hapch16repro
advertisement

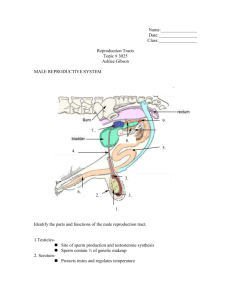
Page 1 of 13 Human Anatomy and Physiology Chapter 16-The Reproductive System Notes ___________________-primary sex organs-ie. Testes and ovaries _______________________--sex cells produced by gonads as well as gonads secrete sex hormones _______________________________-remaining reproductive structures Joint purpose of Reproductive system is produce offspring---via sperm in males and ___________ in females Zygote becomes embryo and then fetus I. Anatomy of Male Reproductive System Testes have exocrine-sperm producing- function and endocrine-testosterone producing Accessory structures in delivery of sperm to exterior or to female 1. TESTES Plum shaped---4 cm –sized surrounded by fibrous connective tissue capsule-_____________________________________-“white coat” Extensions of capsule extend into testes and divide into wedgeshaped ______________________each containing 1-4 ______________________________________-sperm producing portion Seminiferous tubules empty into another set of tubules--_________________________on each side of testis-sperm travel from rete to enter 1st part of duct system_______________________________-hugging external testis In soft tissue around seminiferous tubules are ____________________________-that produce androgens-esp. testosterone---thus different tissue process sperm and then hormones 2. DUCT SYSTEM-inc. edididymis,ducus deferns, and urethra A.___________________________-highly coiled tube-~6 m-capping superior testis and extends posterolaterally-temporary storage for immature sperm entering from testis Takes sperm about _____________days to travel epididymis,maturing along the way...and become motile During ejaculation,epididymis contracts to expel ___________into-_________________________________ Page 2 of 13 B. Ductus Deferens (= vas deferens)-extends upward from epididymis through inguinal canal,to pelvic cavity and arches over superior bladder…enclosed w/ blood vessels and nerves and connective tissue sheath______________________ and it travels up through inguinal canal Loops medially over ureter and goes down posterior bladder-expands as ampulla and empties into ________________________________--this passes through prostate gland and merges w/ urethra Main function of ductus deferens is to _______________________________________________ At ejaculation smooth muscle squeeze sperm forward by __________________________________ A __________________________________is a contraceptive procedure that ligates-“ties-off” ducus deferns in part that lies in scrotum---sperm are still produced-but don’t reach body exterior and are phagocytizedrendering male sterile C. Urethra From base bladder to tip of penis-terminal feature of male system-carries urine and sperm-however both never travel @ same time---bladder sphincter constricts @ ejaculation preventing this 3 regions: 1) ________________________________-surrounded by prostrate 2)____________________________________-from prostatic urethra to penis and 3)___________________________________________-runs length of penis 3. ACCESSORY GLANDS AND SEMEN-inc. paired seminal vesicles,single prostate,bulbourethral glands and semen A.________________________________________@ base of bladder make ~60% of seminal fluid-secretion rich in ______________________________________________________________ _________________________________which nourish and activate sperm Each of its duct joins vas deferens on same side to form _____________________________________----thus sperm and seminal fluid enter urethra during ejaculation B. Prostate-single doughnut –shaped gland-encircles prostatic urethra below bladder Its glandular milky secretion helps activate sperm---during ejaculation-fluid enters urethra through several small ducts Since near rectum,can be palpitated rectally Older men suffer hypertrophy of gland, strangling urethra-making urination difficult and increases risk of bladder infections________________________ and kidney damage Page 3 of 13 Treatments include :surgery,drugs or microwaves to shrink prostate,insertion of small balloon to push prostate away from urethra,incineration w/low energy radiation __________________________________-inflammation of prostatecommon _______________________________-most prevalent cancer in men-slow growing,usually C. ___________________________________________-tiny pea-sized glands posterior to prostate,produce thick,clear mucus draining into penile urethra----is 1st