chapter1
advertisement

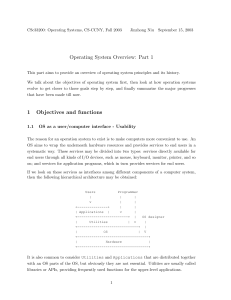
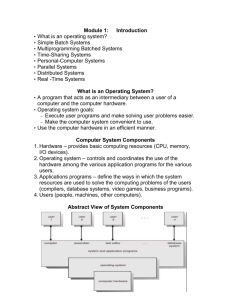
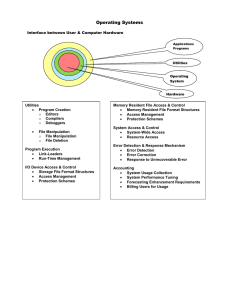
Chapter 1 Operating System Overview Contents Operating System Objectives and Functions The Evolution of Operating System Major Achievements Characteristics of Modern OS Examples(NT、UNIX) OPERATING SYSTEM OVERVIEW 1.1 Objectives and Functions (p45) 1.1.1 Overview 1.1.2 The Operating System as a User/Computer Interface 1.1.3 The Operating System as Resource Manager 1.1.4 Ease of Evolution of an Operating System OPERATING SYSTEM OVERVIEW 1.1.1 Overview An operating system is a program that manages the computer, controls the execution of application programs and acts as an interface(接口) between the user of a computer and the computer hardware. Objectives ٭Convenience(方便) ٭Efficiency(有效) ٭Ability to evolve(易扩展) OPERATING SYSTEM OVERVIEW 1.1.2 OS as a User/Computer Interface (I) End User Programmers Operating System Designer Applications Programs Utilities (Compiler, Database…) Operating System Computer Hardware Figure 2.1 Layers and Views of a Computer System OPERATING SYSTEM OVERVIEW OS as a User/Computer Interface (II) The operating system masks(隐藏) the details of the hardware from the programmer,and provides the programmer with a convenient interface for using the system. The types of system interface ٭Command interface: system command (internal、 external) ٭Graphics interface: windows ٭Programmer interface: system call, c-lib OPERATING SYSTEM OVERVIEW Services of the Operating System (I) Program creation ٭Such as: fork (unix)、CreateProcess (win) Program execution ٭Such as: execl, execp Access to I/O devices ٭Such as: read/write Controlled access to files ٭Such as: read/write OPERATING SYSTEM OVERVIEW Services of the Operating System (II) System access ٭Provide protection and authorized Error detection and response ٭Such as: error Accounting OPERATING SYSTEM OVERVIEW 1.1.3 OS as Resource Manager (I)(p47) Types of Resource: CPU、Memory、Devices CPU: chapter 3.4.5.6.9.10 Memory: chapter 7.8 I/O Devices: chapter 11.12 OPERATING SYSTEM OVERVIEW OS as Resource Manager (II) As a control mechanism is unusual in two respects ٭The OS functions in the same way as ordinary computer software; that is, it is a program executed by the processor. ٭The OS frequently relinquishes control (释放控 制)and must depend on the processor to allow it to regain control(获取控制). OPERATING SYSTEM OVERVIEW OS as Resource Manager (III Figure 2.2) Management of CPU Management of I/O Device Management of Memory Management of Files Concept: ٭Kernel、Nucleus(内核): Always in main memory, contains the most-frequently-used functions OPERATING SYSTEM OVERVIEW 1.1.4 Ease of Evolution(p49) Reasons for evolution ٭hardware upgrades ▪ Exp: support paging ٭new services ٭fixes Implements ٭software engineering: modules、layer、 object design OPERATING SYSTEM OVERVIEW 1.2 The Evolution of Operating Systems 1.2.1 Serial Processing 1.2.2 Simple Batch Systems 1.2.3 Multiprogrammed(多道) Batch Systems 1.2.4 Time-Sharing Systems OPERATING SYSTEM OVERVIEW 1.2.1 Serial Processing(p50串行处理) Example ٭Input Calculate Print Problems ٭Scheduling: The estimated time is not accurate ٭Setup time: Between the setup procedure, if an error occurred, then must go back to the beginning of the setup sequence ٭Contradiction between human and machine OPERATING SYSTEM OVERVIEW 1.2.2 Simple Batch System Objectives:Solution contradiction between human and machine ٭User submits the job on cards or tape to a computer operator (use JCL(job control language)) Implement: Monitor OPERATING SYSTEM OVERVIEW From the Point of View of the Monitor (p51) Interrupt processing Device Drivers Job Sequencing Control Language Interpreter Monitor is responsible for the running of every job monitor Controls are transferred between monitor and other user programs User Program Area Memory layout for a resident(驻留) monitor OPERATING SYSTEM OVERVIEW From the Point of View of the Processor When CPU runs command of monitor, the monitor gains the control. When CPU runs command of user program, the user program gains the control. Transfer the control: First monitor gains the control, when user program load in, it gains the control, when the user program finish or error, the monitor regains(重获) the control. OPERATING SYSTEM OVERVIEW JCL (Job Control Language) $JOB $FTN …Fortran $LOAD $RUN $END //begin //using Fortran compile and link //instructions //load in runable modules //running. //finish do the job OPERATING SYSTEM OVERVIEW Other Hardware Feature Desirable(p53) Memory protection(内存保护): User space and system space are independent. ٭E.g. Hardware can detect outside accessing error. Timer interrupt(时钟中断): When the timer expires, an interrupt occurs. Privileged instructions(特权指令): Can be executed only by the monitor. Interrupts: ٭Improvement efficiency ٭Easy for relinquishing(释放) and regaining control OPERATING SYSTEM OVERVIEW 1.2.3 Multiprogrammed Batch Systems Uniprogramming(单道) has low efficiency(效率): ٭CPU---I/O contradiction Read one record Execute 100 instructions Write one record TOTAL 0.0015 seconds 0.0001 seconds 0.0015 seconds 0.0031 seconds Percent CPU Utilization = 0.0001/0.0031=3.2% Figure 2.4 System Utilization Example OPERATING SYSTEM OVERVIEW Multiprogramming/Multitasking There are many user programs in the memory. Hardware need for Multiprogramming. ٭Interruption For example: p55 Fig2.5 OPERATING SYSTEM OVERVIEW Example of Multiprogramming 256k available memory Notes: not consider the resource competition Type of JOB JOB1 Heavy Computer JOB2 Heavy I/O JOB3 Heavy I/O Duration 5min 15min 10min Memory required 50k 100k 80k Need disk No No Yes Need terminal No Yes No Need printer No No Yes Table 2.1 Sample Program Execution Attributes OPERATING SYSTEM OVERVIEW Analysis OPERATING SYSTEM OVERVIEW Analysis Single ٭Processor use=5/(5+15+10)=17% ٭Memory use=[(50*5+100*15+80*10)/256/30] =33% ٭Disk use=10/30=33% ٭Printer use=10/30=33% ٭Total time= 5+15+10=30 ٭Throughput =6 job/hour ٭Mean response time=(5+20+30)/3=18 OPERATING SYSTEM OVERVIEW Analysis Multiprogramming ٭Processor use=5/15=33% ٭Memory use=[(50+100+80)*5+(100+80)*5+100*5]/256/15 =65% ٭Disk use=10/15=67% ٭Printer use=10/15=67% ٭Total time=15 ٭Throughout =12job/hour ٭Mean response time=(5+10+15)/3=10 OPERATING SYSTEM OVERVIEW Sophisticated(复杂性) of Multiprogramming (p57) Memory management Scheduling ٭Algorithm(算法): The processor(处理器) must decide which one to run. OPERATING SYSTEM OVERVIEW 1.2.4 Time-Sharing Systems Multiple users simultaneously(同时) access the system through terminals(终端) Concepts: ٭time slice(时间片): q ٭user num(用户数): n ٭response time(响应时间): t ٭t=n×q Mode: multi-terminals、multi-windows OPERATING SYSTEM OVERVIEW Batch Multiprogramming vs Timer Sharing Batch Multiprogramming Principal objective Source of instruction to operating system Time Sharing Maximize processor use Minimize response time Job control language commands provided with the job Commands entered at the terminal OPERATING SYSTEM OVERVIEW Reducing the Swapping Loads by Partial Swapping(p59) Reducing the spending for accessing disk OPERATING SYSTEM OVERVIEW 1.3 Major Achievements(p60) 1.3.1 Processes(进程) 1.3.2 Memory management 1.3.3 Information protection and security 1.3.4 Scheduling and resource management 1.3.5 System structure OPERATING SYSTEM OVERVIEW 1.3.1 Processes A program in execution The animated spirit(活动精灵) of a program The entity(实体) that can be assigned(分派) to and executed on a processor Three major types of computer system ٭Multiprogramming batch operation ٭Time sharing ٭Real-time transaction(处理) systems OPERATING SYSTEM OVERVIEW Errors May Happen in Multiprogramming Improper synchronization(同步): Signals being lost or duplicate(重复) signals being received. Failed mutual exclusion(失败的互斥) Nondeterminate(不确定) program operation: The result is not unique Deadlocks(死锁) To solute these problems, introduce process concept OPERATING SYSTEM OVERVIEW Process entity(实体) An executable program The associated data needed by the program The execution context(上下文) of the program OPERATING SYSTEM OVERVIEW Process Image and Process Switch(切换)(p63) OPERATING SYSTEM OVERVIEW 1.3.2 Memory Management Process isolation(隔离) Automatic allocation and management Support of modular(模块化) programming Virtually memory Long-term storage Protection and access control(访问控制) OPERATING SYSTEM OVERVIEW Virtual Processor Read, Write Virtual Memory Copy (a) User’s View Real Processor Virtual Address Files Long-term Store Mapper (Address Translate) Memory Address Main Memory Swapping Auxiliary Memory (b) Operating System Designer’s View Fig 2.10 Two Views of a Storage System OPERATING SYSTEM OVERVIEW 1.3.3 Information Protection and Security Access