PEDESTRIAN/BICYCLISTS
advertisement

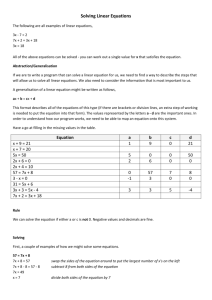
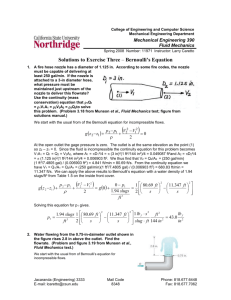
TMP Development Module 7 What is a TMP? Set of coordinated transportation management strategies applied to manage work zone impacts of the project Scaleable – projects with larger anticipated impacts may require more strategies Required in all FA projects – TMP=TCP in some projects TMP=TCP+TO+PI components in others TMP Development Process TMP Development, Implementation, and Assessment 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. 11 Step Process Compile Project Material Determine TMP Needs Identify Stakeholders Develop TMP Update/Revise TMP Finalize Construction Phasing/Staging and TMP TMP Development, Implementation, and Assessment 7. 8. 9. 10. 11. 11 Step Process (continued) Re-evaluate/Revise TMP Implement TMP TMP Monitoring Update/Revise TMP Based on Monitoring Post-Project TMP Evaluation TMP Team Approach Better coordination throughout the process from development to implementation Involve all involved offices internally TMP Coordinator Planning Design Traffic engineering Construction Operations (maintenance)? Step 1 - Compile Project Material Staff responsible for each stage of the project (planning, preliminary engineering, design, construction) begins by compiling available project materials such as: Project definition Construction phasing/staging alternates Preliminary work zone management strategies. Preliminary cost estimates for strategy implementation Information from other projects in the corridor to evaluate the combined or cumulative impact of the projects. Step 2 - Determine TMP Needs Necessary Components of TMP Impact assessment Duration of project Possible Strategies Determine if it is a significant project: Based upon the agency's policy and procedures, project's anticipated work zone impacts. Step 2a - Basic TMP Basic TMPs – Applied on construction or maintenance projects with minimal anticipated impacts Projects typically only involve the development of a TCP – layout of devices, phases, etc. Step 2b - Intermediate TMP Intermediate TMPs – Used for construction or maintenance projects that are anticipated to have more than minimal disruption, but have not been identified as significant projects. Include more detailed work zone impacts analysis and management strategy information than Basic TMPs, including some element of PI and/or TO strategies as well as TCP. Step 2c - Major TMP - Significant Projects Major TMPs are intended for significant projects. Major impacts to road users, residents and businesses TMPs for significant projects shall consist of a TCP, and also address PI and TO components. In addition to the TMP components required by the Rule, TMPs may also contain cost estimates, coordination strategies between stakeholders, secondary mitigation strategy(s), analysis of potential impacts on detour routes, and analysis of the potential effects of the management strategies. Step 3 – Identify Stakeholders Internal and external that can provide valuable input to the agency on what strategies to include in the TMP to help manage the work zone impacts of a project. DOT Contractor Federal Agencies Road Users TMP Emergency Responders Local Government Property Owners Step 4 – Develop TMP The level of detail of the TMP during early planning is largely dependent upon the type of planning activity, the expected impacts of the project, and the availability of data. At a minimum, early planning should entail a qualitative exercise to list the potential impacts of a project, along with a list of potential management strategies, and the expected costs of those management strategies. Step 5 – Update/Revise TMP The TMP is updated or revised as the project progresses through its various developmental stages as more project-specific information becomes available. Step 6 – Finalize Construction Phasing/Staging and TMP PS&Es shall include either all the applicable elements of a TMP, or the provisions for a contractor to develop a TMP. TMP development should begin prior to project