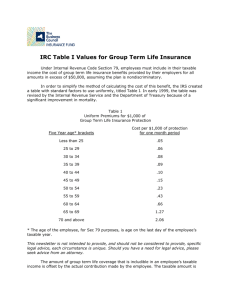
recent developments in indirect tax legislations and its
advertisement

Introduction to Key Rules under Service Tax Agenda Service Tax Rules, 1994 Point of Taxation Rules, 2011 Place of Provision of Services Rules, 2012 Recent Amendments in Service Tax Appellate Procedures 2 Introduction • Finance Act, 1994 defines the liability of an assessee for payment of service tax • Rules, which are a form of delegated legislation act as tool for application of provisions laid down by an act • In case of service tax, these delegated legislations include: − Service Tax Rules,1994 − Point of Taxation Rules, 2011 − Place of Provision of Services Rules, 2012 • Important principle of delegated legislation states that a rule cannot be read in isolation • Rules need to be interpreted with the provision of the concerned section 3 Service Tax Rules, 1994 4 Index Rule 1 – Short title and commencement Rule 2 – Definition Rule 3 – Appointment of Officers Rule 4 – Registration Rule 5 – Records Rule 6 – Payment of Service Tax Rule 7 – Returns Rule 8 – Form of appeals to Commissioner of Central Excise (Appeals) Rule 9 – Form of Appeals to Appellate Tribunal Rule10 – Procedure and facilities for large taxpayer 5 Rule 2 – Definitions • This rule provides the definition of various terms used in various subsequent rules Rule 3 – Appointment of Officers • The Central Board of Excise and Customs may appoint such Central Excise Officers as it thinks • The officers are appointed to exercise the powers of the Act within such local limits as it may assign to them 6 Rule 4 - Registration • Who should register – Every person liable to pay service tax shall register within 30 days from the date on which service tax is levied • Single registration is required for multiple taxable services • Incase of transfer of business, fresh registration is required • Premises to be registered Premises to be registered Incase of centralized billing & providing services from more than one premises Register premise from where centralized billings are located No centralized billing & providing services from more than one premises Registration is required for all the premises 7 Rule 4A – Issuance of Invoice, Bill, Challan or Consignment Note • Every person providing taxable is required to issue invoice for the taxable service provided mentioning all the prescribed details • Invoice has to be issued within 30 days from the date of completion of provision of service or receipt of payment, whichever is earlier • Exceptions in the following cases: Banking Company or Financial Company • Invoice to be within 45 days issued Goods transport agency – Continuous Supply of Service • Invoice should contain specific details related to the goods to be transported by road • Invoice to be issued within 30 days of the date when each event specified is complete • Service Provider shall also issue consignment note to the recipient of service(Rule 4B) • In case of Input Service Distributer, invoice shall be issued for each of the recipient of the credit distributed 8 Rule 5 – Records • Computerized records in accordance with various laws in force are also acceptable • Every assessee shall furnish the list of documents as maintained for accounting transactions at the time of filing return for the first time • Records to be preserved for the period of 5 subsequent years Rule 5A – Access to registered premises • Any officer authorized by Commissioner can carry out any scrutiny or verification of any registered premises to safeguard the interest of revenue • Every assessee shall within 15 days from the date of demand shall submit all the necessary documents as prescribed in the rules 9 Rule 6 – Payment of Service Tax • Due date of payment of Service tax to Central Government is as follows: 6th day of the month following the calendar month, if paid electronically; 5th day of the month in any other case subject to permission from jurisdictional Assistant / Deputy Commissioner after recording reason in writing; 31st March, in case the services are provided in the month of March • Every assessee mandatorily required to pay Service tax electronically • An assessee may take credit of excess Service tax paid on account of specified reasons subject to refund of such excess payment / issuance of credit notes to the customer 10 Rule 6 – Payment of Service Tax • Service Tax can be paid in advance and adjustment of the same is permitted in the subsequent period • Details of self adjustment to be intimated to the Superintendent within 15 days from the date of such payment • Assessee can opt for provisional assessment of payment of service tax • In case of delayed payment, Interest has to be paid as under: Delay in payment of Service Tax Rate of Interest Up to 6 (Six) months 18% p.a. Between 6 (Six) months and 1 (One) year 24% p.a. More than 1 (One) year 30% p.a. 11 Rule 6 – Payment of Service Tax – Composition