Ancient Greece and Rome - Fort Thomas Independent Schools
advertisement

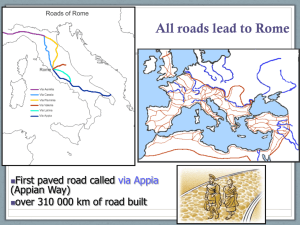
Classical Mediterranean Societies - Greece and Rome A.P. World History Basic Overview Greece • • • • Indo-European people Balkan Peninsula and Aegean Sea Commerce/Manufacturing through empire Agriculture basis Minoan Civilization • 2800- 1450 BCE Crete • Sailed to southern Greece, Egypt for trade • Ruled by king • Evidence of archives, art, opulent buildings • Destroyed by tidal way or invasion • Historians unsure QuickTime™ and a decompressor are needed to see this picture. Mycenae • 1600-1100 BCE 1st Greek state • Alliance of powerful monarchies living within stone walls • Warrior culture; established commercial network • King to remember- Agamemnon • Knowledge comes from Homer’s poetry • Collapse b/c fight each other, earthquake Layout of Mycenae QuickTime™ and a decompressor are needed to see this picture. Greek ‘dark ages’ • 1100 – 750 BCE: few records • Immigrated to Ionia (western Turkey) • Iron replace bronze, adopt Phonecian alphabet • Epic poem- long poem of hero’s deeds • Iliad: Trojan War; Paris kidnapped Helen (wife of king of Sparta), follow hero Achilles • Odyssey- Odysseus’ 10 year return home Political Structure • Formed City-states, polis • 1st Democracy • Most formed on hilltop, with marketplace, surrounded by agriculture • Athens • Sparta Social Structure • Only free, land owning, native-born men could be citizens entitled to the full protection of the law in a city-state • 3 groups • Citizens with political rights (adult males) • Citizens without political rights (women, child) • Non-citizens (slaves, aliens) Tyranny comes to city states • Wealthy classes seize power, aristocrats fight back • Peasants support tyrants who promised reform, control • Hired soldiers, built new walls, contradicted Greek political ideas • By 600s BCE city states turn to democracies and oligarchies Sparta • 800-600 BCE: need more land, turn to conquest • Conquered people became serfs • Women live at home, men in barracks • more freedom, job to raise healthy warrior sons • Oligarchy- king and council vote, no discussion • Frowned on travelers, new ideas, art • Main focus: military training and conquest QuickTime™ and a decompressor are needed to see this picture. QuickTime™ and a decompressor are needed to see this picture. Athens • Originally: Ruled by oligarchy of aristocrats with land • Economic and political troubles • After several reforms, leaders council of 500 propose laws; all citizens authority to pass laws after debate • Age of Pericles (461-429 BCE): democracy, culture, power thrive • Turned to direct democracy Pericles Pericles introduced several reforms. 1.Strengthen Greek democracy by paying people in public offices. - This way everyone could afford to work for the gov’t. and not just the rich. 2. Increased Size of Navy - Protect trade vessels - 200 ships Spent large amounts of money - Parthenon (Dedicated to Athena) QuickTi me™ and a decompressor are needed to see thi s pi ctur e. Influence • Philosophy • Aristotle- science, politics; observation, investigation; best government: constitutional government • Plato- nature of reality, truth, beauty; ideal ruler philosopher-king • Socrates- questions • Stoicism- what’s the point of life? To achieve happiness; moderation • Art • Architecture: Acropolis • Drama: plays (Sophocles - Oedipus Rex, Antigone) • Religion • Greek Mythology Greek Architecture QuickTime™ and a decompressor are needed to see this picture. Greek Architecture QuickTime™ and a decompressor are needed to see this picture. QuickTime™ and a decompressor are needed to see this picture. The Parthenon Athens vs. Sparta • 431BCE: Peloponnesian War- war between Athens & Sparta(w) • Athens try to stay behind protected walls, held for 20yrs • Alexander the Great • Crushed rebellions after father’s (Philip II of Macedon) reign • Spread Greek language and culture to Africa and Asia • Blended culture called Hellenistic, or greek-like • Hellenism QuickTime™ and a decompressor are needed to see this picture. Ancient Rome Geography • centrally located in the Mediterranean Sea; allowed for sea trade • the Alps mountains provided defense to the north Early Roman History • Earliest settlers were the Greeks, Latins and Etruscans (Northern Italy) • Etruscans dominate Italian