PPT: Env. Value Systems
advertisement

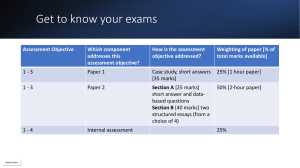
1.1 Environmental Value Systems Environmental Systems and Society Mrs. Page 2015-2016 Modified from https://iboess.wikispaces.com/Topic+7+Environmental+value+systems Topic 1.1 Environmental Value Systems Knowledge and Understanding: Significant historical influences on the development of the environmental movement have come from literature, the media, major environmental disasters, international agreements and technological developments. (See Timelines & Influential Events Assignments) An EVS is a worldview or paradigm that shapes the way an individual, or group of people, perceives and evaluates environmental issues, influenced by cultural, religious, economic and socio-political contexts. An EVS might be considered as a system in the sense that it may be influenced by education, experience, culture and media (inputs), and involves a set of interrelated premises, values and arguments that can generate consistent decisions and evaluations (outputs). There is a spectrum of EVSs, from ecocentric through anthropocentric to technocentric value systems. An ecocentric viewpoint integrates social, spiritual and environmental dimensions into a holistic ideal. It puts ecology and nature as central to humanity and emphasizes a less materialistic approach to life with greater self-sufficiency of societies. An ecocentric viewpoint prioritizes biorights, emphasizes the importance of education and encourages self-restraint in human behavior. Topic 1.1 Environmental Value Systems Knowledge and Understanding: An anthropocentric viewpoint argues that humans must sustainably manage the global system. This might be through the use of taxes, environmental regulation and legislation. Debate would be encouraged to reach a consensual, pragmatic approach to solving environmental problems. A technocentric viewpoint argues that technological developments can provide solutions to environmental problems. This is a consequence of a largely optimistic view of the role humans can play in improving the lot of humanity. Scientific research is encouraged in order to form policies and to understand how systems can be controlled, manipulated or changed to solve resource depletion. A progrowth agenda is deemed necessary for society’s improvement. There are extremes at either end of this spectrum (for example, deep ecologists– ecocentric to cornucopian–technocentric), but in practice, EVSs vary greatly depending on cultures and time periods, and they rarely fit simply or perfectly into any classification. Different EVSs ascribe different intrinsic value to components of the biosphere. Topic 1.1 Environmental Value Systems Applications and skills: Discuss the view that the environment can have its own intrinsic value. Evaluate the implications of two contrasting EVSs in the context of given environmental issues. Justify, using examples and evidence, how historical influences have shaped the development of the modern environmental movement (See Timelines & Influential Events Assignments) Theory of knowledge: EVSs shape the way we perceive the environment—which other value systems shape the way we view the world? Environmental Value System The “world view” or set of paradigms that shape the ways that individuals and groups approach environmental issues. What is a System? Make a list of “systems” If you had to come up with 1 definition what would it be? A set of parts that work together to make the whole function. Generally the whole is more efficient than all the parts. Can you have systems within systems? Explain. System Diagrams Storages = boxes Flows = arrows Inputs = things going into the system Outputs = things coming out of the system INPUTS STORAGE OUTPUTS Thinking about your values system – what are the inputs and outputs? Inputs and outputs Inputs: Family, peers, media, religion, education, science, politics, economics Outputs: Decisions, perspectives, course of action Draw a system diagram of your EVS Environmental Value Systems Ecocentric Anthropocentric Technocentric (Nature Centered) (People Centered) (Technology Centered) Minimum disturbances to nature People are managers of the Earth Technology solves problems Ecocentrism Nature Centered Nature: environmental conservation is central to decisionmaking Society: humans are part of nature Individual responsibility and accountablility All life has inherent value We should not cause extinction of other species We should protect habitats and ecosystems Humans are not more important than other species Resources are limited We need the Earth more than it needs us Anthropocentrism People (humanity) centered Nature: the environment is a resource for humans to use as needed Society: human health and well-being are central in decisionmaking People as environmental managers of the environment Governmental regulation; taxes, legislation, regulation Population control given equal weight to resource use Humans are the most important species People living in MEDC’s (more economically developed countries) are more likely to hold this