File
advertisement

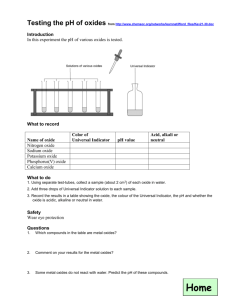
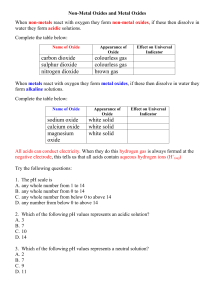
Acid and Bases 5.3 and 5.4 -Types of OxidesMany acids and bases are formed by dissolving oxides in water At the end of this, you should able to: Classify oxides as acidic or basic based on metallic/non-metallic character Give examples of each Discuss neutralization reactions What is an oxide? An oxide is a compound of oxygen and another element. Most oxides can be grouped into two types: acidic oxides (or non-metal oxide (NMO) produce an aq sol’n pH less than 7) basic oxides (or metal oxides (MO) produce an aq sol’n pH greater than 7) Acidic oxides (NMO) Oxides of non-metal (NMO) Acidic oxides are often gases at room temperature. Acidic oxides (NMO) React with water to produce acids. Example: sulphur trioxide + water SO3 + H2O sulphuric acid H2SO4 Acidic oxides (NMO) React with basic oxide (MO) to produce ternary salts (ionic compound, MNMO). Example: sulphur trioxide + sodium oxide SO3 + Na2O sodium sulphate Na2SO4 Acidic oxides React with bases to produce salts and water Example: carbon dioxide + sodium hydroxide CO2 + 2NaOH sodium carbonate + water Na2CO3 + H2O Examples of acidic oxides Acidic Oxide Formula Acid Produced with Water sulphur trioxide SO3 sulphuric acid, H2SO4 sulphur dioxide SO2 sulphurous acid, H2SO3 carbon dioxide CO2 carbonic acid, H2CO3 phosphorous(V) oxide P4O10 phosphoric acid, H3PO4 Facts about Acidic Oxides When CO2 (from combustion reactions) reacts with H20 in the atmosphere, carbonic acid is formed. The acidity (low pH) produced is of concern to all aquatic animals that have shells like zooplankton, snails, crab…since it thins their shells... making them weaker, more prone to infection…all food webs are affected too. Nitrogen monoxide produced in the car engine is a respiratory irritant. It is mostly removed from the exhaust with a catalytic converter Sulphur trioxide produces sulphuric acid which comes down as acidic rain and snow and destroys aquatic and terrestrial ecosystems Basic oxides (MO) Oxides of metal (MO) Basic oxides are often solids at room temperature. Most basic oxides are insoluble in water. Calcium oxide (quicklime) Basic oxides (MO) React with non-metal oxides (NMO) to produce ternary salts (ionic compounds, MNMO) Example: Magnesium oxide + carbon dioxide MgO + CO2 magnesium carbonate MgCO3 Basic oxides (MO) React with acids to produce salts and water only. Example: Magnesium oxide + hydrochloric acid MgO + 2HCl magnesium chloride + water MgCl2 + H2O This is a neutralisation reaction Examples of basic oxides Basic Oxide Formula magnesium oxide MgO sodium oxide Na2O calcium oxide CaO copper(II) oxide CuO Facts about basic oxides CaO is called lime. Adding NaOH is the most CaO to acidic lakes by widely used chemical in dropping it from a plane the world- billions of kg results in a less acidic lake or of sodium hydroxide is neutral lake and is called made and sold all over “liming” the world When lime is added to water, it forms a solution of calcium NaOH is used to make hydoxide(quicklime)... paper, detergent, important in glass, paper and aluminum…thousands cement of products Neutralization Reactions…upset stomach…too much acid? Try a Tums (CaCO3) It is a ternary salt with a polyatomic ion. It will react with HCl in the stomach and produce CaCl2 and H2CO3 which further breaks down to CO2 and H2O + no more acidity, Ca +2 ions absorbed… good for bones - gas produced… Try milk of magnesia (Mg(OH)2) Only slightly soluble in water so the basic characteristics not felt in the mouth and esophagus (aq.). MgCl2 and H2O produced + no more acidity - difficult to swallow since slightly bitter Do not try NaOH…very soluble in water…ouch! Acids and Bases in Action Acid rain causes a decrease in reproduction and a crash in populations especially aquatic ones. A lake can be treated with lime. Some lakes are affected more (N Ont., ground is granite) and others less (S Ont., ground is limestone) by acid rain. Limestone= nature’s natural antacid Leavening agents= substances that produce CO2 gas in baking Citric acid (from fruit) reacts with baking soda (NaHCO3) creating CO2 gas, sodium citrate and water Baking powder has dry tartaric acid and baking soda. It is activated by moisture. Recycling of car battery parts requires the work of acids and bases…great example of chemistry at work Both an Acid and a Base! Sodium Hydrogen Carbonate…it rhymes NaHCO3 Can react with a strong acid to produce a salt, water and carbon dioxide thus acting as a base (proton acceptor) NaHCO3 + HCl → H2CO3 + NaCl → H2O + CO2 + NaCl NaHCO3 Can react with a strong base to form a salt and water thus acting as an acid (proton donor) NaHCO3 + NaOH = Na2CO3 + H2O