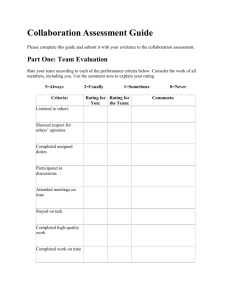
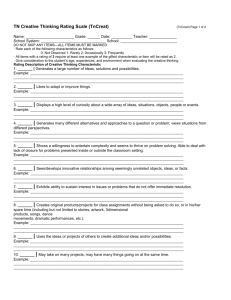
EXAM QUESTION à rating
advertisement

Simone Besseling WK 1 Marketing process - 1. Marketing 2. Communication 3. Media (never starts other way around!) Media planning = process that should result in how to deliver our ads to selected target group in most effective and efficient way. Difference marketing objective vs communication objective (macdonalds example) Marketing --> enlarging turnover, increase number cash transactions with 12% (reach, frequency, continuity, weight, cost)--> MEDIA OBJECTIVES Communication --> Positioning macdonalds as the one with best price/quality product in NL (AIDA, awereness,knowledge,puchase, attention ect) Media planner would most be interested in media research. ATL Above the line = advertising through media such as tv, cinema radio, print to promote brand (impersonal, mass orientated, difficult to measure ) BTL Below the line = marketing/sales activities that directly lead to trial or purchase by using more targeted media like in-store displays, direct mail etc. (more individual, measurabe, nowadays more and more BTL) TTL Through the line = involves both strategies. (example - tv commercial 'come into store to smaple the xcv product' ) Performance based pricing = only paying for measurable results -Based on leads -Based on clicks -Based on transactions -Based on visitots Chapter 2, class wk2 Media channels = a TV, a radio , can also be a book or magazine (but not the content, that is the vehicle) What we use is a media vehicles discovery channel, ads/articles in books/magazines Advertisement = the media vehicle (wat is je message) The book/magazine it is in = the media channel (hoe verstrek je je message?) Nett reach = Number / percentage of people exposed to a media vehicle with the message once during the advertising period. Potential contact with a medium is not always a realistic contact. Some people may not have any contact with the medium at all, some may have contact and some will have contact with your Simone Besseling campaign. The NETT users in this, are the ones who have contact with the medium, and the people who have contact with the campaign. Numerical reach= Number of people seeing/watching message ( 8% of 550.000 = 44.000) Percentage reach=Percentage of people seeing/watching message ( 110.000 of 550.000 = 20%) Fequency is how many times a consumer of the target group is expected to be exposed to the vehicle with the advertisers message within a specific time period. (exposure to media vehicle not the message) --> so might me exposed to watching discovery, but not the ad in the commercial break. B-coefficient = the higher the % of people thatwill remember the ed. (it is found after research. not an estimation) Rating (Rtg) persons who see or hear a particular program as a percentage of the total population (so 100.000 households, 60.000 are watching tv, 20.000 voice of holland, ratio: 20.000/100.000=20%) Rating Points 1% of a particular group, is 1 rating point. So 15.3% is 15.3 rating. EXAM QUESTION rating (tv and radio) = coverage (Printed Media) Coverage includes; number of copies and number of households Share: Number of people turned to a particular TV station as a percentage of all people watching TV at the same time. EXAM QUESTION In media we use ratings or share? Mostly Rating. Difference Rating and share = Rating is people watching tv programma/entire population Share is people watching tv program/ people watching TV. Share tells how a vehicle competes with other vehicles. Rating tells how a vehicle perform in term of place/time to total potential audience. Gross reach= sum of the number of people every individual the medium reaches (people can be counted multiple times) In case multiple counting (received message per person more than once) Gross Rating points (GRP’s) GPR’s = to measure effectiveness of advertisement. It is the unit definition used fot all media to compare media and/or accumulate reach. It includes Reach x frequency GRP formulas F=frequency R=Reach GRP = Gross Rating points GRP = R% x F R% = GRP : F F= GRP :R% **Media buyers when buying media space look at number of GRP's. ** GPR of 257 means, 275% are people you have reached in a particular group. (might mean, reached 50% of target goup, who has seen is 5 times(frequency) Simone Besseling Audience=number of readers/viewers/listeners Accumulative Audience = total people seen your ad (also counted mulptiple) Unduplicated Audience = total people seen ad once. TAI = Total audience impressions (based on numerical reach) RxF (reach(how many, 25n mil) x frequency (hoe many