secretion to pass upon sexual arousal ---functions in cleansing urethra of acidic urine and is a sexual lubricant D. Semen-milky white, somewhat sticky mixture of sperm and gland secretions ;transport medium for nutrients and chemicals that protect and aid in movement of sperm Sperm have little cytoplasm or stored nutrients so __________________ is energy fuel pH ~ 7.2-7.6 helps neutralize acidic vagina(3.5-4.0)-protecting sperm(sperm are sluggish in acidic environment) _______________________________________-antibiotic chemical destroying certain bacteria Hormone_______________ Enzymes to enhance sperm motility Substances to inhibit female reproductive immune response Male infertility---causes include obstruction of duct system,hormone imbalance , environmental estrogens,pesticides, too much alcohol….often _______________________________is checked to analyze sperm count, motility, and morphology,semen volume ,pH, fructose amount…sperm count should not be below 20 million /mL 4. EXTERNAL GENITALIA-ie. Scrotum and penis Scrotum-divided sac of skin outside abdominal cavity,normally hangs loosely,rendering testes temperature below body temp.( @ ~ 5.4 degrees lower)-necessary for healthy sperm production ,changes in scrotal surface area help maintain temp—example -wrinkles as pulls toward body during external cold temp’s Penis-delivers sperm-consists of shaft,glans penis tip and prepuce or foreskin-loose skin covering-often removed at circumcision/Internally-spongy urethra by 3 elongated areas of __________________________________that fill w/ blood during arousal-causing rigid erection II. Male Reproductive Functions A. SPERMATOGENESIS=sperm production-begins @ puberty and is lifelong Millions/day Page 4 of 13 _____________________________primitive stem cells @ periphery of each seminiferous tubule/rapid mitotic division to build stem cell line….from birth to puberty @ puberty __________________________________________(FSH) is secreted in increasing amounts by ant. Pituitary gland…from here on out ,each division produces 1 stem cell-type A daughter ---which remains @ tubule periphery to maintain stem population…and 2nd,type B daughterpushed toward tubule lumen to become primary spermatocyte and will undergo MEIOSIS Gametes @ this stage are called _________________-made by meiosis and have ½ genetic material (2n in humans=23 x 2) As meiosis occurs,primary,then secondary sprematocytes pushed toward tubule of lumen Spermatids NOT functional sperm-nonmotile and excess cellular baggage During last stage-______________________________-excess cytoplasm sloughed off and now have ___________________________________________________,equipped w/high metabolism and motility Sperm head has DNA---essentailly nucleus Anterior to head is _____________________made by golgi and similar to large lysosome---which breaks down @ membrane and releases to help sperm penetrate follicle of egg Filaments make long tail from centriloes in midpiece w/mitochondria wrapped around for necessary ATP All of spermatogenesis-from primary spermatocyte to release of immature sperm takes 64-72 days Sperm in lumen nonmotile and can’t fertilize….moved by peristalsis from tubules into epididymis---there further maturation and increased motility Things that can alter sperm formation:_____________________________________________________ ______________________________________________________________ ____________________________________________________________maybe producing 2 headed and/or multi-tailed sperm B. TESTOSTERONE PRODUCTION PRODUCED BY INTERSITIAL CELLS @ puberty FSH prods sperm production and ____________________________________(LH) is also released by anterior pituitary on from here on out testosterone is produced continuosly,rising levels responsible for secondary sexual characteristics:_________________________________________________ Page 5 of 13 III. ______________________________________________________________ _____________________________________________________________ ______________________________________-testosterone not produced and secondary sex characteristics not produced….castration will cause this or malfunction of interstitial cells…also cause sterility FEMALE REPRODUCTIVE ANATOMY Function in producing gametes(ova) and nurture/protect developing fetus _____________________primary reproductive organs-both exocrine and endocrine in nature A. OVARIES Shape of almonds but about twice as large Internally ________________________-each consisting of an immature