Scheme Air Travel Agent Service Insurance Service Purchase or sale of foreign currency, including money changing Distributer or Selling Agent of lottery ticket • Option to pay 0.6% of the basic fare in case of domestic bookings, and; 1.2% of the basic fare in case of International bookings • Option once exercised, shall be applicable for the entire financial year • Option to pay on the Gross amount charged – Amount allocated for investment or savings, & 3% of the premium charged in the 1st year & 1.5% of the premium charged in the subsequent year • Option is only available in cases where the entire premium paid is only towards risk cover in life insurance • Option to pay service tax according to the % of gross amount of currency exchanged as prescribed in the said Rules • Option once exercised, shall be applicable for the entire financial year • Option to pay service tax according to the rate as specified • Option once exercised, shall be applicable for the entire financial year 12 Rule 6A – Export of Services The service provided or agreed to be provided shall be treated as export of service when,- the provider of service is located in the taxable territory, the recipient of service is located outside India, the service is not a service specified in the section 66D of the Act, the place of provision of the service is outside India, the payment for such service has been received by the provider of service in convertible foreign exchange, and the provider of service and recipient of service are not merely establishments of a distinct person 13 Rule 7 – Returns • Due dates for filing returns are as under: For Half Year April – September – By 25th of October For Half Year October – March – By 25th of April • Delayed filing of service tax return by an assessee allowed with payment of an amount as under Rs 500 for delay up to 15 days from the due date Rs 1000 for delay in excess of 15 days but not exceeding thirty days from the due date Rs 1000 plus Rs 100 for every day of delay from the 31st day till the date of furnishing of return for the delay beyond thirty days from the due date - Subject to maximum of Rs. 20000 • Revised return can be filed within the period of 90 days from the date of submission of Original in order to correct mistake or omission 14 Rule 8 & 9 – Forms of Appeal Appeal before Commissioner of Central Excise (Rule 8) • An appeal to the filed before Commissioner of Central Excise(Appeals) shall be in a form ST-4 • Shall be accompanied by a copy of order in original Appeal before Tribunal (Rule 9) • Appeal under sub section (1) of Section 86 of the Finance Act to the Tribunal shall be made in Form ST-5 • Appeal under sub section (2 & 2A) of Section 86 of the Finance Act to the Tribunal shall be made in Form ST-7 • Appeal filed in Form ST-7 Shall be accompanied by a copy of order passed by the Commissioner of Central Excise & the Central Board of Excise and Customs directing the CCE to apply to the Appellate Tribunal • Memorandum of cross objection shall made in Form ST-6 15 Rule 10 – Procedure & Facilities to a tax payer • A large taxpayer shall submit the returns for each of the registered premises. • A large taxpayer may be required to make available all the documents/ information as required for carrying out scrutiny and verification • A large taxpayer may opt out to be a large taxpayer by giving intimation of at least thirty days in advance • Any notice issued immediately before the date of grant of acceptance by the Chief Commissioner of Central Excise, shall be deemed to have been issued by Central Excise Officers of the said Large Taxpayer unit. • Provisions of these rules, insofar as they are not inconsistent with the provisions of this rule shall mutatis mutandis apply in case of a large taxpayer. 16 Point of Taxation Rules, 2011 17 Introduction to POTR • Why POTR – Rules to determine when is a service deemed to be provided • Why required – Liability to pay Service tax has been linked to deemed provision of service under Rule 6 of Service Tax Rules, 1994 • What does it contain • Provisions to determine point of taxation w.r.t.: – Services generally provided; – Continuous supply of services; – Services to associated entities; – Special services – Levy of tax on new services; – Change in effective rate of tax; 18 Services generally provided • Point of taxation in case of a service provided in India shall be the earliest of following: • When a service is provided or agreed to be provided; • Issue of invoice; or • Receipt of payment. • In case invoice is not issued within time limit, point of taxation shall be the date of completion of provision of the service. • In case of receipt of advance – date of receipt shall be point of taxation. Date of payment • Earlier of date on which the payments are entered in books of account or is credited to the bank account of the person liable to pay tax • In case of change in effective rate of tax, four