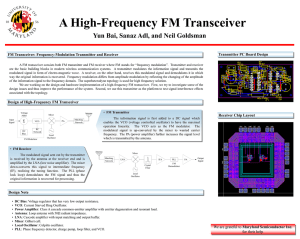
DSB Satellite Receiver System

Presented By: Sarah Scharf, Pierre Desjardins,
GuiPing Zhang, Peter Eseraigbo
Supervisor: Prof. Barry Syrett
Operates in Ku Band 12-18GHz
Design is based on Bell Satellite Receiver
As of 2010 Bell TV had over 2 million satellite customers
DBS Receiver http://sonamjourno.blogspot.ca/2012_09_01_archive.html
Receivers are used in all communication systems
◦ Cellular communication
◦ Military radar and navigations systems
◦ Television broadcasting
Opportunity to develop design skills which are directly applicable to the communication industry
Opportunity to create a basic receiver design and look for possible improvement suggestions
This receiver design can be used by future students to investigate more efficient and cheaper receiver design options
Diagram of our system:
Each individual was assigned a component to research and design
Conducted weekly group meetings
Met with supervisor on an as-needed basis
Communicated both verbally and through email frequently
Pierre: Antenna system and band-pass filter
◦ Reflector dish and Antenna feed
Name Expected
Antenna Gain
3dB Beamwidth
34.5dBi
3.5deg
10dB Beamwidth 5.5deg
Results
32.77dBi
4deg
6deg
Band-Pass Filter (12.25GHz -12.75GHz)
Gui: the two stage LNA is designed with microstrip transmission line and used pseudomorphic high-electronmobility transistors. The designed gain is 20 dB and noise figure is lower than 2 dB.
Using ADS software;
Designed with Microstrip transmission lines instead of lump elements.
Started from Stage one with lower noise figure and then second stage with high gain.
Optimized gain, noise figure and stability in ADS environment.
How to maintain the circuit stability at the meantime achieving enough gain;
Solution is by make a compromise between gain and stability
The minimum specified gain for this LNA is 20 dB
It only has lower than 2 dB noise figure.
And the circuit is stable
This two stage LNA is expected to produce the required gain
Peter: 11.25 GHz Dielectric Resonator
Oscillator (DRO)
• Primary purpose of the oscillator is to generate and maintain a needed waveform at a constant amplitude and specific frequency
Antenna
IF = LO - RF
MIXER IF
Filter
Signal
Processing
IF RF LO
BPF
LNA
OSCILLATOR
LO = Local Oscillator
IF = Intermediate
Frequency
RF = Radio Frequency
LO = 11.25 GHz
RF = 12.5 GHz
IF = 1.25 GHz
LO = 11.25 GHz
Methods and Techniques
Circuit Topology
Topology uses a resonator coupled to microstrip line, functioning as a high-Q bandstop filter that couples a portion of the transistor output back to its input.
Matching Network
Series Feedback
DRO
Advantages of topology
Very high unloaded Q (Several thousand)
lumped elements are limited to few hundred
Low phase noise (Better)
Good output power
Excellent temperature stability of material they are made from
Parallel Resonant
Circuit with transformer coupling
Simulation done using large signal simulator –
Harmonic Balance
Active Device (BJT)
Matching Network
Circuit Shematic Series Feedback DRO circuit in ADS
Getting oscillator to oscillate
◦ Adding current pulse
Achieving desired oscillation frequency
◦ Investigating what circuit components affect oscillator frequency.
◦ Trial and Error. Changing LC values and resimulating until oscillation frequency was achieved.
Results
Sarah: Active BJT Mixer
◦ Methods and Techniques
• BFU710 by NXP selected as active mixer component
Chosen mixer topology
Challenges and Solutions
• I-V curve for
BJT showing approximate bias point
Mixer starting point
Results and Discussion
Approximate layout
Output Spectrum:
Output voltage at 1.25 GHz
Chosen and purchased active components
Design using ADS and HFSS
Simulation of design
Design layouts completed
Send out layouts for manufacturing
Complete and test individual printed circuits
Complete second iteration of design and manufacture if necessary
Present final result in written report
Please stop by our poster for further technical details.
http://www.digitalhome.ca/2011/02/average
-bell-tv-subscriber-spends-75-a-month/ http://www.dbsinstall.com/GeneralInfo/Satell ite_TV_Frequency_Bands.asp
http://www.hpl.hp.com/hpjournal/98feb/feb
98a6.pdf
http://elcodis.com/parts/421841/ATF-
36163-BLKG.html