view. Why? Technocentrism Nature: nature is a model, but can be replaced by technology when needed Society: human health and well-being are central to decisionmaking Technology can keep pace with and provide solutions to environmental problems. We must understand natural processes in order to manage and control these resources We can solve any problem we cause Economic growth is a good thing Where do you think you fall? We all have different influences that affect our views of the world. Based on what you have learned so far, would you classify yourself as a ecocentric, anthropocentric, or technocentric person with regards to the environment? Why? EVS Spectrum Although we tend to group into 3 main groups there are extremes in the spectrum We might not fall complete into one category or another but we need to be able to justify our viewpoints with examples (blogs will help with this) Deep Ecologists Extreme Ecocentric • Nature is of more value than humanity • Concerned about the impacts of human life as one part of the ecosphere (humans are not any more important than any other living thing) • Not all natural resources are for human use, humans should consume less • Seek a more holistic view of the world we live in • Believe everyone should be involved in making decisions regarding the environment Self Reliance / Soft Ecologist Small scale, local community action Individuals make a difference Self-sufficiency in resource management Ecological understand a principle for all aspect of living. Against large scale profits, prefer small scale/local markets Environmental Managers The Earth needs tending: Stewardship Governments legislate and protect the environment No radical political agenda but promote working to create change within the existing social and political structures Current economic growth can be sustained if environmental issues are managed by legal means or political agreement. Believe that the environment can be used if manage properly Cornucopians Extreme Technocentric The world has infinite resources This perspective doesn't really see environmental issues as "problems" as humans have always found a way out of difficulties in the past New resources and technologies will solve any environmental problems as they are encountered. There is no need for radical agendas, socio-economic or political reform Don't care for the environment; human come first Growth and capitalism is the best way to manage the freemarket economy Where do you think the following people fall? Note: If you see a person, idea or quote that resonates with you, you might want to take note so that you can use this information as you justify YOUR OWN Environmental Value System. Chief Seattle “Every part of the earth is sacred to my people. Every shining pine needle, every sandy shore, every mist in the dark woods, every meadow, every humming insect. All are holy in the memory and experience of my people.” Aldo Leapold, 1949 “ A thing is right when it tends to preserve the integrity, stability and beauty of the biotic community. It is wrong when it tends otherwise.” “We abuse land because we regard it as a commodity belonging to us. When we see land as a community to which we belong, we may begin to use it with love and respect.” Aldo Leopold, A Sand County Almanac Rachel Carson “ Like the resource it seeks to protect, wildlife conservation must be dynamic, changing as conditions change, seeking always to become more effective.” "The most alarming of all man's assaults upon the environment is the contamination of air, earth, rivers, and sea with dangerous and even lethal materials. This pollution is for the most part irrecoverable; the chain of evil it initiates not only in the world that must support life but in living tissues is for the most part irreversible. In this now universal contamination of the environment, chemicals are the sinister and littlerecognized partners of radiation in changing the very nature of the world—the very nature of its life." James Lovelock – The Gaia Hypothesis “A billion could live off the earth; 6 billion living as we do is far too many, and you run out of planet in no time.” “ Any species that harms the environment to a point where it threatens its own progeny is doomed and will become extinct...and that's us.” Mahatma Gandhi “The earth, the air, the land and the water are not am inheritance from our fore fathers but on loan from our children. So we have to handover to them at least as it was handed over to us.” “There is a sufficiency in the world for man’s need but not for man’s greed.” George W. Bush "It would be helpful if we opened up ANWR (The Alaskan National Wildlife Refuge – a wilderness reserve). I think it's a mistake not to. And I would urge you all to travel up there and take a look at it and you can make the determination as to how beautiful that country is.” Mar. 29, 2001 Barrack Obama “ One of the things I draw from the Genesis story is the importance of us being good stewards of the land, of this incredible gift. And I think there have been times where we haven’t been [good stewards], and this is one of those times