Property Tax System-Overview
advertisement

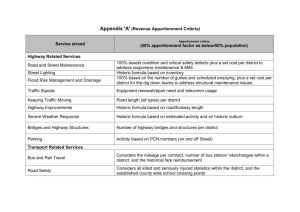
By: Santa Clara County Controller-Treasurer’s Office Property Tax Assessments Property Tax Roll Types Role of Different Agencies Apportionments Projections Demystifying California Property Tax Apportionment System • • • The People's Initiative to Limit Property Taxation was approved by California voters on June 6, 1978. Article 13A of the Constitution of the State of California An annual increases of assessed value of real property to an inflation factor, not to exceed 2% per year. Allowed reassessment of a base year value for Supplemental event (a) change in ownership, or (b) completion of new construction. A reassessment may be an assessed value increase resulting in a supplemental bill(s), an assessed value decrease resulting in a supplemental refund(s) or retaining the same assessed value (no change). Government properties or properties that are used for non–commercial purposes. EXEMPTION Welfare Exemption: hospitals, religious properties, charities, and nonprofit schools and colleges. Homeowner Exemption Veteran Exemption PERSONAL PROPERTY • Property other than land, buildings, and other permanent structures, which are commonly referred to as “real property” such as manufacturing equipment, business computers, and office furniture. • Aircraft – personal and commercial • Boats When determining the market value of personal property, county assessors take into account the loss in value due to the age and condition of personal property—a concept known as depreciation. Unlike property taxes on real property, which are due in two separate payments, taxes on personal property are due on August 31. The State Board of Equalization is responsible for assessing certain real properties that cross county boundaries, such as Public Utilities :Transmission Lines, Optical Lines, Electric Facilities. Telecommunication: Interexchange and Commercial Mobile Regulated Railway: Railroad tracks and cars. Canals. The County Assessor is responsible for assessing inter-county pipelines PROP 8: PROP 60: PROP 90: allows transfers from one county to another county PROP 110: provides property tax relief for severely and PROP 58: Transfers of the principal place of residence TEMPORARY REDUCTION OF PROP 13 Base Values due to Market declines. allows transfers of base year values within the same county (intracounty). Must be at least 55 years old. in California (intercounty) and it is the discretion of each county to authorize such transfers. Must be at least 55 years old. permanently disabled claimants when they sell an existing home and buy or build another. between parents and their children (there is no limit on the value of the residence) The 1 percent rate established by Proposition 13 (1978). Tax rates to pay for local voter– approved debt. Property assessments. Mello–Roos taxes. Parcel taxes. SECURED SUPPLEMENTAL UNSECURED UNITARY COUNTY ASSESSOR: Assesses Values of the Properties Certifies the Values to the County Treasurer-Controller TAX COLLECTOR Collects the taxes Issues Refunds Prints and Mails tax bills Processes Roll corrections Certifies the Tax Collections to the Treasurer Controller for Apportionment TREASURER-CONTROLLER Extends the Annual Tax Rolls Apportions the Tax Collections and Refunds [due to Roll Corrections] Distributes the Funds to Taxing Entities Provides Fiscal Reports Apportionment ◦ Two Apportionment methods: Teeter Non-teeter Teeter ◦ Author: Mr. Desmond Teeter, the Auditor-Controller for Contra Costa County (1940s) ◦ Allows counties to apportion secured, unitary, assessment, supplemental to jurisdictions at 100% of billed amount rather than tax collections ◦ County collects delinquent tax payments & penalties ◦ R&T § 4701-4722 Benefits: Simplified property tax estimation and allocation process Stable and reliable annual property tax revenues Santa Clara County: Teeter: Secured & Supplemental Non-teeter: Unsecured Non-Teeter Cities: City of Sunnyvale Town of Los Gatos Apportionment Factors To distribute property tax revenue Revenue and Taxation Code AB8 Apportionment factors Allocate Secured, Unsecured and Homeowner Exemption tax revenues [R&T §96.5] Supplemental Apportionment factors Allocate Supplemental tax revenue 4653.4] [R&T §75.6,75.7 & Unitary Apportionment factors Allocate unitary tax revenue [R&T § 100] AB8 Apportionment factors ◦ The Assembly Bill 8 (“AB8”) 1979 