letting, even for design-build projects. Some elements could be accomplished early in process – alternate route work or beginning of PI plan Some may not be in PS&E – agency in house Step 7 – Re-evaluate/Revise TMP If alternative construction phasing/staging plans or other management strategies have been suggested, technical specialists from the contractor or agency need to review the TMP to see if changes are needed. Step 8 – Implement TMP The TMP is implemented. In some cases, components of the TMP may need to be implemented prior to construction (e.g., public relations campaign, improvements to detour routes, etc.). Step 9 – TMP Monitoring Monitor operational performance of work zone during the construction phase Are predicted impacts realistic? Are the strategies in the TMP effective in managing the impacts? Do any adjustments to TMP need to be initiated? Step 10 – Update/Revise TMP Based on Monitoring If performance requirements are not met, the agency and/or contractor should revisit the TMP and consider alternate management strategies and/or phasing/staging approach(es) that meet the approval of the agency. Step 11 – Post-Project TMP Evaluation TMP performance assessment can aid in addressing the following concerns: Which management strategies have proven to be either more or less effective in improving the safety and mobility of work zones? Are there combinations of strategies that seem to work well? Should TMP policies, processes, procedures, standards, and/or costs be adjusted based on what has been observed or measured? Are the best decisions in planning, designing, implementing, monitoring, and assessing work zones being made? Performance assessment may involve two tracks: 1) the overall TMP process 2) actual field performance of the work zone and TMP. TMP PROCESS –CA Example MAJOR START Conceptual Planning and Design Request TMP Data Sheet Establish TMP Team (Ops, Design, Traffic, Const, CHP) What Kind of TMP is required? Minor Prepare Data Sheet Arrange for Funding of TMP Strategies Blanket Maintenance and Permits activities Detailed Plans & Specs (inc.TMP) Modify Strategies as Needed Start early TMP elements Begin Construction Implement TMP ** Modify TMP Strategies as Needed / Monitor traffic initially / Provide Lessons Learned Construct Project Ohio DOT’s TMP Development Process Start Project Stage 1 Design MOT Policy Exception Requests MOTAA Developing the TMP (Putting the components together) Traffic Control Plan Layout of traffic control devices to guide road users through or around work zone. Determined after analysis of strategies Contain any restrictions on work hours Include Work Zone Speed Limits – State policy? TYPICAL TRAFFIC CONTROL PLANS CONTENTS: LANES WIDTHS WORK AREA & DIMENSIONS CONSTRUCTION SEQUENCE SCHEDULE, STAGES & ACTIVITIES /STAGE ADJACENT HAZARDS TEMPORARY DRAINAGE TYPE OF AREA (CBD, RURAL, URBAN) GEOMETRICS LOCAL ORDINANCES SPECIAL PROVISIONS PAY ITEMS TYPICAL TRAFFIC CONTROL PLANS CONTENTS: LOCATION/TYPES OF TC DEVICES SIGNS, BARRIERS, PAVEMENT MARKINGS, ARROW BOARDS, CMS, ETC… EMERGENCY ACCESS PEDS./BYCLIST ACCESS EQUIPMENT, WORKERS ACCESS CROSSOVERS/EMERGENCY OPENINGS EXISTING REGULATORY SPEED LIMIT/OTHER SIGNS TRAFFIC CONTROL NOTES LIGHTING/GLARE SCREEN GEOMETRICS LOCAL BUSINESS/RESIDENT ACCESS DETOURS, IF APPLICALIBE PEDESTRIAN/BICYCLISTS Situations That Warrant Special Considerations: Sidewalks Traverse Work Zone Designated School Route Significant Pedestrian/Bicyclist Activity ADA compliance Existing Generators (Parks, Schools, Shops) Additional TMP Components for Significant Project Transportation Operations Plan Improvements to alternate route Traffic Signal retiming Intersection geometric improvements Utilize existing infrastructure – detectors, cameras, TMC Traffic Operations Plan Incident management plan for work zone Pre-stationed tow operators during peak hours Motorist Assist Patrols Utilize existing with added units Contract during project Demand reduction strategies Carpools Increase transit ridership ITS real time traffic information systems Other Considerations