Static Code Analysis and Governance
advertisement

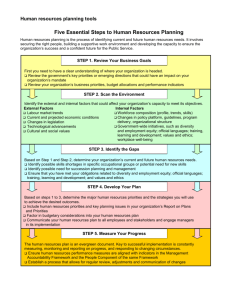
Static Code Analysis and Governance Effectively Using Source Code Scanners About Me • Jonathan Carter – Principal Security Consultant @ Pure Hacking • Governance Business Unit • Application Security – Enterprise Security Architect and Designer – Security Researcher @ Fortify • API’s, Frameworks, Threat Intelligence Presentation Flow People Process Technology 1. What do scanners do? 2. How do they do it? 3. What do you need to worry about? 4. How do you address these concerns? What do analyzers do? 1 Translation Source Code Analysis 2 Reporting API Rules Security Intelligence Vulnerabilities 3 People Process Technology Translation Mechanics Presentation Layer 1 Business Layer Translation Data Layer Source Code Model • Translation builds a model of how data flows through various layers • Allows full interoperability of languages People Process Technology Translation Example 1. Engine Reads .NET Source Code and Encounters: String URLparameter = Request[“URLElement”]; 2. Engine Translates Statement into Intermediate Language: Object ‘URLParameter’ Declared of Type String; Temporary Object ‘t1’ Declared; ‘t1’ = Result of ‘Request’ object’s ‘GetElement’ Method Executed; ‘URLParameter’ = ‘t1’; 3. Engine Adds New Content to Existing Translation of Code People Process Technology Translation Pitfalls • Translation step is not easy – Does the Translator Support the Language? – Are there subtle differences between different versions of a particular language? – How will the user know when translation fails? Potential False Negatives: – Language Versions Not Supported – Translation Incorrect People Process Technology Translation Solutions Here’s What You Can Do: 1. Verify that scanner supports all languages involved in your scan 2. Ask vendors about roadmaps for languages 3. Ensure you know how to detect translation failures. Scan Mechanics ASP.NET Rules ADO.NET Rules T-SQL Rules Java Rules Model Intelligence Analysis Vulnerabilities People Process Technology Scan Example 1. Engine Translates .NET Source Code into Intermediate Language <% = Request[“URLElement”] %> Model 2. Engine Recognizes That ‘Request’ Object is Dangerous Source Dangerous Source Rule Model 3. Engine Recognizes Dangerous Output and Declares XSS Presence .NET XSS Rule Model XSS Scan Pitfalls • Scan step is even trickier than translation – Do rules cover a particular library, API? – Are rules accurately describing the conditions for a vulnerability to exist? – Are the analyzers correctly applying a rule all the time? – Are the rules good at detecting the vulnerabilities you care about? – Are the rules being overly paranoid in describing risk? Scan Pitfalls Potential False Positives: 1. Engine models data flow and control flow incorrectly • Engine applies rules incorrectly 2. Rules identify data sources as untrustworthy and your organization disagrees 3. Rules don’t take into account dynamic nature of your code 4. Old Rules People Process Technology Scan Pitfalls Potential False Negatives: 5. Code is simply missing and analyzer never applies rules to it 6. Rules Don’t Recognize New Methods, Classes People Process Technology Scan Pitfall False Taint Promotion 1. Engine lacks enough computing resources to perform a full scan 2. To compensate, engine cuts corners during scan phase and makes broad generalizations about various data structures 3. Engine reports a large number of false positives Scan Pitfall Philosophical Limitations in Static Analysis 1. Not Really Suited for Identifying Architectural Issues 2. Not Ideal for Finding Vulnerabilities in Dynamic Code Scan Solutions Here’s What You Can Do: 1. Verify that the scanner uses the latest rules 2. Verify that rules adequately cover all of the libraries your code may use 3. Ensure that the engine provides detailed evidence of every vulnerability it reports. People Process Technology Scan Solutions Here’s What You Can Do: 4. Contact product’s technical support when the evidence for a vulnerability is simply wrong 5. Ensure that the scanner’s rules identify any custom data sources and sinks 6. Examine Scan Logs to ensure scan failures are not occurring. People Process Technology Scan Solutions Here’s What You Can Do: 7. Verify that the engine is including all of its rules when performing a scan 8. Exclude any data source rules for data sources your organization considers trustworthy 9. Gather feedback from developers about the accuracy of the results People Process Technology Reporting Mechanics Vulnerabilities Report 3 Project Preferences Report Engine produces various reports People Process Technology Reporting Example 1. Engine Identifies XSS Vulnerability in Scan .NET XSS Rule Model XSS 2. Previously, User Specifies Classification Scheme for Vulnerabilities Risk and Vulnerability Grouping Scheme 2. Engine Produces PDF + XSS Custom Vulnerability Reporting Pitfalls Potential Problems: 1. Report does not take into account risk appetite of organization 2. Reports do not capture useful security metrics. 3. Vulnerability Description / Remediation advice not satisfactory People Process Technology Reporting Solutions Here’s What You Can Do: 1. Demand to see sample reports from vendors before purchasing the scanner 2. Verify that the report’s risk assessment strategy is inline with your organization’s risk methodology 3. Inspect the engine’s capability to customize reports based on security metrics People Process Technology Reporting Solutions Here’s What You Can Do: 4. Verify that you can produce reports that reflect your organization’s security metrics 5. Ask your software developers if they find the reports useful in identifying and fixing the issues People Process Technology Process Impacts Design Maintain Deploy Build Test • • • • • • • Vendor Engagement Code Development Build Code Review QA Security Auditing Vulnerability Management • Change Management • Risk Assessment Process Impacts • Impacts to Processes Are Profound – Where should a scan occur in the SDLC? – How should the results be managed? – Should the organization refuse to release until scans are clean? – How does the organization aggregate the risks? – Does every project get a scan or just some? – How does the organization patch and maintain the scanner? People Process Technology People Impacts Design Maintain Deploy Build Test • • • • • • • • Vendors Software Developers Testers Security Auditors Release Engineers Project Managers Risk Analysts Operational Staff People Process Technology People Impacts • Impacts to People Are Profound – Who’s responsible for running the scan? – Who do we turn to when results look suspicious? – Who verifies that things are getting fixed? – Who agrees to audit the results? – Who accepts the risks of the associated vulnerabilities? – Who maintains the rules? People Process – Who audits the quality of the scans? Technology Conclusions • Source Code Analyzers are powerful and amazingly complex under the covers • Anyone who tells you they are the complete solution is probably in sales ;-) Conclusions Developers – Education about the scanner is critical to identifying false positives and negatives Risks Staff – Verify that scanner’s method of risk assessment is aligned with yours. Conclusions Auditors – Don’t be overwhelmed by a lot of issues. Chances are good there are a lot of non-issues (risk appetite). Risk Owners – Insist that the results have been verified by someone who wrote the code Contact Info