Pair Development Framework 091306
advertisement

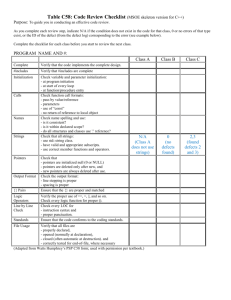
Pair Development Framework Monvorath (Molly) Phongpaibul Outline Pair Development Guideline Pair Development management issues Pair Development Guideline The ETVX Paradigm Task Entry Validate Exit Fagan’s Inspection Inspection Entry OK Task Valid? No Yes Exit Pair Development Pair Development Entry OK Task Exit Validate Where can pair activity take place? SSRD Modeling ** Activities with “Anchor” points: MBASE/RUP Personal Software Process (PSP) and Collaborative Software Process (CSP) Fagan’s Inspection Process Pair Development Processes Plan, Capabilities & Requirements Pair Requirement Modeling Test-plan Pair Design & Analysis Pair Testing Test cases Pair Programming Testing Pair Requirements Modeling Activity Entry Criteria Operational Concept Description (OCD) Problem Description Organization Background Organization Goals & Constraints Project Goals & Constraints Current System SSRD Guideline (for model) SSRD / Requirement Checklist (if provided) Defect Classification List Pair Design and Analysis Activity Entry Criteria System and Software Requirement Description (SSRD) SSAD Guideline SSAD / Architecture Design Checklist (if provided) Defect Classification List Pair Programming Activity Entry Criteria System and Software Architecture Description (SSAD) Coding Standard Coding Checklist (if provided) Defect Classification List Test Cases and Test Description (if provided) Pair Test Plan Activity Entry Criteria System and Software Requirement Description (SSRD) System and Software Architecture Description (SSAD) Risk Items Test Plan Guideline / Standard Test Plan Checklist (if provided) Test Coverage Checklist Pair Test Testing Activity Entry Criteria Code / Program System and Software Requirement Description (SSRD) Test Plan Test Description Guideline / Standard Test Result Guideline / Standard Test Coverage Checklist Pair Development Meta Task Model Preparation Sub Task Objective: Evaluate the entry criteria and understand what is available. Educate the developer . Familiarize the developer with the entry criteria such as requirement specification, design specification, checklists and test cases. Task Role Review and understand the specification from the previous stage. Pair Review the standard being used. Pair Review the checklists to increase awareness of the observer. Pair Review the defect classification list to agree on the types of defects. Pair If there is personal checklist available, review your partner’s personal checklist so that you know the strengths and weaknesses of your partner. Pair Planning Action Sub Task Objective: Make agreement on what needs to be done and what is the methodology of how to solve the problem. Ensure that the pair have the same goals and objectives. Make agreement on what is the communication protocol Reduce jelling time. Task Role Set up goals and objectives for the required work. Pair Discuss output requirements and expectation of the task being produced. Sample output can help clarify what is expected. Pair Set up the exit criteria for the required work. Pair Set up the protocol to use when execute the task. For example: Pair What is the methodology to solve the problem? What is the communication protocol between the pair? What happens when an observer finds a defect? When is it a good time to switch roles? Execution Sub Task Objective: Implement the artifact based on the goals and objectives which is set in purpose action sub task. Ensure that the artifact being produced is follow the methodology which is discussed in purpose action sub task. Collect the useful data for quality control and process improvement. Task Implement the artifact following the standard and specification. Role Driver Ensure that the artifact properly implements and conforms to the standard and specification. Observer Use both checklist and personal checklist to identify defects whenever necessary and giving suggestions for alternative implementations. Observer If the pair agrees on the defect, the driver fixes the defects. Driver Record the defects in the Defect Recording Log with defect classification. Observer Execution Sub Task (Pair Testing) Execution (Testing) Effort and Defect Data Collection Generate Test Cases Test Cases /Description Run Test Cases Test Results Pass Test Case No Identify Defects Yes Execution Sub Task (Pair Testing) Objective: Implement the test cases based on goals and objectives which are set in purpose action sub task. Ensure that the test cases being produced is follow the methodology which discuss in purpose action sub task. Ensure the test cases is full coverage. Collect the useful data for quality control and process improvement. Task Generate the test cases, test descriptions, and test program following the testing standard and test plan. Use test checklist to ensure the test coverage. Role Driver Ensure that the test cases and test descriptions properly implements and conforms to the standard and specification. Observer Use both test checklist and personal checklist to identify defects whenever necessary and giving suggestions for alternative test cases or test descriptions. Observer If the pair agrees on the defect, the driver fixes the defects. Driver Record the defects in the Defect Recording Log with defect classification. Observer Execution Sub Task (Pair Testing) Task Role Distribute the test to be execute between the pair. For efficiency, test cases can execute individually. Pair If any test cases can not run properly, pair get together to identify the defects on the test cases. Pair Record the results of test cases on test results. Ensure that the test results are properly record and have enough detail to reproduce the test defects. Driver Observer Assurance Sub Task Objective: Ensure that the work product meet the exit criteria Ensure that all the concerns have been discuss. Ensure that there is no implication of the define defects. Ensure that the artifact being produced reaches the quality goals which set up in purpose action sub task. Task Role Go trough work product and all main defects in the defect log. Pair Identify and discuss all defects found and the possible implications of these defects elsewhere in the work product. Pair Check work product against exit criteria and quality goals. Pair If the work product reach exit criteria and quality goals then exit, otherwise repeat the execution sub task. Pair Pair Development Management Issues Planning Issues Which activities and which modules should be done by a pair? Risk-based Value-based How to allocate individual to the pair? Pair Compatibility Jelling Time vs. Training Time Pair Rotation When the pair member should switch roles (driver/observer)? What is the environment when working in a pair? Peer Review Decision Model Peer Review ? Measurement What to be measure and how can we capture the data? Development Effort Defects List Defect Type: (http://www.research.ibm.com/softeng/ODC/ODC.HT M) Size of Work Product Pair Development data collection ( four different forms) Plan Announcement Pair Development Log Area of Concern Log Summary QMIS ( http://morro.usc.edu:12345/qmis/login.jsp ) What Is a Defect? An instance of non-conformance with the initiating requirements, standards, or exit criteria Can exist in the accuracy/completeness of requirements, standards, and associated interface/reference documents Identified by team consensus during inspection meeting based on requirements/standards Defect Categories Severity a. Major A Condition that causes an operational failure, malfunction, or prevents attainment of an expected or specified result Information that would lead to an incorrect response or misinterpretation of the information by the user An instance of non-conformance that would lead to a discrepancy report if implemented as is b. Minor A violation of standards, guidelines, or rules, but would not lead to a discrepancy report Information that is undesirable but would not cause a malfunction or unexpected results (bad workmanship) Information that, if left uncorrected, may decrease maintainability Defect Categories (continued) Class a. Missing Information that is specified in the requirements or standard, but is not present in the document b. Wrong Information that is specified in the requirements or standards and is present in the document, but the information is incorrect c. Extra Information that is not specified in the requirements or standards but is present in the document Type Describes what kind of areas the inspection document has defects in (often an “-illity”; e.g. grammar, syntax) Inspection teams should define and tailor the classes to the work product Questions and Recommendation - Thank You -