egg-oocyte-surrounded by 1 or more layers called _________________________________ As developing egg matures follicle enlarges and produces fluid filled antrum-At this point follicle is called vesicular or _________________follicle,which is mature and ready to released during _______________________________. After ovulation,ruptured follicle is transformed into _____________________________--“yellow body”,which degenerates Ovulation ~ every 28 days….in older women ovaries are scarred and pitted from release of many eggs Ovaries secured to lateral pelvis by _______________________________and medially by ___________________________and in between held by fold of peritoneum-broad ligament B. DUCT SYSTEM-uterine tube,uterus and vagina 1. Fallopian(uterine) tubes—internal duct system receive ovulated oocyte and provide fertilization site each about 4” long,extends medially from ovary to empty in superior uterus enclosed and supported by broad ligament little or no contact between fallopian tubes and ovariesinstead contact @ distal end is by funnel-shaped ___________________________________________that has fingerlike projections-fimbriae that surround ovary WHICH create fluidlike current that carries oocyte into fallopian tube---to thus journey to uterus At this point is where many potential eggs are lost in peritoneal cavity Page 6 of 13 Cilia and peristalsis move oocyte along to uterus-taking about 3-4 days,but egg is viable ~24 hrs. after ovulation,so fertilization is usually in fallopian tube To reach oocyte,sperm must swim up through vagina and uterus to fallopian tubes---swimming against a downward beat of Cilia! Because fallopian tubes and ovaries are not physically continuous,this makes this area vulnerable to infection,such as bacterta of Gonorrhea…maybe causing __________________________________________which can cause scarring and closing of tubes 2. Uterus-located in pelvis between bladder and rectum Hallow/functions to receive,retain,and nourish a fertilized egg About the size and shape of a pear in women who haven’t been pregnant Suspended by broad ligament and anchored by round and uterosacral ligaments _________________=main portion _________________-superior,rounded region above fallopian tube entrance ______________-narrow outlet into vagina below Wall is thick w/3 layers:1)inner mucosa__________________________-At implantation-fertilized egg burrows here/This layer sloughs off during ________________-menstruation every 28 days-- if not fertilized 2)________________________-interlacing bundles of smooth muscle making bulky middle layer-contracts during labor 3) perimetrium-outer serous layer(visceral peritoneum) __________________________________-common in women 30-50-risks factors inc. cervical inflammation,STDs,multiple pregnancies,promiscuity/detected w/Pap smear/slow growing ,usually 3. Vagina-thin-walled tube 3-4”long/between bladder and rectum from cervix to body exterior=birth canal./also organ of copulation Distally partially enclosed by __________mucosawhich is very vascular and bleeds when ruptured C. EXTERNAL GENITALIA=VULVA Page 7 of 13 mons pubis-fatty,rounded area overlying pubic symphysis-hair after puberty laterally are 2 skin flods w/hair-labia majora (encloses vestibulewhich houses external urethra opening and vagina )and l.minora ____________________________________ surround vagina and secretes for distal vagina Clitoris-small protrusion that is corresponding to penis w/erectile tissue but no reproductive duct ___________________-between ant. labial folds,anus and ischial tuberosities IV.FEMALE REPRODUCTIVE FUNCTIONS AND CYCLES A. OOGENESIS AND THE OVARIAN CYCLE Females’ reproductive ability begins at puberty and ends around 50’s(menopause) In developing female fetus,_______________________-female stem cells multiply rapidly to increase their numbers,then daughter cells-primary oocytes-push into ovary connective tissueand primary follicle forms around them By birth,oogonia cease to exist and a lifetime supply of primary oocytes are in place--waiting 10-14 years to undergo MEIOSIS! @ puberty , ant. Pituitary produces_____________________________FSH-stimulates a small # of primary follicles to grow and mature each month and then ovulation occurs monthly….constituting the _________________cycle @ puberty ~ 250,000 oocytes remain w/ a small # activated each month….appx 500 of the 250,000 ova are released in the limited # of years of fertility The FSH prods the follicle to enlarge ,accumulating fluid in central