working days’ grace period is given 19 Continuous supply of services • What shall constitute continuous supply: Service provided or to be provided under a contract; and Service to be provided continuously or on recurrent basis; and The contract is for a period exceeding three months; or Central government can notify certain services to be in the nature of continuous supply • Point of taxation in case of continuous supply shall be: Date of which payment is liable to be made by service recipient, if – Whole or part of the payment is determined or payable periodically or from time to time; and Such date is specified in the contract • If before the event for payment specified in the contract An invoice is issued; or A payment is received service shall be deemed to be provided on earlier of the two events 20 Associated enterprises • Point of taxation in case of transactions with associated enterprises located outside India shall be earliest of the following: – Date of payment; – Date of debit in the books of accounts of the person receiving service • • Special services Applicable in case of royalty payments for copyrights, trademarks, designs or patents In case consideration is not ascertainable at the time of performance of service and additional consideration is determined later point of time, point of taxation shall be earliest of the following: – Payment; – Receipt of benefit by provider; – Issue of invoice 21 New Services • In case of new services taxed for the first time – No tax will be payable to the extent invoice has been issued and payment received before such services became taxable; – No tax will be payable if the payment is received before the services become taxable and the invoice is issued within the period specified as per Service Tax Rules, 1994 It appears that there has been disregard to the concept of provision of service and the only relevance is issue of invoice or payment whichever later after change of rate. This is in contrast to case w.r.t. change in rate where in case services have been provided before change in rate, no hardship even if payment or invoice is received after change in rate. 22 Reverse charge mechanism Invoice issued on or after October 1, 2014 Point of taxation in case of Reverse charge Invoice issued before October 1, 2014 Date of payment or 3 months from the date of invoice, whichever is earlier Payment made within 6 months of invoice Date of payment Payment not made within 6 months of invoice Date of invoice 23 Change in effective rate of tax • In case of change in effective rate of tax, the point of taxation will be determined in the following manner: (assuming the change is effective from 1st January 2014) Point of taxation where taxable services are provided before 1st January 2014 Issue of invoice th 10 January th 15 December th 15 December Receipt of payment 1 st January th 15 January th 15 December Point of taxation st 1 January th 15 December th 15 December Applicable Rate New Rate Old Rate Old Rate Point of taxation where taxable services are provided after 1st January 2014 Issue of invoice Receipt of payment Point of taxation th 15 December st 1 December th 15 January th 15 January th 15 December th 15 December th 15 January st 1 December th 15 January Applicable Rate New Rate Old Rate New Rate 24 Place of Provision of Services Rules, 2012 25 Place of Provision of Services Rules, 2012 (‘POPOS Rules’) – Why Introduced • Introduced vide Notification No.28/2012-ST dated 20th June,2012 to determine the taxing jurisdiction for a service. • The POPOS Rules, determine the place where the service is provided and shall be deemed to have been provided. • The POPOS Rules, replaced the ‘Export of Service Rules, 2005’ and ‘Taxation of Services (Provided from outside India and received in India) Rules, 2006’. • Primarily meant for Cross-border Services. • Equally applicable for those service providers, who have operations with suppliers and customers in the State of Jammu and Kashmir. 26 Place of Provision of Services Rules, 2012 (‘POPOS Rules’) – Why Introduced • Origination of such rules – POPOS Rules are framed aiming at addressing the situations whereby service provider is located at one location and the service receiver is located at another location and the services are rendered at some other location however, consumed over a large geographical territory. As a result, it is necessary to comply with certain rules determining the exact place of provision. Illustration: ABC Inc., is located outside India, having its customers in India. In order to train the customers of ABC Inc. in India, they engage XYZ Inc., a group outside India. In such a case, both the services provider (XYZ Inc.) and service recipient (ABC Inc.) are located outside India, however, the services are rendered in India and consumed in India. The POPS Rules help to determine the place of provision of service in such situations and thus arrive at taxability of services involved • Avoids double taxation of services. • Applicable from July 1, 2012. 