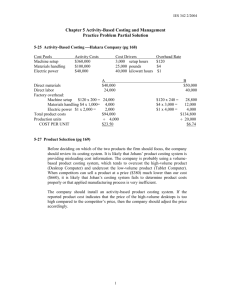
Accounting Question 1 In an ice cream manufacturing plant, raw
advertisement

Accounting Question 1 1. In an ice cream manufacturing plant, raw materials are added in the mixing and flavoring stage of the production process. Which journal entry reflects the addition of flavoring ingredients in the production process? Choose 1 answer. A. Debit Raw Materials, Credit work in process-mixing B. Debit Work in Process- Mixing, credit Raw Materials C. Debit Work in Process-Flavoring, credit Raw Materials D. Debit Raw Materials, credit work in process-flavoring 2. During the month of June, the shaping department transferred 5600 units to the next department that was 100% complete with respect to both materials and conversion. At the end of the month there were 500 partially completed units in process that were 35% complete with respect to materials and 20% complete with respect to conversion. Work in process costs to be accounted for at the beginning of June totaled $9300 for materials and $16400 for conversion. Materials costs totaling $226000 were added by the department during June. What is the weighted average cost of materials per equivalent unit for June? Choose 1 answer. A. $43.58 B. $40.74 C. $39.65 D. $47.96 3. Your company uses the FIFO method in its process costing system. In cutting the department in June, units were 80% complete with respect to conversion in the beginning work in process inventory and 33% complete with respect to conversion in the ending work in process inventory. Other data for the department for June follows: Conversion Units Cost Beginning work in process inventory 25,000 30,000 Unit started into production, 140,000 175,000 And costs incurred during the month Completed and transferred out 135,000 What would be the cost per equivalent unit for conversion cost? A. B. C. D. $1.21 $1.64 $1.35 $1.40 4. What will be the effect of overhead if a plant is operated at less than capacity and the predetermined overhead rate is based on the estimated total units in the allocation base at capacity? A. Overhead applied will be equal overhead B. Ovehead will be underapplied if the plant is operated above capacity C. Overhead will be overapplied D. Overhead will under applied 5. Which two acceptable treatments for overhead balances at the end of the period. Choose 2 answers. A. Close out to cost of goods sold B. Adjust the overhead allocation percentage C. Allocate to finished goods D. Adjust direct labor expense 6. Which cost pool is used to assign overhead in an activity-based costing system? A. Customer-level activities. B. Similar-level activities C. Organizational monitoring activities D. Group-level activities 7. How do activity-based costing and the traditional cost system treat idle capacity costs differently? A. Traditional costing ignores idle capacity costs but activity-based costing does NOT ignore idle capacity costs. B. Activity-based costing treats idle capacity costs as period costs and traditional costing spreads idle capacity costs evenly over the number of products produced. C. Activity-based costing treats idle capacity as costs spread evenly over the number of products produced and traditional costing treats idle capacity costs as period costs. D. There is no difference in the treatment of idle capacity costs in the two costing methods. 8. How the first-stage allocation defined in an activity-based costing system? A. The assignment of costs to activity cost pools. B. The identification of activities and activity cost pools. C. The process by which overhead costs are assigned to activity cost pools. D. The method used to directly trace costs to activate and cost objects. Accounting Question 2 1. What is the second-stage allocation in an activity-based costing system? A. The activity rates that are used to apply costs to products and customers. B. The decision to trace overhead costs to activities and cost objects. C. The creation of activity cost pools. D. The decision to divide costs into activity cost pools. 2. In the variable costing period’s income statement, where should the period’s fixed costs be included? A. The fixed costs are expensed as period costs and NOT included in the value of the inventory. B. The income statement allows for the allocation of the fixed expenses into the inventory value. C. In variable costing, you do NOT include the fixed costs in the Income Statement. D. The variable costs as well as the fixed expenses are included in the cost of goods sold. 3. When fixed manufacturing expenses are generated in the manufacturing process how do they impact the net income of both absorption costing and variable costing? A. In absorption costing, the fixed manufacturing expenses in included in the inventory values, unlike variable costing. B. In variable costing, all fixed costs, NOT just manufacturing costs, are absorbed into the inventory values, unlike absorption costing. C. In the absorption costing, the fixed manufacturing costing is expensed to the period, unlike variable costing. D. In a variable costing, the fixed manufacturing expenses, is included in the inventory values unlike absorption costing. 4. When using absorption costing as compared to variable costing, which action creates a difference in the net income? A. In a variable costing, fixed manufacturing are expensed into the cost of goods sold. B. In variable costing, the inclusion of selling and administrative fixed costs increases the value of the inventory. C. Both methods provide the same net income. D. In absorption costing, a higher cost of goods are sold due to the inclusion of the fixed manufacturing expenses with the variable costs. 5. Which two statements reflect advantages of using the variable costing method rather than the absorption costing method? Choose 2 answers: A. Variable costing provides managers with information needed to implement cost controls. B. Variable costing better matches fixed expenses to the period in which they are incurred. C. Variable costing reflects total costs of operations. D. Variable costing is required in IRS filings. 6. What is an advantage of the absorption cost approach? Choose 1 answer. A. Absorption costing assigns full costs of production to products. B. Absorption costing ties most closely to cash flows. C. Absorption costing matches fixed costs to the period incurred. D. Absorption costing is well suited to cost volume profit (CVP) analyses. 