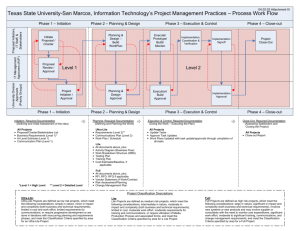
Project Planning
advertisement

Project Management for Public Health Professionals February 2011 David Sabapathy, MD, MBA, PEng Department of Community Health Sciences 3rd floor TRW building Faculty of Medicine University of Calgary Calgary, Alberta Canada T2N 4Z6 david.sabapathy@albertahealthservices.ca Section 3 Project Planning Learning Objective Acquire practical skills to develop a Project Management Plan to effectively and efficiently achieve a health objective Initiation Definition Planning Execution Close-Out Course Map Initiation Definition 1. Idea 2. Authority Planning 3. Project Charter 4. Design Execution 5. Schedule 6. Resource Plan Project Management Plan Initiation Definition Planning Execution Close-Out Close-out 7. Project Outcomes 8. Evaluatio n Project Planning With the design complete, we know WHAT we’re doing. Now we need to decide HOW to do it Initiation Definition Planning Execution Close-Out Specific Learning Objectives 1. Outline how to complete the following steps in the project life cycle Project Planning 2. Use the project life cycle to address a health priority for a developing country Project Planning – – 3. Develop a project schedule and Gantt chart Understand the basics of developing a project budget Develop a strategy to implement project management for a health priority in a developing country in a way that is culturally-suitable and enables uptake Initiation Definition Planning Execution Close-Out Topics Project Life Cycle: Stage 3 – Project Planning Project scheduling Gantt charts Budgeting Initiation Definition Planning Execution Close-Out Learning Method In-Class Case Study Initiation Definition Planning Execution Close-Out Activity Modules x3 Project Management Plan Scheduling Initiation Definition Planning Execution Close-Out Scheduling Steps Outcome of Project Definition stage Project Scope Scheduling of Project Scope has 5 Steps 1. Task Sequencing - Put work packages in correct order 2. Work Package Estimation - Estimate time and resources 3. Schedule creation – Gantt chart 4. Task Constraints – Determine float and critical path 5. Resource Levelling – Re-assign and level resources Initiation Definition Planning Execution Close-Out Step 1: Task Sequencing All tasks obey sequence constraints Example: Getting ready for work Task Minutes Shower 11 Shave 5 Get out of bed 18 Eat breakfast 13 Get dressed 5 Bicycle to work 22 Read the paper 12 Initiation Definition Planning Execution Close-Out Step 1: Task Sequencing Define relationships between work packages Do not be concerned with resource constraints E.g. Even if there’s not enough FTEs to complete a work package early in the project, this should not affect the sequencing of this work package Initiation Definition Planning Execution Close-Out Work Package Sequencing Work Packages are the only tasks in the project that will be completed (not summary tasks). Only sequence Work Packages and do not let Resource Constraints affect sequencing. Initiation Definition Planning Execution Close-Out Step 1: Task Sequencing Two ways to display task relationships Predecessor Table Network Diagram Initiation Definition Planning Execution Close-Out # Task Minutes Predecessor Resources 1 Get out of bed 18 2 Shower 11 1 You 3 Shave 5 1 You 4 Get dressed 5 1, 2 You 5 Eat breakfast 13 1, 2, 3, 4 You 6 Read the paper 12 1, 2, 3, 4 You 7 Bicycle to work 22 1, 2 ,3 ,4 ,5 ,6 You You Step 1: Task Sequencing Concurrent tasks 2, 3 and 5, 6 Resource independence Start and End milestones 2 Start 4 5 7 1 3 Initiation Definition Planning Execution Close-Out 6 End MIP Case: Task Sequencing Triple Constraint Scope – defined by WBS Time – 6 months Resources – 46,000,000 TZS (50,000 USD) – 6 FTEs - 4 project team members and 8 clinic managers @ 0.5 FTE Outcomes Time Initiation Definition Planning Execution Close-Out Resources MIP Case: Task Sequencing Measles Immunization Project Project Management Monitor progress Strengthen Partnerships Communicate status Identify partners Level 0 Enhance Accessibility Provide Education Draft and sign agreement Survey population Develop program Level 1 Evaluate program Deliver program Level 2 Work Packages Secure vaccine supply Resolve cold-chain Design survey Review agreements Analyze deficiencies Develop Contracts Sign contracts Perform root-cause analysis Initiation Definition Planning Execution Close-Out Improve process Communicate process Conduct survey Evaluate process Recruit volunteers Educate population Level 3 MIP Case: Task Sequencing Level 0 Level 1 Measles Immunization Project - WBS 1.1 Project Management 1.1.1 Monitor progress 1.1.2 Communicate status 1.2 Strengthen Partnerships 1.2.1 Identify partners 1.2.2 Draft and sign agreement 1.3 Enhance Accessibility 1.3.1 Secure vaccine supply 1.3.1.1 Review agreements 1.3.1.2 Analyze deficiencies 1.3.1.3 Develop contracts 1.3.1.4 Sign contracts 1.3.2 Resolve cold-chain Level 2 1.3.2.1 Perform root-cause analysis 1.3.2.2 Improve process Level 3 1.3.2.3 Communicate process 1.3.2.4 Evaluate process 1.4 Provide Education 1.4.1 Survey population 