27 POPOS Rules - Selection of Applicable Rule Performance based services Rule 4 Services in relation to immovable property Rule 5 Services relating to events Rule 6 Services at more than one location Rule 7 Provider and recipient located in taxable territory Rule 8 Certain specified services Rule 9 Goods transportation services Rule 10 Passenger transportation services Rule 11 Services provided on board or conveyance Rule 12 None of the above – general rule Rule 3 Service falling under more than one rule Later Rules prevails 28 General Rule – Rule 3 – Location of the recipient of service. Principle effect to the general rule: Particulars A. Location of service recipient is in taxable territory Taxability under service tax Yes B. Location of service recipient is outside the taxable No territory C. Location of service provider is outside the taxable Yes, however, the liability to pay territory and location of service recipient is in taxable service tax is on the receiver of territory service. Illustrations: XYZ Ltd. provides Management Consultancy Services to their UK client ABC plc. – place of provision of service is outside India ABC Inc. provides management advisory services to its subsidiary Company XYZ Ltd. in India – the place of provision of service is India as XYZ Ltd is located in India. However, the service tax liability is to be discharged by XYZ Ltd. 29 Rule 4- how to determine the location of service recipient Location of Service Recipient Place of registration – Single/ Centralized Usual place of residence – place of incorporation No FE and BE The establishment more directly concerned with the use of service Services used at more than one establishment Business establishment (‘BE’) or Fixed establishment (‘FE’) (in case services are used at a place other than BE) No • Location of service provider - not available in the ordinary course of business – Location of service provider. 30 Rule 4 – Performance based services - location where the services are actually performed • Physical “Work on Goods” : place of performance :- The essential characteristic of a service to be covered under this Rule is that the goods temporarily come into physical possession or control of the service provider and without this happening, the service cannot be rendered. Thus, the service involves movable objects or things that can be touched, felt or possessed. Illustration: XYZ Corp (an entity located outside India), provides maintenance and warranty services for the telecommunication equipment to their subsidiary company located in India by deputing engineers for such maintenance activities. In turn, the Indian subsidiary reimburses the cost of such maintenance services to XYZ Corp. – performance of services takes place in India- Services taxable in India 31 Rule 4 – Performance based services - location where the services are actually performed……………….. Continued • Electronic “Work on Goods” : situation of goods :- In case the services provided from a remote location by way of electronic means, the place of provision shall be the location where the goods are situated at the time of provision of service. Illustration: IT Firm located in Delhi provides repair service in respect of software by electronic means to a company in China. The place of provision service in this case is in China as the software is located in China. • Services w.r.t goods temporary imports in India only for repairs intended to be exported subject to fulfillment of certain conditions– Not governed by Rule 4 • Repairing of imported goods which are brought to India in the normal of course of business will be taxable though re-exported • Services in relation to reconditioning or reengineering of imported goods are subject to Service tax even if re-exported after such processes. • Physical presence of service provider as well as receiver : place of performance: In case of services provided to an individual, which require the physical presence of the receiver or the person acting on behalf of the receiver, with the provider for the provision of the service. 32 Rule 5 – Location of Immovable Property • The place of provision of services provided directly in relation to an immovable property shall be the place where the immovable property is located or intended to be located. Illustration: ABC Ltd (an Indian Company) has a group company located in UK. The UK Company arranges for an office on rent located in UK and recharges the rent to ABC Ltd. Location of immovable property outside India- rent recharged to ABC Ltd. not taxable Rule 6- Services relating to events – Actual place of occurrence of such event • The place of provision of services provided by way of admission to, or organization of, a cultural, artistic, sporting, scientific, educational, or entertainment event, or a celebration, conference, fair, exhibition, or