Recruiting Preparing Retaining and Supporting Culturally
advertisement

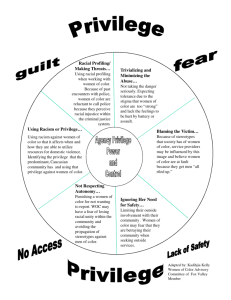
Recruiting, Preparing, Retaining and Supporting Culturally Competent Educators Jean Haar, Candace Raskin, Timothy Berry—Minnesota State University, Mankato Disrupting the Racially Predictable Achievement Gap in US Schools: Recruiting, Preparing, Retaining and Supporting Culturally Competent Educators Outcomes: ✤ Understand the current racial disparity in academic performance between white students and students of color. ✤ Learn how the College of Education at Minnesota State University, Mankato is working to intentionally shift their approach to recruit, prepare, and retain teachers and leaders who are culturally competent. ✤ Review the program components and research on the impact of the Institute for Courageous Principal Leadership at Minnesota State University, Mankato in the development racial equity leaders. Data Depicted Story of Racial Disparity in Performance • White children have outperformed African American and Hispanic children consistently since 1975. • National Trend MN Trend • This reflects a 36-year trend - making the data predictable as well as consistent. • To be specific, NAEP data reports no significant change in the width of the gap in achievement levels between students of color and White students. • 2014 data reveals a pattern for predictable racial disparity that mirrors our national pattern. In the last five years, in both math and reading, the data reveals a steady and unchanged racial discrepancy between the achievement levels of White and Black students, where White students show results that are approximately 30 percent higher than Black students. *National data comes from National Assessment of Educational Progress (2013) *Minnesota data from Minnesota Department of Education (2014) Actions Recruit, Retain, Prep and Support Teacher Prep Recruit • • Leadership Prep College Prep Teachers of Tomorrow (ToT) Admissions policies • • Faculty Curriculum • Recruitment position and work Personalized advising • Faculty engaged in racial conscientiousness • Review Professional Education process Monitor policies, procedures Retain • • Department goals University priority pilot for ToT • • Prep • Culturally responsive instruction and educators Focus on ALL students understanding racial identity and how it translates to teaching • Minneapolis/MSU • Transforming culture Transformational Principal • Intercultural Academy Competency and • St. Paul Principal Development Advisory Leadership Development Board • Interactive theatre of Isms • Cultural competency sessions Scholarships Licensure exam prep/edTPA support • Institute for Courageous Principal Leadership • Racial Equity conference • Support • • • Reorganization of support services • Support for faculty/program initiatives The power of language lies in how words are defined! What is your identity? ✤ Culture? ✤ Ethnicity? ✤ Race? Culture ✤ Culture - as a macro level concept, is the way that people agree to live and behave within a given society. This includes the accepted and valued beliefs, traditions, policies, practices, behaviors, and rules of that society. These acceptances are based on contexts such as religion, geography, language, and natural resources. Ethnicity ✤ Ethnicity – An intersection of ancestry, color, culture, and nationality. This is usually reflected by such factors as religious practices, food choices, language/dialect, and music expressions. Race ✤ Race - It is important to define race as a social construct that means skin color. In some cases, groups are identified by ethnicity (i.e. Asian American). There is no scientific evidence or support for placing human beings into different racial categories. Diversity ✤ Diversity – recognizing the ways in which all individual persons can have characteristics that are unique and distinguishable even within same cultural, ethnic, and racial groups. This is consistent with the concept of intersectionality found in Critical Race Theory (CRT). Privilege ✤ Privilege - An invisible package of assets and advantages which can be counted on but remain oblivious to groups who have such advantages. Examples include dominant cultural groups such as heterosexual males, Whites, able bodied, etc. Example: In the United States, people can hav e the ability to see racism as something which put s people of color at a disadvantage, but not t o see one of its corollar y aspects, White privileg e. Keys To Cultural Competency ✤ Macro and micro level intersection ✤ Understand dominant culture impact on marginalized groups ✤ Raise consciousness in order to reduce disparity ✤ The power of language lies in how words are defined Example: Race consciousness and racial equity practice is necessary for one to be culturally responsive. The Institute for Courageous Principal Leadership at Minnesota State Mankato is making a difference toward changing the predictable achievement trajectory for children of color. ✤ The Center for Engaged Leadership provides comprehensive programming for Minnesota K-12 principals now “in the field”. Faculty members presently work with over 180 principals from 16 urban, suburban and rural districts in our Institute for Engaged Principal Leadership. Principal Institute’s Mission Every participating leader ensures, access, fairness, equity and opportunity—every child, every day. Principal Institute Vision In an era of unprecedented educational challenge and need, further prepare principals to lead with fearlessness, skill, self knowledge and racial competence so that under their leadership, EVERY child fully achieves. Knowing Self Knowing my purpose – my “Why” – my beliefs Knowing research proven best practices Strategically implementing best practices with fidelity The data shows increased student achievement Now I’m gaining confidence in my leadership I’m resilient in my leadership Resulting in high student achievement for all Which allows me to lead courageously Racial Equity Confidence Courage Results High Student Success for All Evidence of Impact Institute for Courageous Principal Leadership - Research Study A Systemic Model for Interrupting Racism in Minnesota Schools: Dedicated to Race Equity, Consciousness, Engagement and Collaboration to Mobilize Action Leading Courageously for Racial nd Equity 2 Annual Conference With a commitment to preparing leaders who disrupt the predictable achievement trajectory for children of color in Minnesota schools, the Department of Educational Leadership held its second annual conference: “Leading Courageously for Racial Equity.” Panels, presentations and performances helped stimulate honest discussions on a topic many others avoid. Next Steps ✤ Support ongoing actions from Intercultural Competency and Development Advisory Board ✤ Reinforce culturally response teaching, research, advising, and service ✤ Monitor and adjust procedures and policies ✤ Promote and support culturally responsive professional development ✤ Align college level work with university strategic direction and performance measures Questions and Conversation Presenter Info Dr. Jean Haar, Dean College of Education Jean.haar@mnsu.edu Dr. Candace Raskin, Professor/Chair, Dept. of Educational Leadership candace.raskin@mnsu.edu Dr. Timothy Berry, Assistant Professor, Dept. of Educational Leadership timothy.berry@mnsu.edu