1.4.1.1 Design survey 1.4.1.2 Conduct survey 1.4.2 Develop program 1.4.3 Deliver program 1.4.3.1 Recruit volunteers 1.4.3.2 Educate population 1.4.4 Evaluate program Initiation Definition Planning Execution Close-Out Work Packages MIP Case: Task Sequencing # Task 1 1.1.1 Monitor progress 2 1.1.2 Communicate status 3 1.2.1 Identify partners 4 1.2.2 Draft and sign agreement 5 1.3.1.1 Review agreements 6 1.3.1.2 Analyze deficiencies 7 1.3.1.3 Develop contracts 8 1.3.1.4 Sign contracts 9 1.3.2.1 Perform root-cause analysis 10 1.3.2.2 Improve process 11 1.3.2.3 Communicate process 12 1.3.2.4 Evaluate process 13 1.4.1.1 Design survey 14 1.4.1.2 Conduct survey 15 1.4.2 Develop program 16 1.4.3.1 Recruit volunteers 17 1.4.3.2 Provide education 18 1.4.4 Evaluate program Initiation Definition Planning Execution Close-Out Predecessor Resources MIP Case: Task Sequencing Measles Immunization Project Project Management Monitor progress Strengthen Partnerships Communicate status Identify partners Level 0 Enhance Accessibility Provide Education Draft and sign agreement Survey population Develop program Level 1 Evaluate program Deliver program Level 2 Work Packages Secure vaccine supply Resolve cold-chain Design survey Review agreements Analyze deficiencies Develop Contracts Sign contracts Perform root-cause analysis Initiation Definition Planning Execution Close-Out Improve process Communicate process Conduct survey Evaluate process Recruit volunteers Educate population Level 3 MIP Case: Task Sequencing Measles Immunization Project WBS Strengthen Partnerships Identify partners Provide Education Draft and sign agreement Survey population Design survey Predecessor Table Develop program Conduct survey Deliver program Recruit volunteers # Task 1 Identify partners 2 Draft and sign agreement 3 Design survey 4 Conduct survey 5 Develop program 1, 2, 3, 4 6 Recruit volunteers 10 7 Educate population 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6 8 Evaluate program Initiation Definition Planning Execution Close-Out Predecessor 3, 4 1, 3, 4 3 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7 Evaluate program Educate population MIP Case: Task Sequencing Predecessor Table # Task 1 Identify partners 2 Draft and sign agreement 3 Design survey 4 Conduct survey 5 Develop program 1, 2, 3, 4 6 Recruit volunteers 1 7 Educate population 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6 8 Evaluate program Network Diagram Start Predecessor 3, 4 3 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7 1 3 1, 3, 4 6 8 2 4 Initiation Definition Planning Execution Close-Out 5 7 End Step 2: Work Package Estimation Recall the top-down process of Apportionment Now time for more detailed bottom-up estimation Each work package has 3 time and resource estimates: 1. Labour estimates 2. Equipment estimates 3. Material estimates Initiation Definition Planning Execution Close-Out Step 2: Work Package Estimation Labour estimates require 3 inputs: 1. Labour hours – time required for 1 FTE to complete 2. Staffing in FTEs* – # FTEs assigned to the work package 3. Wait time – necessary delay in completing work package Equipment and material estimates important but not covered in this course * FTE = Full-time equivalent. An FTE of 1.0 means that the person is equivalent to a full-time worker, while an FTE of 0.5 signals that the worker is only half-time. Initiation Definition Planning Execution Close-Out Work Package Estimation The estimated duration of a Work Package is the sum of the Active Time and Wait Time. Active Time is an estimate of people’s time spent on the task. Wait Time is an estimate of the necessary delay to complete the task Initiation Definition Planning Execution Close-Out MIP Case: Work Package Estimation # Task A Labour / 1 FTE (days) B Staffing C % FTE for each Staff D Total FTEs (B x C) E Active Time (A / D) F Wait Time G Duration (E + F) 1 Identify partners 10 1 PTM; 1 CM 0.5; 0.5 1 10 10 20 2 Draft and sign agreement 8 1 PTM; 1 CM 0.5; 0.5 1 8 8 16 3 Design survey 5 1 PTM 0.5 0.5 10 0 10 4 Conduct survey 15 1 PTM, 2 CM, 5 V 0.5; 0.5; 0.5 4 4 4 8 5 Develop program 15 1 PTM, 2 CM 0.5; 0.5 1.5 10 5 15 6 Recruit volunteers 10 8 CM 0.5 4 3 20 23 7 Educate population 20 1 PTM, 2 CM, 5 V 0.5; 0.5; 0.5 4 5 10 15 8 Evaluate program 5 2 PTM 0.5 1 5 2 7 PT = Project Team Member; CM = Clinic Manager, V = Volunteers Initiation Definition Planning Execution Close-Out Step 3: Schedule Creation Work package sequencing and durations complete Can now create a Gantt chart Graphical method for displaying a project schedule WBS on vertical axis, timeline on horizontal axis Initiation Definition Planning Execution Close-Out Gantt Chart Creation Two elements are required to create a Gantt Chart: Work Package Sequence & Work Package Duration Initiation Definition Planning Execution Close-Out MIP Case: Schedule Creation Sequence Duration Gantt Chart Initiation Definition Planning Execution Close-Out MIP Case: Schedule Creation Initiation Definition Planning Execution Close-Out Step 4: Task Constraints Every task has four dates Early start – earliest a task can begin