similar events, and of services ancillary to such admission, shall be the place where the event is actually held. 33 Rule 7 – Part performance of a service at different locations – Rendered greatest portion of service • Where any service referred to in Rules 4, 5, or 6 is provided at more than one location, including a location in the taxable territory, its place of provision shall be the location in the taxable territory where the greatest proportion of the service is provided. Illustration: An Indian firm provides a ‘technical inspection and certification service’ for a newly developed product of an overseas firm (say, for a newly launched sports car which has to meet emission standards in different States or countries). For instance, the testing is carried out in Hyderabad (20%), Delhi (25%), and an New York (55%). Notwithstanding the fact that, the greatest proportion of service is outside the taxable territory, the place of provision will be the place in the taxable territory where the greatest proportion of service is provided, in this case Delhi. This Rule is, however, not intended to capture insignificant portion of a service rendered in any part of the taxable territory like mere issue of invoice, processing of purchase order or recovery, which are not by way of service actually performed on goods. 34 Rule 8 – Place of provision of services where provider and recipient are located in taxable territory – Recipient of service. • Place of provision of a service, where the location of the provider of service as well as of the recipient of service is in the taxable territory, shall be the location of the recipient of service. • This Rule covers situations where the place of provision of a service provided in the taxable territory may be determinable to be outside the taxable territory, in terms of the application of one of the earlier Rules i.e. Rule 4 to 6, however, since, the service provider, as well as the service receiver, are located in the taxable territory, the applicability of Rule 8 arises. Illustration: An electronic equipment belonging to XYZ Ltd (India based) develops a technical snag in Sri Lanka. Engineers are deputed by Siemens, Mumbai, to undertake repairs at the site in Sri Lanka. But for this rule, Rule 4(1) would apply in this case and the place of provision would be Sri Lanka i.e. outside the taxable territory. However, by application of Rule 8, since, the service provider (ABC, Mumbai), as well as the receiver (XYZ Ltd), are located in India the place of provision of this service will be India. 35 Rule 9 – Specified Services – Location of service provider The place of provision of the following services shall be the location of the service provider: (a) Services provided by a banking company, or a financial institution, or a non-banking financial company, to account holders; (b) Online information and database access or retrieval services; (c) Intermediary services; (d) Service consisting of hiring of means of transport, up to a period of one month. (e) Services consisting of hiring of all means of transport other than Air crafts and vessels except yachts, up to a period of One month Illustrations: a. Opening and operation of bank accounts, transfer of money including telegraphic transfers. b. Web based services providing access or download of digital content by an entity without any presence in India c. Intermediary – As defined under Rule 2 of POPS Rules, accordingly, the services of travel agents, tour operators, commission agent for a service (not for goods) and recovery agents. d. Hiring of vessels, aircrafts, motorcars, buses, trucks and vehicles designed for transport of sick or injured persons. 36 Rule 9 – Specified Services – Location of service provider • Definition of intermediary was restricted only to services effective till September 30, 2014 • The new definition of intermediary is now widened to include intermediaries facilitating supply of goods • Services provided by Indian commission agents facilitating supply of goods on behalf of their clients located outside India can be taxable by virtue of Rule 9 Illustrations: M/s. XYZ, India have been engaged in promotion and marketing activities of the goods of the client located say in Singapore. By virtue of amendment in definition of ‘intermediately’, now services provided to the client located in Singapore could not be treated as ‘export’ and exigible for Service Tax. 37 Rule 10 – Place of Provision of a service of transportation of goods – Destination of goods • The place of provision of services of transportation of goods, other than by way of mail or courier, shall be the place of destination of the goods. ‒ Except that the place of provision of services of goods transportation agency shall be the location of the person liable to pay tax (as determined in terms of rule 2(1)(d) of the Service Tax Rules, 1994). Illustration: A consignment of diamond is consigned from Delhi to Mauritius. The place of provision of goods transportation service will be Mauritius (outside India, hence not liable to service tax). 