Provides procedures for an equitable allocation of property taxes change in proportion with the increase or decrease of assessed values (“AV”) To allocate to each jurisdiction the amount it received in the prior year, plus the change that has occurred in the current year within its boundaries Increment Allocation Factor (IAF) apply on the change of AV Annual calculation ‘Modified AB8’ ◦ ADA from the State ◦ Basic Aid and Non-County-of-county districts are not eligible Prior year’s factors for prior year’s collections Apportionment Schedule ◦ Major revenue Secured: 10 times a year Unsecured: 3 times a year Supplemental: 13 times a year ◦ Link to Apportionment schedule: http://www.sccgov.org/sites/fin/ControllerTreasurer%20Department/Property%20Tax%20 Apportionment/Pages/PROPERTY-TAXDISTRIBUTION-SCHEDULE.aspx FY2013-14 Santa Clara County Property Tax 1% Distribution (After VLF) County City School Community College 7% Special District VLF-County 6% School K-12 45% Special District 6% School Community College Other 21% City 9% County 12% School K-12 VLF-City 4% RDA Successor Agency 11% RDA Successor Agency VLF-County VLF-City Others Roll Corrections Assessor’s Certified Roll Current Year’s Projection Estimated Roll Corrections Others Assessor’s Monthly Roll Growth Next Fiscal Year’s Projection Current Year’s Projection Roll Corrections Assessor’s Annual Roll Collections Others Next Fiscal Year’s Projection Roll Corrections Market Trend/Economy Historic Data Others Current Year’s Projection Roll Corrections Collection Market Trend Historic Data Others Next Fiscal Year’s Projection Historic Data Roll Corrections Market Trend Others County Supplemental vs. Transfer Tax 35,000,000 30,000,000 25,000,000 20,000,000 Transfer Tax Revenue 15,000,000 Supplemental Revenue 10,000,000 5,000,000 2004 2005 2006 2007 2008 2009 2010 2011 2012 2013 Correlation (r) 0.638880558 Current Year Annual Tax Increment Loss Available in August meeting Available in November meeting Same distribution timing as RPTTF [January 2 and June 1] Available on October 1 and April 1 January 2 and June 1 • Current Year Pass-through • RPTTF Residual Estimate • RPTTF Residual Distribution • Trust Fund H&S § 34170.5 (b) The county auditor-controller shall create within the county treasury a Redevelopment Property Tax Trust Fund for the property tax revenues related to each former redevelopment agency, for administration by the county auditor-controller. • Distribution [H&S §34183] Timing: Jan 2 & Jun 1 What’s distributed Administrative Fees & audit fee to County Auditor-Controller; Pass-through Payment to the affected taxing entities of former RDA; Recognized Obligation Payments to Successor Agency's Recognized Obligation Retirement Fund (RORF); Successor Agency's Administrative Cost Allowance under H&S 34171; SCO Billings under H&S34184(d); Residual Balance of the RPTTF to local agencies and school entities Demystifying the California Property Tax Apportionment David G Elledge May 2006 Prop 13/ 1978 ◦ limited the tax rate for each individual piece of property to one percent, exclusive of bonded indebtedness approved by the voters SB154/ three weeks after passage of Prop 13 ◦ to divide up the one percent property tax rate based on an historical shares methodology to maintain an “as you were” approach ◦ Example: City A received 5% prior to passage of AB8, City A would receive 5% of property taxes collected at 1% Problem with SB154 ◦ Geographical boundaries ◦ SB154 Base Year Error ◦ State Assistance (Bailout) Long Term Solution: AB8 ◦ Distribute growth in assessed valuation ◦ Redistribute property taxes resulting from changes in jurisdictional boundaries/services TEA ◦ Tax Equity Allocation ◦ No/low property tax cities 31 cities existed prior to Prop 13 never levied a property tax, no share in the property tax apportionment ◦ AB 709 first TEA legislation Required 17 counties to shift some of their property tax to 49 qualifying cities ◦ AB1197 amended TEA legislation provide most qualifying cities receive 7 percent of the property tax ◦ Santa Clara County TEA cities: Cupertino, Los Altos Hill, Monte Sereno & Saratoga ERAF ◦ Educational Revenue Augmentation Fund ◦ 1992/93 ERAF I State Budget Shortfall ◦ 1993/94 ERAF II State Budget Shortfall ◦ 2004/05 and 2005/06 ERAF III (temporary) http://www.sccgov.org/sites/fin/ControllerTreasurer%20Department/Property%20Tax%20Apportio nment/Pages/Property-Tax-Apportionment.aspx Q&A