where we’ve got to take the warning seriously [about climate change]. And part of what my religious faith teaches me is to take an intergenerational view, to recognize that we are borrowing this planet from our children and our grandchildren…. We have to find resources in ourselves to make sacrifices so we don’t leave it to the next generation. We’ve got to be less wasteful, both as a society and in our own individual lives … As president, I hope to rally the entire world around the importance of us being good stewards of the land.” Source: 2008 Democratic Compassion Forum at Messiah College Apr 13, 2008 Comparing EVS’s Different societies tend to have different EVS’s We will look at a few examples to understand more about how the inputs influence value systems Communism & Capitalism in Germany Communism was viewed as a solution to capitalistic greed and many believed that this would result in more equal distribution of wealth, thereby also decreasing many social issues including environmental damage 1989 Berlin Wall came down Journalists found that the pollution in Eastern Berlin was much greater than in Western Berlin. Although the industry of a capitalistic society pollutes, it seems that ex-soviet communism polluted much more! Capitalism and the Environment Economic growth is put above all other factors, and in many cases, this growth comes above environmental values. Private businesses in these societies are mostly to blame for the environmental degradation in these areas. Communism and the Environment Even though communist societies are meant to distribute wealth evenly, most of these countries are victims of the term “tragedy of the commons”. Tragedy of the commons: “a situation where individuals acting independently and rationally according to each's selfinterest behave contrary to the best interests of the whole group by depleting some common resource.” Wikipedia When no one owns the resource, no one takes care of it. Summary of Capitalistic & Communistic EVS They both have different economical principles that also tie back to their environmental values. Capitalism is heavily based in private businesses, and socialism is based in government-owned businesses. In terms of environmental values, capitalism allows for free speech and greater environmental awareness than communism in most cases. Communism and capitalism also find it difficult to restrict environmental abuse because both emphasize short-term efficiency and profits while ignoring long-term costs of environmental degradation. Common Native American EVS’s There are many EVS’s among different tribes so this is a generalization Tendency to live in communities and share property Subsistent economy based on trade Low impact technology Tribal law requires agreement based on consensus Laws are passed down by oral tradition Most tribes have a matrilineal (mothers) descent, extended families, and small population densities Most tribes are polytheistic and animals, plants, and nature are often regarded as objects with spirituality Christianity and Islam EVS’s Together these 2 religions have over 3.6 billion followers Similarities in beliefs: Separation of spirit and matter (body and soul) God is the creator of the world and universe. Idea of “dominion” over the Earth “Replenish the Earth , and subdue it, and have dominion over it”Genesis “Earth (and its bounty) have been given to humans for their subsistence” – Quran Christianity – Earth has been “gifted” to humans as caretakers, not rulers Islam – Animal world is a community equal to the human one 3rd pillar of Islam – charity, humans are trustees Buddhism’s EVS To live in harmony with nature is a crucial Buddhist practice. Every living thing in the world is dependent on each other Humans are no more important than other living things. The Buddha manifested a complete compassion and is respectfully seen as the compassionate protector of all beings. Buddha taught that for those who wishes to follow his Path should practice loving-kindness, not to harm the life of all beings - not only to protect mankind, but also to protect animals and vegetation. Similarities Between Christianity, Islam, & Buddhism All religions have a respect towards nature. Christianity & Islam states that one must have a proper relationship with the Creator and the rest of the Creation (nature). Christianity and Islam have an aspect of humans being stewards of the land. Buddhist society states that a person needs to be in harmony with nature in order to be in harmony with himself. They recognize it is not theirs to ruin and that the nature and earth was there before humans. It is all about respect and appropriate use. Differences Between Christianity, Islam, & Buddhism In Christianity & Islam, God created nature, therefore we as humans, have the obligation to respect, protect, and not harm the nature. In Buddhism, one has to be responsible for one’s actions. What we do to nature, it will reflect to ourselves. The origins and reasons are different. In Christianity and Islam the aim is to please God. Buddhists respect and follow the teachings of Buddha.