times watched, 5x p.p) = 125 million TAI Effective Reach = Number of consumer reached at least three times Effective Rating Points (ERP) =Gross reach of a campaign for those people who were reached at least three times. As a percentage of the target group. EXAM QUESTION As a media planner you’d rather talk about ERP’s than Rating Points (RP’s) Effective Frequency = number of range of exposures required to produce a desired impact (eg sales, brand awareness, brand liking) At least 3 to be effective frequency, or more. EXAM QUESTIONS! : Check bottom page: http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Advertising_media_selection#Pulsing Continuity - keeps same (lack of brand loyalty, intense competition, ) Short PLC Continuity - pulsing advertising under-arm deodorants, sell all year, but more in summer months. Need it whole year, product with limited budget intense competition. Continuity - flighting advertising Like halloween costumes (little waist of advertising) Summer holidays, Winter holidays, ice creams, seasonal products. Intro PLC Product in introductory stage of PLC (product life cycle) reach is more important Product in maturity stage of PLC frequency is more important LAST QUESTION EXAM Class assignment - Newspaper reach and frequency (handed out fist class) Answers: 1) 40 2)26 3)12 4)a 18 Simone Besseling Week3 A disruptive technology or disruptive innovation is an innovation that helps create a new market and value network, and eventually goes on to disrupt an existing market and value network (over a few years or decades), displacing an earlier technology. --> INTERNET Web1.0 - one way Web 2.0 - 2 way traffic - sender and retriever start communicating via the web - start of social media Web 3.0 - Personalized content, internet anywhere/anyplace (mobile) , datadriven, real time web Interactive advertising is growing faster than traditional advertising (its better measuarable, changable, testable). Search is much less expensive than Direct marketing. page view (PV) or page impression = request to load single page of intenet site. pages per visit = average pages per visit. bounce rate = total number of visits viewing one page (navigate away from site after seeing entrance page) Conversion ratio = average number of visitors who visit the site who make a purchase of perform some sort of action. IMPORTANT Affliation = marketing practice in which a business rewards one or more affiliates for each visitor brought by the affiliate's own marking efforts. 90% of all Affiliate marketing is conducted on a CPA model or Cost per Sale. Simone Besseling Week 4 EXAM QUESTION exam - Difference between strategy and tactict a: Strategy, long term planning, WHY, overall things. tactics is short term 'doing' HOW, detailed. Strategy questions -- Target group description, media behavior, mass media/one to one approach, media channel choice, rough budget allocation Tactics questions -- Media vehicle selection, number of ads & scheduling, detailed budget allocation. Qualitative aspects = impact, context, timing aspects, message life, relevancy, memorization ect. Quantitative aspects = circulation, reach data, costs (CMP. CPC, CPA, CPL) Mass media (newspapers/televidion or more one to one approach (internet) Cross selling is – you buy a book about prosche, and Porsche could say are you interested in a testride? Combining products. Amazon is the best example. Second one free, of for half price. High conversion; your desired goal (it can be a sale, or a test ride) Umfelt/ context = environment in which you advertise. Receiver aspect = determined bij sitation in which receiver get's in touch with message (at home, way to office, with friends ect.) Ssender aspects = The medium itself, content of medium, pace. What page, what other ads. Advertisers think in quarters Q1,Q2,Q3,Q4. Most expensive is Q4, consumers spend more (chrismas, sinterklaas ect) so media vehicles raise prices! Week 5+6 From P's to E's -Product to Experience -Place to Everyplace -Price to Exchange -Promotion to Evangelism Quantitative : Medium Selectivity - How good or bad does a certain medium rech my target group Selectivity index = %of target group in total reach ------------------------------------------- x100 %of target group in the universe Simone Besseling Less than 100 = target group under represented. Vehicle not selective on target group 100 = target group is proportionally presented more than 100 = target group is over represented: vehicle is selective on target group Reach Vs frequncy TV = Reach Radio = Frequency Magazine = Frequency Newspaper= Frequency Oudoor = Reach Direct mail = Reach Banners = Reach