peninsula from 635-509 BCE • Traded with Greeks and Phoenicians • Monarchy that becomes corrupt over time • 509 BCE: kick out last Etruscan king • Romans establish a republic • “Res Publica” - the Affairs of the Public Roman Society • Twelve Tables- code of law • First written law form in Rome that acknowledged the status of the Plebeians • Two groups form: • Patricians: rich, powerful landowners • Plebeians: own little or no land; treated like 2nd class citizens - Many will try to change this! Government • Romans allowed all citizens the right to vote; allowed conquered peoples citizenship • Roman Assembly: place of government; three-house body Roman Assembly • Senate: only patricians allowed (served for life); controlled taxes & spending; could veto any bill passed by assembly • Assembly of Centuries: only soldiers allowed; could vote on laws but had no veto power; chose consuls (2) who carried out the laws • Assembly of Tribes: made up of plebeians; could only make laws for plebeians; had no veto power; chose tribunes (10) to look after the rights of the plebeians Punic Wars: Rome vs. Carthage 1st Punic War (264 BCE) • rivalry developed because Carthage prevented Roman trade in W. Mediterranean • Carthage surrendered after 20 years of fighting • Rome took Sicily & cash from Carthage Second Punic War (218 BCE) • Hannibal (Carthage) led 50,000 men & 60 elephants over the Alps mountains in surprise attack against Rome • Scipio Africanus (Rome) attack Carthage; Hannibal returned to defend the city Second Punic War (218 BCE) • Battle of Zama: Rome defeated Carthage • Rome received Spain & gold; later, Rome took Greece, Macedonia, Asia Minor Third Punic War • Romans sent army to destroy Carthage because they wanted the land for farming QuickTime™ and a decompressor are needed to see this picture. Problems of Roman Expansion • Population increase • Senate gained power during Punic War, plebeians lost power • No manufacturing • People lost morals Attempts at reform • Tiberius Gracchus: • proposed limiting land ownership & dividing up land of some large landowners • Gaius Gracchus: • proposed 1st welfare system for the poor • Both stabbed to death by Roman Senators Roman Civil War Marius vs. Sulla • Marius: Roman general • Sulla: Roman general supported by Senate • Sulla won; became dictator for 3 years then retired First Triumvirate • Caesar, Pompey, Crassus • Caesar went to fight in Gaul (France); sent back his Commentaries detailing only his victories (“Venni, Vetti, Vicci”) • Senate told Caesar not to cross Rubicon River with his army Second Roman Civil War Caesar vs. Pompey & the Senate • Caesar defeated Pompey in Greece, then Egypt • Rome took control of Egypt (Cleopatra), Middle East • 45 BCE: Senate voted Caesar dictator for life Caesar Institutes Reform • Allowed plebeians in senate; Caesar retained veto power • Land redistribution: gave land of patricians to plebeians • Provided jobs for unemployed Ides of March March 15, 44 BCE • Caesar assassinated in Forum by Brutus & Cassius for wanting to become king Second Triumvirate • Octavian, Marc Antony, Lepidus Octavian - great - nephew of Julius Caesar; Also known as Caesar Augustus Third Roman Civil War Octavian vs. Marc Antony • Octavian defeated Marc Antony at Battle of Actium, won war Roman Empire • Roman Rule: empire had population between 70-100 million • Pax Romana (Roman Peace): 27 BCE - 180 CE • Established by Augustus in response to problems faced by the growing empire • Tried to restore the glory of the former republic • Most power was in hands of Emperor, very little power given to the Senate • Golden Age of Rome - focused on trade, increasing the standard of living and achievements in the arts • Extensive road system built - 53,000 square miles of road(Via Appia) Roman Empire • Economy: based on trade of goods from as far as E. Africa, S.E. Asia & China • public amusements: gov’t offered free bread & free entertainment (chariot races, gladiators) Roman Empire Architecture: built Circus Maximus, Colosseum, Pantheon (temple for all the gods), Appian Way (road connected Rome & southern Italy), aqueducts Decline & Fall • Political instability • Economic decline • Barbarian invasions • Visigoths: captured & sacked Rome • Huns: plundered cities of northern Italy • End of Roman Empire • 455 CE: Vandals raided, sacked Rome • 476: Roman Empire fell