Chapter 7 - A More Perfect Union
advertisement

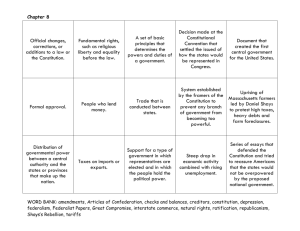
US HISTORY Chapter 7 A More Perfect Union 1777-1790 Lesson 1 – The Articles of Confederation Articles of Confederation Adopted by Second Continental Congress in November 1777 Became first constitution for US Under the Articles, states kept most of their power Congress could conduct foreign affairs, maintain armed forces, borrow money, & issue currency Congress could NOT regulate trade, force citizens to join the army, or impose taxes Under the Articles, each state had one vote in Congress...9/13 states had to approve any laws...13/13 states had to approve amendments Lesson 1 – The Articles of Confederation Land Ordinance of 1785 Established the procedure for surveying & selling the western lands north of the Ohio River Set up the township system 6 miles x 6 miles 36 sections each 1 mile x 1 mile 1 section reserved for schools Lands sold at auction to raise money to pay off debt from Revolutionary War Lesson 1 – The Articles of Confederation Northwest Ordinance Passed in 1787 Created the Northwest Territory (lands east of the Mississippi River and north of the Ohio River) NW Territory was to be divided into 3-5 smaller territories and each of the smaller territories could apply for statehood once their population reached 60,000 Slavery was made illegal here first attempt by the govt. to stop the spread of slavery Lesson 1 – The Articles of Confederation Land Act of 1800 Law written by William Henry Harrison (NW Territory rep in the House of Representatives) Law made it easier to buy land in NW Territory by setting up payment plan Settler had to buy at least 320 acres for $2/acre…paid one-half of the cost up front and rest in four yearly payments Lesson 1 – The Articles of Confederation Problems with the Articles Value of currency decreased, price of goods increased Congress had huge debt with no power to pay it off (couldn’t tax) Britain held onto forts in the Great Lakes region Spain cut off access to the lower Mississippi River Lesson 2 – Forging a New Constitution Shays’ Rebellion Began in 1786 (MA) Farmers were thrown in jail because they couldn’t pay their debts Group of farmers, led by Daniel Shays, forced courts in western MA to close Lesson 2 – Forging a New Constitution Shays’ Rebellion Jan 1787 – Shays & 1000 followers marched to Springfield, MA to overtake the federal arsenal there MA state militia fired on the men, killing four Shays & his men scattered...end of the rebellion Scared a lot of Americans...they believed the govt. was too weak to protect them Lesson 2 – Forging a New Constitution Constitutional Convention Many called for a change to the Articles Convention began in Philadelphia in May 1787 Purpose was to change the Articles 55 delegates...12/13 states represented (RI) George Washington selected as President of the Convention James Madison kept meticulous notes...later became known as the “Father of the Constitution” Meetings were not public...delegates wanted to be free to change their mind After the Convention began, decision was made to scrap the Articles and write a new Constitution Lesson 2 – Forging a New Constitution Virginia Plan Plan was written by James Madison, presented by Edmund Randolph Called for a two-house legislature, a chief executive chosen by the legislature, and a court system Legislature – both houses would be based on population Small states immediately objected Lesson 2 – Forging a New Constitution New Jersey Plan Presented by William Paterson Called for a one-house legislature based on equal representation Legislature would be able to set taxes and regulate trade (unable to do these under the Articles) Legislature would select executive branch (more than one person) Lesson 2 – Forging a New Constitution The Great Compromise Settled the debate b/w large & small states Called for a two-house legislature Lower House (House of Representatives) – based on population Upper House (Senate) – based on equal representation...each state gets two Senators Lesson 2 – Forging a New Constitution 3/5 Compromise With one house being based on population, question was raised on how to count slaves Compromise was to count 3/5 of all slaves for representation & taxation purposes Also agreed that Congress could not interfere with slave trade until 1808 Lesson 2 – Forging a New Constitution Approval of the Constitution September 17, 1787 – delegates assembled to sign the Constitution Constitution was sent to the states...would become the law of the land once 9/13 states approved it Lesson 3 – A New Plan of Government Federalists v. Anti-Federalists Supporters of the new Constitution were called Federalists included George Washington, Ben Franklin, James Madison, Alexander Hamilton, & John Jay Federalist Papers – series of essays written by Madison, Hamilton, & Jay explained why the Constitution should be ratified Anti-Federalists – opposed the Constitution Thomas Jefferson & Patrick Henry...felt a strong national government would take away the individual liberties fought for in the Revolution Lesson 3 – A New Plan of Government Adopting the Constitution Dec 7, 1787 – Delaware became the first state to ratify June 21, 1788 – New Hampshire became 9th state, made the Constitution go into effect NY & VA (2 largest states) still needed to ratify Both ratified after getting assurances that a Bill of Rights would be passed May 1790 – RI becomes 13th state to ratify