Alternating Series and the Alternating Series Test
advertisement

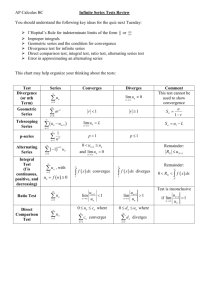
Absolute vs. Conditional Convergence Alternating Series and the Alternating Series Test Series with Positive Terms Recall that series in which all the terms are positive have an especially simple structure when it comes to convergence. Because each term that is added is positive, the sequence of partial sums is increasing. So one of two things happens: 1. The partial sums stay bounded and the series converges, OR 2. The partial sums go off to infinity and the series diverges. What happens when a Series has some terms that are negative? There are several Possibilities: •All the terms are negative. n 0 •Finitely many terms are negative. 3 n8 1 1 1 1 1 2 4 8 16 •Infinitely many negative terms and infinitely many positive terms. 1 1 1 1 1 2 3 4 5 1 1 1 1 1 1 2 4 8 16 32 Alternating Series Definition: An alternating series is one whose terms alternate in sign. For a sequence (cn) of positive numbers, there are two possibilities: c0 - c1+ c2 - c3+c4 . . . Or -c0+c1- c2 + c3 - c4 . . . In some ways, this situation is the most conducive to convergence, since the positive and negative terms have a tendency to cancel each other out, thus preventing the partial sums from getting too large. Note: the Nth term test for divergence still applies. Consider: -1+1-1+1-1+1. . . One of the most important Examples is: The Alternating Harmonic Series 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 The alternating harmonic In order to determine whether the series series converges, seemswe to converge to need to examine the partial sums of the series.a point about here Look at Example 1 on pg. 576 of OZ. 1 1/2 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 This suggests The Alternating Series Test Theorem: (Alternating Series Test) Consider the series c1 - c2 + c3 - c4 . . . and -c1+ c2 - c3+ c4 . . . Where lim ck 0 c1 > c2 > c3 > c4 > . . .> 0 and n Then the series converge, and each sum S lies between any two successive partial sums. That is, for all k, either S k S S k 1 or S k 1 S S k , depending on whether k is even or odd. The Idea behind the AST We have already seen the crucial picture. a0 S7 S is between S7 and S8 and | S 7 S8 | | a8 | S a0-a1 Note: S8 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 The error estimate given at the end of the theorem is also obvious from the picture. The Idea behind the AST We have already seen the crucial picture. a0 S7 S a0-a1 S8 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 There were two things that made this picture “go.” • The size (in absolute value) of the terms was decreasing. • The terms were going to zero. Absolute and Conditional Convergence Definition: Let an be any series • If an converges, then an is said to converge absolutely. • If an diverges but an converges, then a is said to converge conditionally. n Fact: Any series that converges absolutely, also converges in the partial sum sense. In this case, the absolute sum of the series is greater than or equal to the sum of the series. The converse is not true. It is possible for a series to converge but not to converge absolutely. Quintessential example: the alternating harmonic series. The Alternating Series Test (revised) Theorem: (Alternating Series Test) Consider the series c1 - c2 + c3 - c4 . . . and -c1+c2 - c3 + c4 . . . Where lim ck 0 c1 > c2 > c3 > c4 > . . .> 0 and n Then the series converge, and each sum S lies between any two successive partial sums. In particular, for all k, the error in approximation is S Sk Sk 1 Sk ck 1.