given the tasks preceding it Early finish – earliest task can finish given the tasks preceding it Late start – latest a task can start given the tasks preceding it Late finish - latest a task can finish given the tasks preceding it Two steps to defining dates Early start/finish - Forward pass through network diagram Late start/finish - Backward pass through network diagram Initiation Definition Planning Execution Close-Out Step 4: Task Constraints Float or “slack” The difference between Early start/finish and Late start/finish is schedule flexibility! Float = Early start – Late Start Critical path = Path through all tasks with zero float Tasks with zero float must be completed by their early finish date or the project will be delayed! Initiation Definition Planning Execution Close-Out Critical Path The Critical Path is the sequence of tasks that must be completed on schedule if the project is to be on schedule. Any delay in a task along the Critical Path will result in a project delay. Attention must always be paid to the Critical Path. Initiation Definition Planning Execution Close-Out Step 5: Resource Levelling Task duration estimates implied a certain resource allocation Examine schedule: Resources under or over-allocated at any time? Adjust schedule to have consistent, continuous use of fewest resources Initiation Definition Planning Execution Close-Out Activity Module #3: Project Schedule Handout Activity Module #3: Project Schedule Discuss use of project management software Start activity module… Initiation Definition Planning Execution Close-Out Resource Plan Initiation Definition Planning Execution Close-Out Course Map Initiation Definition 1. Idea 2. Authority Planning 3. Project Charter 4. Design Execution 5. Schedule 6. Resource Plan Project Management Plan Initiation Definition Planning Execution Close-Out Close-out 7. Project Outcomes 8. Evaluatio n Resource Plans Resource Plan WHAT is required for each task (human resources, equipment, materials, finances) WHEN its required Useful communication tool for Project Stakeholders Initiation Definition Planning Execution Close-Out Human Resources What People When Needed Human Resource plan already done during project scheduling! We determined WHAT people we need and WHEN we need them Now communicate in a Gantt chart format to stakeholders Initiation Definition Planning Execution Close-Out Human Resource Plan A Human Resource Plan is a useful communication tool that identifies when people are scheduled to work on a project task. Initiation Definition Planning Execution Close-Out Project Budgeting Two steps Cost Estimation – What is the cost? Cost Budgeting – When is the money required? Manages project risk associated with finances Initiation Definition Planning Execution Close-Out Cost Estimation Iterative process More accuracy with time Accuracy costs money Recall our first pass: Apportionment Estimate Accuracy Project Life Cycle Timeline Initiation Definition Planning Execution Close-Out Estimation Project estimation (scope, time, resources) improves as the project life cycle unfolds. Improved estimation requires additional cost. Initiation Definition Planning Execution Close-Out Estimation Techniques 1. Analogous estimates (top-down estimates) Our Apportionment process during the Project Definition stage Less costly, less accurate Needs historical reference point 2. Bottom-up estimates Estimate work packages from WBS More costly, requires expert input, more accurate 3. Parametric modeling Project parameters in mathematical model (e.g. $5 per sqft * 2500 sqft) Historical data accuracy, parameters quantifiable Initiation Definition Planning Execution Close-Out Assumptions All estimates involve assumptions Document the basis for your cost estimate Without documentation, a cost estimate is unexplainable Initiation Definition Planning Execution Close-Out MIP Case: Cost Estimation Bottom-up Estimation for each work package in the WBS Check against apportionment Initiation Definition Planning Execution Close-Out MIP Case: Cost Estimation Initiation Definition Planning Execution Close-Out MIP Case: Cost Estimation Initiation Definition Planning Execution Close-Out Cost Budgeting Work package cost estimates spread over time Enables timely recognition of cost deviations from plan Two inputs Work package cost estimates Project schedule Initiation Definition Planning Execution Close-Out MIP Case: Cost Budgeting Initiation Definition Planning Execution Close-Out Budgeting Tips Use multiple techniques Revisit estimates at each point along project life cycle Compare to historical data when available Use expert estimates where possible Document estimation methods and assumptions Recognize that there are variables beyond your control Initiation Definition Planning Execution Close-Out End of Section 3 Project Planning Project Management for Public Health Professionals February 2011 David Sabapathy, MD, MBA, PEng Department of Community Health Sciences 3rd floor TRW building Faculty of Medicine University of Calgary Calgary, Alberta Canada T2N 4Z6 david.sabapathy@albertahealthservices.ca