Existing state policies Work zone speed limits Reduced at all times? Reduced when workers present and exposed? Use of Law Enforcement? Use of Positive Protection – PCB or other 23 CFR 630 Subpart K MUTCD Sec 6C.01 “Reduced speed limits should be used only in the specific portion of the TTC zone where conditions or restrictive features are present…A TTC plan should be designed so that vehicles can reasonably safely travel through the TTC zone with a speed limit reduction of no more than 10 mph.” Increase in Fatal Plus Injury Accident Rates From Before to During Construction Percentage Increase (%) 160 140 147.9 120 100 80 112.5 98.6 60 40 20 4.1 0 0 10 15 20 25 30 Speed Limit Reduction (mph) Rural - traveled way & detours Increase in Speed Variance from Upstream to Work Zone Percentage Increase (%) 100 90 80 70 60 50 40 30 20 10 0 92.6 86.7 82.6 80.6 61.2 34.1 0 Speed Limit Reduction (mph) 10 15 20 25 30 Minimizing Variance Safest traffic operations result when speed variance is minimized Only police enforcement is effective in reducing speeds without increasing speed variance Stationary Police Vehicle on Approach Enforcement Enforcement Impact on Vehicle Speeds Enforcement Policies Problems Work Zone Training for Police Policies on Work Zone Speed Limits Observed Problems Difficult to ticket speeders in work zones Officers have little guidance on when or where to deploy Lack of ticketing Officers are stationed in unsafe positions Observed Problems (cont.) State laws affect enforcement options TTC plans are not designed for enforcement Officers are in short supply Do not allow this… Reduction in Mean Speeds Between Upstream and Work Locations 12 Reduction in Mean Speed (mph) 10 10 8 6 8 Police Present No Police 7 4 4 2 0 Speed Limit Reduction (mph) 0 10 Comparison of Speed Variance Between Upstream and Work Locations Increase in Speed Variance (mph) 25 20 21 15 10 17 Police Present No Police 11 5 0 1 Speed Limit Reduction (mph) 0 10 Incident Management Plan Ensure access to all areas for emergency vehicles Hospitals nearby? Trauma centers? Plan to provide access within work site Identify alternate routes Pre-sign for use during incidents? Pre-station tow operators during peak hours Business Access Temporary entrances Signing Pavement Advance notification of phase changes Keep owners informed Work Schedules Christmas Weekends shopping season Residential Access Keep residents informed as project begins and progresses Maintain access if possible Neighborhood association meetings, newletters, mailings, etc. Additional TMP Components Public Information Strategies to inform public of work zone conditions Website Real time traffic information system Community outreach – residents and businesses Twitter TV – Radio – commuters Occasionally contracted out to PR firm for major campaign Billboards on Project Project logo Progress THE STEVENSON RECONSTRUCTION Brochures for Media Kits and Public Distribute early – may influence alternate route choice 16-46 NHI 380072A Example Checklist FHWA Guide Example Checklist FHWA Guide Example Checklist DDOT Example Checklist DDOT Guide Example Checklist DDOT Guide Example Checklist DDOT Guide Summary Estimate and budget for TMP development and implementation early in project development (update as appropriate throughout project) Consider and address WZ impacts from a broad transportation management perspective (rather than solely a traffic control perspective) Coordinate with key parties to jointly identify WZ impacts issues to account for and management strategies to address them Strive to use strategies that keep lanes open, especially during peak traffic times TMP Overview 53 Summary (cont.) Consider using extended closures or full closures versus numerous night closures Consider strategies that facilitate decision-making by the public to avoid the WZ (e.g., public awareness, advance signage in locations prior to key motorist decision points) Training is important for all personnel involved in TMPs Management support is needed for effective TMP efforts TMP Overview 54 Questions ?