Marathon (490 b.c.); Peloponnesian Wars (431 b.c.–404 b.c.); Alexander the Great's conquests Yu Zhang 2014 1 Art History Cheat Sheet Name:__________________ Foundations (336 b.c.–323 b.c.) Roman (500 b.c.– a.d. 476) Roman sculptures: derived from Greek art, realism: real people, politicians, senators, clothes as a sign of power. Roman painting: some depth Statue of Augustus, Fresco from the Villa of Mysteries Julius Caesar assassinated (44 b.c.); Augustus proclaimed Emperor (27 b.c.); Diocletian splits Empire (a.d. 292); Rome falls (a.d. 476) South Asian Art (653 b.c.– a.d. 700) Buddhist and Hindu art: large statues of Buddha, Shiva, Vishnu etc. in temples Standing Buddha, Shiva Nataraja Birth of Buddha (563 b.c.); Silk Road opens (1st century b.c.); Buddhism spreads to China (1st–2nd centuries a.d.) p. 72-73 Islamic cermaics, mosaics, flower and geometric motifs, calligraphy The Dome of the Rock, Jug with molded Decorations, Seljuq style Qu’ran Birth of Islam (a.d. 610) and Muslim Conquests (a.d. 632– a.d. 732) Early American Art (b.c.1700- a.d. Ceremony art in temples, mosaics, carvings and large Nazca’s Hummingbird, Teotihuacan’s Olmec civilization (1700-400 bc.) givesrise to 500) land forms anthropomorphic mask, Maya’s Temple of the Jaguar Teotihuacan and Mayans in central America. Chavìn give rise to the Moche and Nazca in S. America. p.74-75 Early Islamic (476-1200) Yu Zhang 2014 2 Art History Cheat Sheet Name:__________________ Foundations Early Middle Ages/ Medieval Art (500 – 1200) Christian Art: evolution from symbols to icons, lack of authorship, decorative motifs inspired by Viking art. Mosaics. Christian Subterranean symbols. Osberg Ship, Book of Kells. Mosaic of Emperor Justinian and Attendants. Justinian partly restores Western Roman Empire (a.d. 533–a.d. 562); Iconoclasm (a.d. 726–a.d. 843); Viking Raids (793–1066); Battle of Hastings (1066); Late Medieval/PreRenaissance Art (12001400) Emergence of different artists, styles, and development of linear perspective. Romanesque: decorative doors, small windows, geometric designs. Gothic: flying Cimabue’s Madonna and Child in Majesty Crusades I–IV (1095– 1205); Giotto’s Jesus before Calf Black Death (13471351); Hundred Years’ War (13371453) Early and High Renaissance (1400–1550) Yu Zhang 2014 Gislebertus’s Last Judgement Carving of Eve buttresses, tall and elegant, stained glass, pointed arches Chartres Cathedral Rebirth of classical culture, development of linear perspective, individual artists, about humanism, Raphael’s School of Athens, Botticelli’s Birth of Venus, Da Vinci’s Mona Lisa, Bosch’s Garden of Gutenberg invents movable type (1447); Turks conquer Constantinople (1453); Columbus knowledge (not only about religion) Early Delights lands in New World (1492); Martin Luther starts Reformation (1517) 3 Art History Cheat Sheet Name:__________________ Foundations Mannerism (1527–1580) Reaction against classicism, contorted bodies, elongation, artificial light and colors Parmigiano’s Madonna withthe Long Neck, St. Francis Receiving the Stigma, Archimboldo’s Spring, Allegory of the Immaculate Conception Magellan circumnavigates the globe (1520–1522) Baroque (1600–1750) Splendor and flourish for God; art as a weapon in the religious wars, dark paintings, mythological and allegorical subjects Bernini’s Ecstasy of St. Theresa, Caravaggio’s Beheading of St. John the Baptist, Vermeer’s Girl with the Pearl Earrings, Sala di Apollo, Aurora Thirty Years' War between Catholics and Protestants (1618–1648) Rococo Airy, light, creamy colors, delicate. Less serious topics than the Baroque. Grand Tour: focus on nature and scholarly Return of the Bucintoro on Ascension Day, An Experiment on a Bird in the Air Pump, Ruined Gallery of the Villa Adriana Louis XIV at throne (1638-1710s) Yu Zhang 2014 4 Art History Cheat Sheet Name:__________________ Foundations Yu Zhang 2014 5