antrum/Primary oocyte replicates chromosomes and MEIOSIS occurs-producing 1 ____________________________and polar bodies Follicle development to the point of rupture takes about 14 days with _______________________ occurring at just about this time Ovulation occurs at the response to ______________________________________LH Secondary oocyte is still surrounded by follicle cell capsule now called__________________________(“radiating crown”)…abdominal pain can accompany this-mittelschmerz 1 developing follicle dominates each month/mature follicles not ovulated are overripe and deteriorate Besides triggering ovulation each month,LH aso causes ruptured follicle to turn into corpus luteum(Both c.luteum and maturing follicle produce hormones) If ovulated, secondary oocyte is penetrated by sperm in fallopian tube,THEN oocyte undergoes_________________________________making another polar body and ovum Page 8 of 13 ….its 23 chromosomes are combined w/23 of sperm in fertilized egg If not fertilized, deteriorates Polar bodies deteriorate Sperm v. egg:-sperm relies mostly on surrounding for nutrients,while—egg larger and______________________-stocked w/ nutrients B. UTERINE (MENSTRUAL) CYCLE receptive to implantation only briefly---~ 7 days after ovulation events of ____________________________________ are cyclic changes that endometrium goes through monthly in response to ovarian hormone changes Anterior pituitary ______________________________ hormones FSH and LH regulate Ovarian estrogen and progesterone Typically cycle is 28 days w/ovulation occurring midway 3 stages: 1)_____________________________________--superficial functional layer of thick endometrium is sloughed off-accompanied by 3-5 days bleeding---passing out vagina as menstrual flow/average blood loss 50-150mL(1/4-1/2 cup)….By day 5 ovarian follicles begin to produce estrogen 2)_____________________________________________---is stimulated by estrogen levels to cause basal layer of endometrium to regenerate ,glands form w/in and endometrial blood supply increases…endometrium restores to velvety,thick and well vascularized—ovulation @ end of this phase in response to LH 3)____________________________________________-progestrone levels have risen(by corpus luteum) and act on estrogen charged endometrium and increase blood supply more/also increasing size of endometrial glands and begin supplying nutrients into uterine cavity to sustain an embryo until implanted If fertilization does occur,embryo produces hormone similar to LH-causes ______________________________________________________ If fertilization does NOT occur,c. luteum degenerates and LH levels drop…This causes vessels supplying endometrium to go into spasms and kink—causing endometrial cellsdeprived of O2 –to die ….setting stage for next menses Cycle can vary from 21-40 days ,but time of ovulation is usually @ 14-15 days C. HORMONE PRODUCTION BY OVARIES Begin @ puberty Follicle cells of growing follicles produce_______________________-causing the appearance of secondary sex characteristics :enlargement of fallopian tubes, vagina and external genitalia ;development of breasts ;axillary and pubic hair ;increased fat in hips and breasts and in general; Widening and lightening of pelvis; Onset of menses Estrogen also has metabolic effects---ex-maintaing blood cholesterol(high HDL) and help Ca2+ uptake Other ovarian hormone is ______________________________made by c.luteum as long as LH is present in blood…stopping 10-14 days after ovulation/helps establish Page 9 of 13 menses w/estrogen,but does NOT contribute to secondary sex traits…plays a role in pregnancy by inhibiting contraction of endometrium and prepares____________________________________________________(source of progesterone in pregnancy is placenta) V.MAMMARY GLANDS In both sexes ,but has normal functions in female---being important only once reproduction is accomplished—stimulated to increase size by estrogen Are actually modified sweat glands and part of integument ,in that sense….and anterior to pectoral muscles ________________________-center pigmented area w/protruding nipple Internally has 15-25 lobes radiating around nipple/lobes are padded and separated by connective tissue and fat Within each lobe are smaller _______________________ w/clusters of alveolar glands that ________________________-produce milk into lactiferous ducts opening via the nipple to the outside ________________________________-2nd most common cause of death in American women---1 in 8 developing this condition….