Bob Ball - Physical Nav
advertisement

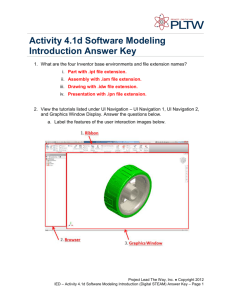
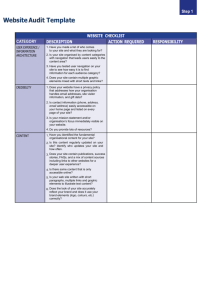
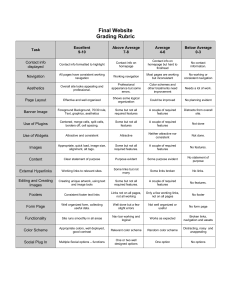
Move to Improve: Promoting Physical Navigation to Increase User Performance with Large Displays Robert Ball Virginia Tech November 10, 2006 Motivation: Cuban Missile Crisis: September/October 1962 U-2 Spy plane takes high-resolution pictures of parts of Cuba http://www.gwu.edu/~nsarchiv/nsa/cuba_mis_cri/1.jpg Picture taken of SA-2 missile construction site http://www.gwu.edu/~nsarchiv/nsa/cuba_mis_cri/1.jpg Analysis of pictures U-2 Spy place takes high-resolution pictures. Analyst must interpret pictures with this: Why: physical navigation Inside the CIA’s National Photographic Interpretation Center (NPIC), Washington D.C., 1962. http://www.gwu.edu/~nsarchiv/nsa/cuba_mis_cri/7.jpg Related Work Games! Related work – other domains and applications Physical navigation related work HMD Headmounted display CAVE Experiment Motivation Research Questions: Do users prefer physical navigation with large, high-resolution displays? Why? If so, does this result in improved user performance? Is physical navigation truly more beneficial than virtual navigation in terms of performance time? Experimental Design – data and visualization 3,500 houses for sale in Houston, TX Semantic zooming scheme, zooming only resulted in more information being displayed. To see all of the houses with all the details shown would require about a 100-monitor display. Experimental Design – display, interaction, and tracking 24 tiled monitors Wireless mouse Vicon system Experimental Design – tasks 4 tasks: Navigation Search Pattern finding Insight finding Between-subject design Insight task: Within-subject design Used paper, pen, and stand. No correct answers. Other tasks: Walked and spoke answer. Only one correct answer. Experiment results - performance 2-way ANOVA: main effects for display width (F(1,1324)=20.56, p<0.01) task type (F(2,1324)=77.05, p<0.01) Tukey HSD analysis showed different task types were all in different groups, so: Task Main effect of display width navigation (F(1,508) = 118.9, p<0.01) search (F(1, 762) = 38.18, p<0.01) pattern finding (F(1, 90) = 3.53, p=0.06) Experiment results – performance, cont. Main effect of display width Task navigation (F(1,508) = 118.9, p<0.01) search (F(1, 762) = 38.18, p<0.01) pattern finding (F(1, 90) = 3.53, p=0.06) Performance time (s) Performance Times 30 25 20 15 10 5 0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 Display width (in number of columns) Navigation Search Experiment results - Performance We found no significant results based on the level of insight for the fourth task. So, we focus on results for the first three tasks in this section. Virtual Navigation Analysis – zooms 2-way ANOVA: main effects for task type (F(3,1400)=416.2, p<0.01) display width (F(1,1400)=34.8, p<0.01) near-significant interaction of task type and display width (F(3,1400)=2.4, p=0.06). Virtual Navigation Analysis – zooms per task navigation - zooms (F(1,508)= 144.6, p<0.01) navigation - panning not significant search - zooms (F(1,762) =114.1, p<0.01) search - panning (F(1,762) = 26.7, p<0.01) pattern - zooms not significant pattern - panning (F(1,90) = 7.8, p<0.01) Number of zooms Number of zooms Tasks - Metrics Main effect of display width 25 20 15 10 5 0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 Display width (in number of columns) Navigation Search Pattern Virtual Navigation Analysis – pans 2-way ANOVA: main effects for task type (F(3,1400)=301.3, p<0.01) display width (F(1,1400)=63.86, p<0.01) interaction of task type and display width (F(3,1400)=17.22, p<0.01). Virtual Navigation Analysis – pans per task navigation - zooms (F(1,508)= 144.6, p<0.01) navigation - panning not significant search - zooms (F(1,762) =114.1, p<0.01) search - panning (F(1,762) = 26.7, p<0.01) pattern - zooms not significant pattern - panning (F(1,90) = 7.8, p<0.01) 200 150 100 50 0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 Display width (in number of columns) Navigation Search Number of pans - pattern task Number of pans Tasks - Metrics Main effect of display width Number of pans Number of pans - navigation and search tasks 1200 1000 800 600 400 200 0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 Display width (in number of columns) Physical Navigation Analysis Douglas-Peucker algorithm used to guarantee that what we were analyzing was actual movement - not jitter. Physical Navigation Analysis, cont. 2-way ANOVA for total X distance: main effects for task type (F(3,1400)=75.1, p<0.01) display width (F(1,1400)=24.1, p<0.01) interaction of task type and display width (F(3,1400)=4.0, p<0.01) Physical Navigation Analysis – per task Main effect of display width navigation not significant search (F(1,762) = 4.52, p=0.03) pattern finding 120 100 80 60 40 20 0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 Display width(in number of columns) Total Distance in the X Direction pattern task (F(1,84) = 16.62, p<0.01) Movement in inches . Task Movement in inches . Total Distance in the X Direction search task 500 400 300 200 100 0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 Display width(in number of columns) Visualization of physical movement Experiment conclusions Do users prefer physical navigation with large, high-resolution displays? YES When faced with a choice of physical or virtual navigation, 100% of the participants chose only to physically navigate. Experiment conclusions If so, does this result in improved user performance? YES Performance time (s) Performance Times 30 25 20 15 10 5 0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 Display width (in number of columns) Navigation Search Experiment conclusions Is physical navigation truly more beneficial than virtual navigation in terms of performance time? YES Virtual navigation has a greater negative correlation on performance than physical navigation. The number of zooms correlated with performance with a correlation coefficient of 0.69. The number of pans correlated with performance with a correlation coefficient of 0.68. However, physical distance traveled did not significantly correlate with performance. Future work Do the results from this study extrapolate to 3D data? To non-geospatial data? How does fatigue/longitudinal use of such displays affect the results of this experiment?