QA Reviews: Lessons from the Sharp End
advertisement

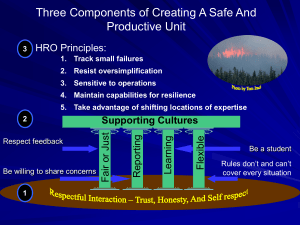
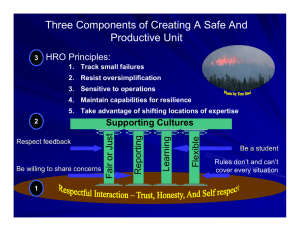
QA Reviews: Lessons from the Sharp End 3rd Annual Emergency Medicine Symposium, SJRMC David J. Adinaro MD, MAEd, FACEP Chief, Adult Emergency Department, EM Residency Research Director Disclosures Disclosures I have nothing to report in terms of financial disclosures. However…. My biases Biases I have been both a Practitioner and Consumer of emergency medicine Biases I believe That I have the best job in the world That I work with the best people in the best profession That we do noble work Biases I believe That I have the best job in the world That I work with the best people in the best profession That we do noble work That we can do better Those who do not learn from history…. “No plan survives contact with the enemy.” Moltke the Elder (1800-1891) No captain can do wrong placing his ship besides that of the enemy. Admiral Lord Nelson (1758-1805) Objectives » Understand ways to improve patient safety » Understand the concepts of the sharp end, the blunt end, and HROs » Review the working of EDQA committee Definitions » The Sharp End » The Blunt End » High Reliability Organizations » EDQA The Sharp End The Sharp End » Where the work is done and errors are made\discovered » Real time decisions based on available information » Last line of defense in error prevention » In healthcare made up of doctors, nurses, techs The Blunt End » Distal to the sharp (work end) » Often remote from real time decisions but contribute to the care given and errors made » ED Exec, Hospital Administration, State regulations, National Policies Sharp and Blunt Ends in Errors HRO A High Reliability Organization (HRO) is an organization that has succeeded in avoiding catastrophes in an environment where normal accidents can be expected due to risk factors and complexity HRO » » » » » » » Hypercomplexity - HROs exist in complex environments that depend on multiteam systems that must coordinate for safety Tight coupling - HROs consist of tightly coupled teams in which the members depend on tasks performed across their team Extreme hierarchical differentiation - In HROs, roles are clearly differentiated and defined. Intensive coordination efforts are needed to keep members of the teams working cohesively Multiple decision makers in a complex communication network - HROs consist of many decision makers working to make important, interconnected decisions High degree of accountability - HROs have a high degree of accountability when an error occurs that has severe consequences Need for frequent, immediate feedback - HROs exist in industries where team members must receive frequent feedback at all times Compressed time constraints - Time constraints are common to many industries, including health care HRO » Aircraft carrier flight deck operations » Nuclear Power Plants » Fireground Operations (especially wildfire) HRO » Preoccupation with failure » Reluctance to simplify interpretations » Sensitivity to operations » Commitment to resilience » Deference to expertise Flight Deck Operations So you want to understand an aircraft carrier? Well, just imagine that it's a busy day, and you shrink San Francisco Airport to only one short runway and one ramp and gate. Flight Deck Operations Make planes take off and land at the same time, at half the present time interval, rock the runway from side to side, and require that everyone who leaves in the morning returns that same day. Flight Deck Operations Then turn off the radar to avoid detection, impose strict controls on radios, fuel the aircraft in place with their engines running, put an enemy in the air, and scatter live bombs and rockets around. Flight Deck Operations Now wet the whole thing down with salt water and oil, and man it with 20-year-olds, half of whom have never seen an airplane close up. Flight Deck Operations Oh, and by the way, try not to kill anyone. 