~10% hereditary and half traced to BRCA 1 and 2 gene/80% of women w/ gene contract cancer---other risk factors inc. early menses,late menopause,estrogen replacement therapy….Breast cancer is signaled by change in skin texture ,puckering and nipple leakage…can be detected by self examination and by ________________________________-X-rays that reveal tumors too small to feel(<1 cm.) VI. SURVEYOF EMBRYONIC DEVELOPMENT AND PREGNANCY A. ACCOMPLISHING FERTILIZATION Sperm must reach secondary oocyte-viable 12-24 hours after leaving ovary/sperm viable ~ 24-48 hrs….Therfore, intercourse must occur no more than 2 days before ovulation and no later than 24 hrs. after ovulation---when oocyte is appx. 1/3 way down fallopian tube Sperm attracted to oocyte by “homing device” chemicals—locating oocyte Sperm take __hours to reach fallopian tube,however many leak out or are destroyed by vagina’s acidity---only a few hundred –few thousand make it to area of egg’s location When sperm reach oocyte,cell surface hyraluronidase enzymes break down “cement” holding follicle cells of corona radiate around oocyte Once path cleared through corona,1000’s sperm undergo_________________________________________where acrosome membrane break down-releasing enzymes to lyse through oocyte membrane….then a single sperm can make contact w/oocyte membrane receptors---pulling head(nucleus) of sperm pulled Page 10 of 13 into oocyte cytoplasm….****sperm reaching this point after acrosomal reactions have started are the more likely to fertilize After a sperm has reached oocyte,2nd meiosis occurs---making ovum and polar body Changes in fertilized egg preventing other sperm entry _____________________________occurs @ moment genetic material of sperm combines w/ that of ovum to make______________________-fertilized egg B.EVENTS OF EMBRYONIC AND FETAL DEVELOPMENT Rapid MITOTIC division as zygote goes down fallopian tube________________________,w/daughter cells becoming smaller and smaller—large # of cells will be building block of embryo-until 9th week By time embryo reaches uterus(3 days after ovulation)=_________________-ball of 16 cells looking like a raspberry…Since uterus not totally prepared for embryo yet, embryo floats in uterine cavity---using uterine secretions for nutreints @ this time---Unattached,continues to develop to ~ 100 cells---It then hallows out to form_____________________or chorionic vesicle @ this same time ,it is secreting a hormone called______________________________(hCG)-this prods c.luteum of ovary continue hormone production(otherwise,endometrium would shed) Pregnancy tests usually detect______________levels Blastocyst also has ________________________-forming large fluid-filled sphere and also an inner cell mass-small cell cluster to one side By day 7 after ovulation,blastocyst attahes to endometrium,eroding away some of lining and envelops into thick mucosa During this time the primary germ layers are forming from inner mass: 1. ______________________gives rise to nervous system and epidermis 2. ______________________forms mucosa and associated glands 3. __________________________gives rises to basically everything else By day 14 after ovulation,implantation is complete and mucosa grown over embryo…The ______________of the blastocyst develops projections called chorionic villi,combining w/uterus to produce __________________________ Once placenta has formed,embryonic body is surrounded by_____________________________-fluid –filled sac and attaches w/blood vessel stalk-_____________________________________ By 3rd week,placenta delivers nutrients and O2 to and removes wastes from embryonic blood---all through ____________________________ By end of 2nd month,placeta becomes endocrine organ producing estrogen,progesterone,and other hormones to maintain pregnancy…c.luteum becomes inactive By week 8--all organ systems laid down in some form and looks human Week 9—Now called__________-now growth and organ specialization are major activities As fetus,grows from ~ 3cm. and 1g to 36 cm(14”),~4kg(6-10 lbs.)