38 Rule 11 – Passenger Transport Services – Embarkation Point for a continuous journey • The place of provision in respect of a passenger transportation service shall be the place where the passenger embarks on the conveyance for a continuous journey. • “continuous journey” means a journey for which: a single ticket has been issued for the entire journey; or more than one ticket or invoice has been issued for the journey, by one service provider, or by an agent on behalf of more than one service providers, at the same time, and there is no scheduled stopover in the journey • “Only such stopovers will be relevant for which one or more separate tickets are issued. • Illustration of continuous journey: A travel on Delhi-London-New York-London-Delhi on a single ticket with a halt at London on either side, or even both, will be covered by the definition of continuous journey. However if a separate ticket is issued, for instance, New York-Boston-New York, the same will be outside the scope of a continuous journey. 39 Rule 11 – Passenger Transport Services – Embarkation Point for a continuous journey…… Continued Illustrations: S. No. Journey Place of Provision Taxability 1 Delhi-London-New York- London-New York (Single Ticket) Delhi Yes, New Delhi, being the place of provision for continuous journey with single return ticket. 2 New York-LondonDelhi (Single Ticket) New York No, New York is place of provision for continuous journey with single return ticket. (a) Delhi-New YorkDelhi (b) New York-BostonNew York (Two Tickets) (a) Delhi (b) NewYork Journey (a) is taxable since place of provision is in taxable territory Journey (b) is not taxable since place of provision is not in taxable territory 3 40 Rule 12 – Services provided on board conveyances – First Scheduled place of departure. • Place of provision of services provided on board a conveyance during the course of a passenger transport operation, including services intended to be wholly or substantially consumed while on board, shall be the first scheduled point of departure of that conveyance for the journey. Illustration: Services of supply of food and beverages is provided as on-board entertainment during Delhi- Mumbai part of a Bangkok-Delhi-Mumbai flight. The place of provision of this service will be Bangkok (outside taxable territory, hence, not liable to tax. In case the above service is provided on a Delhi-Kolkata-Bangkok-Jakarta flight during the Bangkok-Jakarta part, then, the place of provision will be Delhi (in the taxable territory, hence liable to tax). 41 Rule 13- Power to notify services or circumstances • In order to prevent double taxation or non-taxation of the provision of a service, or for the uniform application of rules, the Central Government shall have the power to notify any description of service or circumstances in which the place of provision shall be the place of effective use and enjoyment of a service. Relevance of the aforesaid Rule: The Rule is an enabling power to correct any injustice due to the applicability of rules in a foreign territory in a manner which is inconsistent with these Rules leading to double taxation. Due to the cross border nature of many services it is also possible in certain situations to set up businesses in a non-taxable territory while the effective enjoyment, or in other words, consumption, may be in a taxable territory. 42 Rule 14- Order of application of Rules – Latter rule prevails • Notwithstanding anything stated in any Rule, where the provision of a service is, prima facie, determinable in terms of more than one rule, it shall be determined in accordance with the rule that occurs later among the rules that merit equal consideration. 43 Recent Amendments in Service Tax Appellate Procedures 44 Recent Amendments in Service Tax Appellate Procedures • For filing appeals, the appellant will be required to make a mandatory pre deposit, not exceeding Rs.10 crores, as under: Order issuing authority Authority to whom the appeal is to be made Mandatory pre deposit Any Officer below the rank of Commissioner Commissioner (Appeals) 7.5% of the duty demanded or penalty imposed Commissioner Appellate Tribunal Commissioner (Appeals) Appellate Tribunal Additional 10% of the duty demanded or penalty imposed 45 Recent Amendments in Service Tax Appellate Procedures • Interest to be paid on mandatory pre deposit at a notified rate between 5% and 36% from the date of pre deposit; • Interest not to be paid for pre deposits made before commencement of Finance (No.2) Act, 2014 • 7.5% and 10% to be computed as under * – – In cases where duty alone or duty and penalty is disputed – On the value of duty alone In cases where penalty is disputed – On the value of penalty * Refer to Circular no 984/08/2014-CX Dated 16.09.2014 46 Thank You 47