27 27 HRO » » » » Aircraft carrier flight deck operations Nuclear Power Plants Fireground Operations (especially wildfire) Emergency Departments! ED Operations ED Operations ED Operations HRO » Hypercomplexity » Tight coupling » Extreme hierarchical differentiation » Multiple decision makers in a complex communication network » High degree of accountability » Need for frequent, immediate feedback » Compressed time constraints SJRMC ED Operations » Embraces many aspects of HRO » 2009 Survey of Staff • Feedback related to validated, national Patient Safety Survey • Don’t Drop the Ball Program – Residents, Medical Students, Staff » Yellow Cards » Operations and safety issues » Anonymous SJRMC ED Operations » Emergency Department Quality Assurance Committee » Physician and Nursing Leaders » ED Exec » Case management, nursing educator » Physician\nursing representatives » Quality Assurance representative » Review of identified cases and evaluates them for concerns\problems related to certain aspects of care » Grade care given and also identify SHARP and BLUNT END issues to be resolved. Everyone raise their Hands! EDQA » Started in the Fall of 2009 » Initially met once a month, then twice a month, now weekly for two hours » In 2010 SJRMC saw 126,000 patients » EDQA reviewed 115 EDQA » Some acceleration in 2011 • 56 reviewed to date • 25,000 ED visits » Between 1 and 2 of every 1,000 charts submitted for review EDQA » Peds not well represented • 30% of patients, < 10% of charts » Good mix of admitted and discharged patients » Physicians average 4-8 charts a year reviewed EDQA » A major tool for physician review, early warning, and blunt end decision making » Recently Wayne ED has joined process » Has become a model for other departments in hospital EDQA Where do the charts come from? » Most are identified\referred from our own department • Leadership becomes aware of patient issue • Referrals by those on the sharp end – Sharon Pineda (pinedas@sjhmc.org) • Automatic screens (Admit after RTC < 72 hours, mortality) » A significant number come from other departments • Trauma, STEMI committee, Risk management To date approximately 200 charts have been reviewed during EDQA The information collected on these sheets form the basis of the information that follows Limitations » Specific to St. Joe’s » Small proportion of Peds cases EDQA Review » » » » » » » » Adverse Outcome? Area of Concern Who Referred Documentaton Issue? Care Issue? System Issue? Reccomendations Outcome\EDQA Referral Example #1 » 70 year old female. Hypotensive, signs of sepsis, no IV access » Screen (Sepsis care) » Delay in ABX tx » NO adverse outcome » NO documentation issues » State Trooper • Design of car and malfunction of handguns Example #1 » YES Care Issue »Clinical judgment »Communication\responsiveness »Delay in Abx and IV access » YES System Issue »Awareness of sepsis and tx » SCORE »2 (physician) » RECC: »Phys to ED Chair Adverse Outcomes » Still not well defined » Generally taken to mean did an unexpected event cause increase in the anticipated care of the patient. • Not found in most of the reviewed charts • However, need for unanticipated life sustaining tx found in about 10% of all charts reviewed. Yes 37% No 63% Adverse Outcomes Yes 37% No 63% Adverse Outcomes Breakdown Increased Tx 16% Life Sustaining Tx 36% Care not Affected 12% Incr. Monitoring 36% Area of Concern Delay in Tx 14% RTC 12% Mortality 9% Appropriate Disposition 6% Other 6% Appropriate Care 53% Documentation Issues Yes 32% No 68% Documentation Issues » Vast majority are not found to have documentation issues » Most of these concerns reflect weakness in documentation of communication, care plan, vital signs and reassessment » Tended to weaken impression of care given, leaving more to interpretation Documentation Issues For Nursing documentation » Mostly involved paucity of vital signs documentation » Many involve lack of reassessment, communication during hand off, and notification of change in patient condition For Physician documentation » Most fell in the MDM section • Documentation of consults, conversation with pmd’s • Re-assessment of patients prior to discharge • Plan\events • HPI\PE to match seriousness of patient • Procedure documentation Example #2 » » » » » » 80 year old male. CC: abd pain and vomiting Chest tightness documented in triage Initial EKG nl. Triage level 3 Labs ordered. Seen in Main East (1 hour into care) » Positive troponin » Reviewed EKG »Over-read by ED attending as STEMI » STEMI Activation Example #2 » » » » » Med Staff Appropriateness of care YES Adverse (though care not affected) YES Documentation Issue (Physician) YES Care Issue (Physician) » Judgment\Decision making » Failure to identify STEMI 54 Example #2 » YES System » Should have been Level 2 » Issue with triage process » Benefit of MUSE on all ED Computers » Need for old EKGs » SCORE: 3 » Referred MDPR Care Issues Yes 42% No 58% Physician Care Issues Diagnosis 5% Technique\Skills 5% Knowledge Follow-up 9% Policy Compliance Supervision 4% 1% 1% Communication 19% Planning 6% Clinical Judgment\ Decision Making 50% Care Issues Physician Care » Lack of contact with pmd on discharge of patients (especially, older or complex) » Under-resuscitation of shock » Trauma alert criteria not followed » EKG misinterpretation » Abnl Labs or vital signs not addressed » Protocol not followed STEMI, Stroke, Septic Shock » Delay\No consultant Care Issues No Physician can go wrong placing herself next to a critical patient and treating aggressively. Adinaro/Nelson Rule Nursing Care Issues Diagnosis Technique\Skills 0% 6% Follow-up 9% Knowledge 3% Policy Compliance 13% Supervision 0% Planning 6% Communication 25% Clinical Judgment\ Decision Making 38% Care Issues Nursing issues found less often Psych patient care » Removal of clothing » Identification of suicidal patients » Prolonged restraints\lack of sedation meds Communication of critical information » Lab results » Abnl Vitals » Change in patient condition » Lack of known plan Other Provider Care Issues Diagnosis 3% Technique\Skills 0% Follow-up 11% Communication 33% Knowledge 0% Policy Compliance 4% Supervision 4% Planning 4% Clinical Judgement\Decis ion Making 41% Care Issues Other Department » Clothing not removed from patient » Delay in arrival » Delay in responsiveness to consult » Poor communication between consultant and other services SCORE: Level of Assignment 0. 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. No problem with care/documentation Minor process/documentation problem, clinical outcome not affected Problem with process/documentation, disease/symptoms unchanged, adverse consequences possible Problem with process/documentation, disease/symptoms occurred, made worse Problem with process/documentation, permanent impact/quality of life Death attributable to care provided that is significantly controversial Death attributable to care provided/not provided that should have been provided SCORE: Level of Assignment Permanent Death Condition made Impact , 5 Attributalbe , 2 worse, 18 ,0 No problem, 77 Minor, effect possible, 42 Minor, no affect, 41 Example #3 » » » » 56 yo male CC: feet swelling Triaged 1538, labs obtained on standing orders 1945, 2024, 2054 called no answer 2055 Placed as LWOT and chart removed » » » » » » Next day: 1021 Sent back to ED by clinic due to abnl labs Pale and weak Moved to bed immediately Hypotensive, INR 6. Hb 7.1 Had been 7.9 day before Example #3 » » » » » Med Staff Triage issue YES Adverse: Increased monitoring No Documentation YES Care Issue (other\system) » Long WR time » Labs not checked prior to removal of chart Example #3 » YES System (Human, Safety\culture) » SCORE 2 » RECCOMENDATION: » System to ED Exec » Labs\orders done must be reviewed prior to closing LWOT chart System Issues No 48% Yes 52% System Issues No Info 18% Safety\Culture 39% Human System 20% Computer System 4% Non ED System 19% System Issues – Safety Culture •Call CT surgery early with issues •Alternative to Ultram in elderly •Clothing removal on ETOH patients •Desire to send borderline patients home •Communicating directly with consultants and not through residents in critical cases •Calling PMDs on discharged patients •Ordering MRI when needed •Communication of important EDQA info to staff •Abnormal vital sign reporting and tx System Issues – Human Systems •Changes needed in Front End processes •Charge nurse endorsement of hallway pt. •Clarification of trauma criteria •Delays in Triage-Bed in Peds •Difficult airway procedures. Checklist? •Including anginal equivalents for STEMI screening (EKG) •STEMI med kit in Main East •Location of waiting Level 2 patients •EP to EP turnover (especially psych pt) System Issues – Non ED Systems •Cooling capacity in Cath Lab •Improved coordination among consult services •Delays in Rad study completion times •Improve Surgery – OR communication •Non-notification by non-system paramedics •Unresponsiveness of consultants •Trauma attending presence System Issues – Computer Systems • Lack of previous clinical data in medhost •Lack of physician access\orientation to permanent clinical record •Rapid identification of radiology over-reads at log in •Changes in script for nursing “visited patient” Feedback\Referrals by EDQA MDPR 6% System to ED Exec 18% Other Department 15% 0% Doc to ED Chair 46% Nurse to ED Director 15% A rookie baseball player after a great first game jokes that he wants to retire When asked why he said » I had three hits in three at bats. Put my glove on the ball a half dozen times without error » My stats are perfect » It can only go down from here! Summary • EDQA is a proactive Blunt End activity designed to improve care at the sharp end. • Requires the active participation of Sharp End care providers. •Attend if possible\invited •Refer charts •Benefits individual providers and system as a whole •Fulfills at least one of the goals of a HRO. •More info on SJRMC ED efforts: •http://www.stjosephshealth.org/index.ph p/emergencytrauma Thank You!