…at birth ~ 22” Page 11 of 13 B. 270 days-10th lunar month-full term EFFECTS OF PREGNANCY ON MOTHER ___________________________-period from conception to birth 1. Anatomical changes Uterus goes from fist sized to eventually nearing level of xiphoid process-thorax widens as organs press on diaphragm Center of gravity changes sometimes causing lordosois---thus backaches Placental hormone____________________causes pelvic ligaments and pubic symphsis to relax,widen and become more flexible Good nutrition necessary—needing only about 300 calories extra/day Substances that can cross placental barriers are alcohol,nicotine,many drugs and maternal infections _________________ termination of pregnancy by loss of fetus---spontaneous abortion is a miscarriage 2. Physiological Changes GI system-morning sickness usually first trimester,as mother adjusts to elevated estrogens;heartburn because of displaced esophagus and displaced stomach;constipation – because GI motility decreased Urinary system-kidneys now need to dispose of fetal metabolic wastes,producing MORE urine;also uterus compresses bladder---frequent urination-Ie. stress incontinence Respiratory System-nasal mucosa responds to estrogen by swelling and congested,maybe nosebleeds ;respiratory rate increases but residual volume declines causing_______________difficult breathing in later stages Cardiovascular system-Total body water rises and blood volume increases 25-40%---helping in safeguarding from blood loss effects during labor;BP and pulse increase and raise cardiac output 20-40%;venous return from lower limbs may be impaired---maybe causing varicose veins c. CHILDBIRTH=________________________ Usually w/in 15 days of calculated due date (280 days from last menstrual period) _________________-series of events that expel infant from uterus 1) Initiation of labor Estrogen has reached highest levels causing myometrium to form much ___________________________receptors-to be receptive to that hormone AND interfering with progesterone’s quieting influence on uterine muscle—causing weak uterine contractions---called ______________________________contractions—often producing false labor Then ,cells of fetus produce oxytocin and this stimulates placenta to release ________________________________________stimulating more frequent and powerful contractions Page 12 of 13 Mom’s hypothalamus activated by emotional and physical stress---signals oxytocin release by posterior pituitary gland ---rhythmic ,expulsive contractions-TRUE LABOR…positive feedback mechanism now w/hypothalamus,strengthening contractions Anything that interferes w/oxytocin or proglastins can hinder onset of labor….example--antiproglastin drugs such as aspirin and ibuprofen 2) Stages of Labor 1st-_____________________________from time of true contractions until full-10 cmdilation of cervix….contractions move from upper uterus to vagina,becoming more vigorous and softening cervix and thinning….amnion ruptures-“water –breaking”-----usually 6-12 hours or MORE!!! 2nd-Expulsion stage-full dilation to delivery…urge increases to push 20 min -50 min.--sometimes 2 hrs Infant should be head first-Vertex position-skull as a wedge to dilate cervix…after head,rest of body comes out more easily…umbilical cord clamped off _______________-buttocks-first ________________________-during a difficult 2nd stage,O2 delivery inadequate leading to cerebral palsy or epilepsy….often a C-section done to prevent these rd 3 -_____________________________________-w/in 15 min.placenta usually expelled--placenta and other fetal membranes constitute ____________________ VII. DEVELOPMENTAL ASPECTS Gonads from 8th week and then accessory structures and external genitalia….all depends on presence or absence of testosterone If genetic male fails to produce testosterone-female accessory structures form and external genitalia… --If genetic female exposed to testosterone-male accessory ducts and glands as well as penis and scrotum….both cases are pseudohermaphrodites----a true hermaphrodite possesses ovaries and testes-rare case XO female appears normal but lacks ovaries/YO males perish __________________narrowing of foreskin of penis and misplaced urethral openings _________________________________________-failure of full descent of testes Puberty @ 10-15 yrs. ________________________=period ~11-13---taking another 2 years for dependable ovulation Most common problem in females are infection-sometimes caused by STD’s Male inflammatory conditions include ___________________________________________________________,maybe following STD transmission __________________________-inflammation of testes….maybe following STD or mumps Neoplasms a danger in both genders Page 13 of 13 Women reach peak reproductive abilities @ late 20’s,estrogen declines eventually producing________________-producing a ceasing of menses—irritability and mood changes can accompany Dangers can accompany HRT Its all downhill…!