7. Which statement describes how differential analysis affects decisions? A. It results in costs and benefit that do NOT differ between alternatives being that are considered in the decision. B. It results in a greater number of different types of costs being considered in the decision. C. It results in avoidable costs being eliminated from consideration in the decision. D. It results in costs that differ between alternatives being the only costs that considered in the decision. 8. The following costs being considered as a firm contemplates acceptance of a special order: Total incremental fixed cost of $28,000 Total variable cost $47,000 Total sunk cost $31,000 Which price is closest to the minimum selling price for the special order that will make a positive contribution to profit? A. $47,001 B. $75,001 C. $106,001 D. $28,001 Accounting Question 3 1. What will be the result of using opportunity costs in the decision analysis? A. It will result in appropriate consideration of expenses that are NOT recorded in the firm’s account. B. It will NOT impact the decision analysis. C. It will result in appropriate consideration of economic benefits. D. It will result in appropriate consideration of expenses recorded in the firms accounts. 2. Which statement regarding accounting data would consistently support a decision to retain a product line? A. Contribution margin is greater than traceable fixed costs. B. Contribution margin is great than traceable variable costs. C. Sales revenue is greater than traceable fixed costs. D. Sales revenue is greater than traceable variable costs. 3. A. B. C. D. Which benefit should be used as the criterion for whether to accept or reject a special order? The selling price per unit is greater than the total incremental cost per unit. The selling price per unit is greater than the average fully allocated cost per unit. The selling price per unit is greater than the average fixed cost per unit. The selling price per unit is greater than the marginal cost per unit less the indirect incremental cost per unit. 4. A food manufacturer spends $80,000 on raw materials and refining costs. The refined flour can be sold at the split-off point for $100,000 or, with further processing and packaging, as cake meal for $180,000. Incremental costs of further processing the flour to produce cake meal are $10,000, and further packaging costs are $20,000. What is the incremental profit or loss from further processing of the flour into cake meal? A. $30,000 loss B. $70,000 profit C. $150,000 profit D. $50,000 profit 5. A. B. C. D. Which two statements reflect benefits of flexible budgets? Flexible budgets consider overhead costs in determining estimated costs. Flexible budgets account for actual production levels. Flexible budgets allow revenues and costs to be specified. Flexible budgets facilitate monitoring production levels. 6. What is limitation in a flexible budget system? A. The analysis of costs is NOT possible when there are fixed costs that do NOT change. B. The analysis of costs is accurate when there are fixed costs that do NOT change. C. The analysis of costs is simple in companies that provide a variety of products and services. D. The analysis of costs is NOT simple in companies that provide a variety of products and services. 7. A. B. C. D. What represents a profit center as opposed to a cost center? Independent subsidiary Human resources Sales division Accounting department 8. In a segmented reporting statement of a grocery store, which cost component would be a common fixed cost? A. Store manager B. Meat freezers C. Produce manager D. Pharmacist Accounting Question 4 1.Company X has two sales divisions with separate product lines. Line 1 has a $500,000 contribution margin and line 2 has $400000 contribution margin. Line 1 pays $50000 rent annually for it sales office and line 2 pays $60,000 rent annually for its sales office. Company X headquarters is located adjacent to line 1 sales office and pays $100,000 annual rent. A. B. C. D. What is the segment margin for line 1? $450,000 $400,000 $500,000 $350,000 2. Which is one reason that a firm would use residual income to determine their investment program? A. The use of residual income encourages the managers in the firm to focus on their particular area of concern. B. The use of return on investment is generally more difficult to calculate. C. Residual income provides a focus on the overall financial betterment of the firm. D. Segment reporting is generally too difficult to manage. 3. A. B. C. D. What is an important consideration with transfer pricing? That both divisions in the company be profitable form their point of view in equal proportion. That the transfer price always be based on the costs incurred by the selling entity. That transfer pricing always be based on the current market price outside of the firm. That the selling and purchasing price falls somewhere in the range of acceptable transfer pricing. 4. What does the absorption approach to cost plus pricing rely upon that is considered a disadvantage to this approach? A. Incremental direct cost B. Incremental indirect cost C. Forecast of unit sales D. Forecasted return on investment 5. A. B. C. D. Which cost is contained in a quality cost report? Prevention costs Overhead costs Costs of goods sold Variable product costs 6. Which two journal entries correctly identify the flow of conversion costs through a process costing system? A. Debit salaries and wages payable, credit manufacturing overhead. B. Debit salaries and wages payable, credit work in process C. Debit work in process, credit salaries and wages payable D. Debit work in process, credit manufacturing overhead 7. Which two production processes would be accounted for by a process rather than a job-order costing system? A. Boats B. Bricks C. Beer D. Condominium 8. A. B. C. D. For which two production processes would it be appropriate to use a job-order costing system? Aluminum Paper Apartment construction Commercial air craft 9. A. B. C. D. Which two issues are relevant to a make or buy decision? General overhead costs allocated to the internal production process. Depreciation on owned equipment that would be used in production Quality control assurances and capabilities of the outside producer. Wages of employees who would produce the product internally.