control: for various resources in the system Information flow control(信息流控): to guarantee the data to send to destination Certification(认证) OPERATING SYSTEM OVERVIEW 1.3.4 Scheduling and Resource Management(p66) Three factors must be consider ٭Fairness ٭Differential responsiveness(区分服务): e.g. If a process is waiting for the use of an I/O device, the operating system may wish to schedule that process for execution as soon as possible in order to free up the device for later demands from other processes. ٭Efficiency: Maximize throughput(吞吐量), minimize response time, accommodate(容纳) as many users as possible OPERATING SYSTEM OVERVIEW Some Concepts(p67) Short-term queue ٭Algorithm used to use: round robin(轮转) Long-term queue ٭Algorithm used to use: FIFO Interrupt handler: the method for get the control Service call handler(系统服务处理): the entry point into the operating system OPERATING SYSTEM OVERVIEW OS Service Call Handler Long-term Queue Short-term Queue I/O queue Interrupt Handler Short-Term Scheduler Fig 2.11 Key elements of an Operating System for Multiprogramming OPERATING SYSTEM OVERVIEW System Structure(p68系统结构) Modules(模块化) structure: only suitable for small system; for complex system, difficult for debug Hierarchical(层) structure ٭Level n provides service for level n+1 OPERATING SYSTEM OVERVIEW Hierarchy (Table 2.4) Level Name Objects Example Operations 13 Shell User programming Statements in shell language environment 12 User processes User processes Quit, kill, suspend, resume 11 Directories Directories Create, destroy, attach, detach, search, list 10 Devices External devices Open, close, as printer, displays read, write and keyboards 9 File system Files Create, destroy, open, close read, write 8 Communications Pipes Create, destroy, open, close, read, write OPERATING SYSTEM OVERVIEW Hierarchy Level Name Objects Example Operations 7 Virtual Memory Segments, pages Read, write, fetch 6 Local secondary Blocks of data, device store channels Read, write, allocate, free 5 Primitive processes Primitive process, semaphores, ready list Suspend, resume, wait, signal OPERATING SYSTEM OVERVIEW Hierarchy (Hardware) Level Name Objects Example Operations 4 Interrupts Interrupt-handling programs 3 Procedures Procedures, call stack, display 2 Instruction Set Evaluation stack, micro- Load, store, add, subtract program interpreter, branch scalar and array data 1 Electronic circuits Registers, gates, buses, etc. Invoke, mask, unmask, retry Mark stack, call, return Clear, transfer, activate, complement OPERATING SYSTEM OVERVIEW 1.4 Characteristics of Modern OS (p71) 1.4.1 Microkernel architecture(微内核结构) 1.4.2 Multithreading(多线程) 1.4.3 Symmetric multiprocess(对称多处理) 1.4.4 Distributed operating systems(分布式系统) 1.4.5 Object-oriented design(对象设计) OPERATING SYSTEM OVERVIEW 1.4.1 Microkernel Assigns only a few essential(必要的) functions to the kernel, including address spaces, interprocess communication(IPC)(进程间通信), and basic scheduling. Simplifies implementation, provides flexibility(伸 缩性)and well suited to a distributed environment. OPERATING SYSTEM OVERVIEW 1.4.2 Multithreading Thread:a dispatchable(分派) unit of work Process:a collection of one or more threads and associated(相关) system resources Introduce thread for improve the concurrence degree(并发度) E.g.:a database server accept many connection request and use multithread for process OPERATING SYSTEM OVERVIEW 1.4.3 Symmetric Multiprocessing (SMP p73) A computer hardware architecture and also to the operating system behavior that reflects that architecture. ٭Multiple processors ٭These processors share the same main memory and I/O facilities, interconnected by a bus or other internal connection scheme. ٭All processors can perform the same functions(hence the term symmetric) OPERATING SYSTEM OVERVIEW SMP vs Single Processor Performance: parallel and concurrence(并行与并 发) Reliability/Availability(可靠性/可用性) Incremental growth(可伸展性): enhance the performance of a system by adding an additional processor OPERATING SYSTEM OVERVIEW SMP vs Single Processor (Figure 2.12) OPERATING SYSTEM OVERVIEW 1.4.4 Distributed Operating System Data distributed Task distributed Transparent(透明): a multi-processor with a single processor character High throughout and reliability OPERATING SYSTEM OVERVIEW 1.4.5 Object Design Encapsulation and inherit(封装和继承) Good scalability(尺度特征) OPERATING SYSTEM OVERVIEW