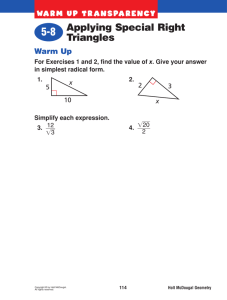
The American Free Enterprise System
advertisement

THE AMERICAN FREE ENTERPRISE SYSTEM Dr. T. D. Mitchell Bonneville High School Idaho Falls, Idaho Economics: concepts and choices, 2011. Holt McDougal ADVANTAGES OF THE FREE ENTERPRISE SYSTEM • Objectives in this section: • Explain why the Unites States is considered to have a capitalist or free enterprise system. • Identify the legal rights that safeguard the free enterprise system. • Analyze how the profit motive and competition help to make the free enterprise system work. Economics: concepts and choices, 2011. Holt McDougal THE AMERICAN FREE ENTERPRISE SYSTEM • Concept Review • A market economy is and economic system based on individual choice, voluntary exchange, and the private ownership of resources. • Key Concept • Free enterprise is another name for capitalism, and economic system based on private ownership of productive resources. This name is sometimes used because in a capitalist system anyone is free to start a business or enterprise. Economics: concepts and choices, 2011. Holt McDougal WHAT IS A FREE ENTERPRISE SYSTEM? • Business in America • Choices are the basis of a market economy. • Business owners can freely choose to start a business. • Managers and workers who operate these businesses voluntarily decide to exchange their labor for the pay the owners offer. • Consumers freely choose which products to purchase. Economics: concepts and choices, 2011. Holt McDougal EMERGING MARKETS • Let’s look at the economies of Mexico and Singapore • In Mexico, government plays a much larger role. • Informal markets have grown up. • In Singapore, the government is so involved workers are required to contribute to a national savings account. Economics: concepts and choices, 2011. Holt McDougal FREE ENTERPRISE AND LEGAL RIGHTS Open Opportunity Legal Equality Free Contract Economics: concepts and choices, 2011. Holt McDougal HOW A FREE ENTERPRISE SYSTEM WORKS Economics: concepts and choices, 2011. Holt McDougal MILTON FRIEDMAN: PROMOTER OF FREE MARKETS • Spent most of his career teaching at the University of Chicago. • Central to his ideas was the belief that the market should be free to operate in all fields. • Easing government restrictions would bring more producers into the market. • Governments most important role in the economy is to control the supply of money. • Advised two presidents • Winner of the Nobel Prize. Economics: concepts and choices, 2011. Holt McDougal MILTON FRIEDMAN TALKS ABOUT GREED Economics: concepts and choices, 2011. Holt McDougal REVIEWING KEY CONCEPTS 1. Explain the difference among the following terms. • Open opportunity • Legal equality • Free contract 2. How is a free enterprise linked to economic freedom? 3. Explain the role of competition in a free market. Illustrate you answer with examples of businesses in Idaho Falls. 4. What do you think might be the next new technology to compete with computers? Economics: concepts and choices, 2011. Holt McDougal HOW DOES FREE ENTERPRISE ALLOCATE RESOURCES • Objectives in the section: • Explain how consumers help determine the way resources are used. • Explain how producers help determine the way resources are used. • Analyze a circular flow model of the U. S. economy. Economics: concepts and choices, 2011. Holt McDougal THE ROLES OF PRODUCERS AND CONSUMERS • Producers seek profit. • Consumers vote with their wallets. Economics: concepts and choices, 2011. Holt McDougal GOVERNMENT IN THE U. S. ECONOMY • Modified free enterprise (circular flow) • Located in the center. • A consumer in the product market. • Also a consumer in the factor market. • Government is a producer. Economics: concepts and choices, 2011. Holt McDougal REVIEW • Compare and contrast the role of consumers and producers in producing resources. Which do you think has the greater power? • Use the circular flow diagram on pg. 80 and what you have learned from this section to explain the ways in which government allocates resources. • What industries in today’s world do you think would be wise to make changes given consumers’ preferences? Give reasons for you selections. Economics: concepts and choices, 2011. Holt McDougal GOVERNMENT AND FREE ENTERPRISE • Objectives in the section: • Understand that one role of government in the U. S. economy is to address market failures. • Analyze why governments provide public goods and infrastructure. • Explain how governments seek to decrease negative externalities and increase positive externalities. Economics: concepts and choices, 2011. Holt McDougal PUBLIC GOODS • Funded by taxes collected by the government. • People cannot be excluded from the benefits. • One person’s use of the product does not reduce the usefulness to others. • Free Riders • Pubic and Private Sectors – shared responsibilities • infrastructure Economics: concepts and choices, 2011. Holt McDougal MANAGING EXTERNALITIES • Negative externality • Paying for negative externalities • Positive externality • Spreading positive externalities • Subsidy Economics: concepts and choices, 2011. Holt McDougal PUBLIC TRANSFER PAYMENTS • Safety net • Redistributing income • Transfer payments • Public transfer payment Economics: concepts and choices, 2011. Holt McDougal CHECKING FOR UNDERSTANDING • Illustrate the two characteristics of public goods with examples. • How is infrastructure linked to the economy? • Give an example of a free rider. • In 2003, Congress passed laws to encourage private charitable organizations to provide social services. They would compete for government funds to carry out community services through their own networks. Do you think this is an effective way to address social issues? Use economic concepts, such as markets, efficiency, and opportunity costs in developing your response. Economics: concepts and choices, 2011. Holt McDougal FINAL THOUGHTS Economics: concepts and choices, 2011. Holt McDougal