Counterplans - Stanford National Forensics Institute
advertisement

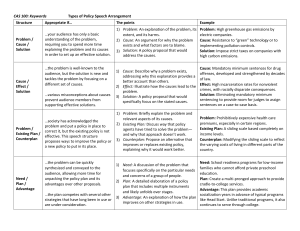
Counterplans Stanford National Debate Institute Summer 2012 Competition Competition Defined The counterplan alone is better than the plan alone or any combination of the plan and the counterplan. Competes through Net Benefits NET BENEFITS: CP>CP+Plan or CP CP+Plan: the permutation. Three types Synthetic-All of the plan plus some of the CP Intrinsic- All of the plan and some or none of the counterplan plus something not in either the plan or the counterplan Severance-Part of the plan and part of the counterplan Status of the CP Conditionality: can kick the counterplan at anytime, including by the judge if the 2ar proves the cp is not competitive Dispositionality: Can kick the counterplan ONLY if there is a permutation Unconditionality: Can never kick the CP. Types Consult Condition Agent PIC’s International Actor Advantage Uniqueness Topic Counterplans: States CP Vanilla States CP Text: The Fifty States and all the territories should < insert plan> Net Benefits: Any thing that links to the USFG Politics Federalism Spending Lopez Text: The United States Supreme Court should, in a narrow ruling on the next available test case, rule that federal authority over the provisions of the plan violates the Tenth Amendment and devolve authority to the fifty states and relevant territories. Uniform Acts “In the United States, a Uniform Act is a proposed state law drafted by the U.S. Uniform Law Commission (ULC) and approved by its sponsor, the National Conference of Commissioners on Uniform State Laws (NCCUSL).” AND “The National Conference of Commissioners on Uniform State Laws (NCCUSL) is a body of lawyers, both private practitioners and government attorneys; judges, both state and federal; and law professors, typically appointed by the governor of each state. The NCCUSL drafts laws on a variety of subjects and proposes them for enactment by each state, the District of Columbia, the U.S. Virgin Islands, and Puerto Rico. NCCUSL was established in 1892. The NCCUSL, while influential, does not have any direct legislative power itself; uniform acts become laws only to the extent they are enacted into law by state legislatures.” UA cont’d “ Among the most influential uniform acts are the Uniform Commercial Code, Uniform Probate Code, Uniform Trust Code, Uniform Partnership Act, Uniform Limited Liability Company Act, Uniform Transfers to Minors Act, Uniform Certification of Questions of Law Act, Uniform Enforcement of Foreign Judgments Act, Uniform Controlled Substances Act, Uniform Arbitration Act, Uniform Environmental Covenants Act, Uniform Conservation Easements Act, Uniform Management of Institutional Funds Act, Uniform Interstate Family Support Act, Uniform Child Custody Jurisdiction and Enforcement Act, and Uniform Anatomical Gift Act. However, there are well over 100 uniform acts.” UA cont’d Text: The Uniform Law Commission will submit to the fifty states and all relevant territories for ratification a uniform act to [blank]. UA cont’d Uniform acts solve comparatively better than federal legislation and avoids the politics/federalism disads William Henning, 3/15/2011, (Prof. of Law, Univ. of Alabama) "The Uniform law commission and cooperative federalism: implementing private international law conventions through uniform state laws," p. 39-41 The Uniform Law Commission (ULC) is a non-partisan, nonprofit, unincorporated association comprised of commissions formed in each state of the United States and also the District of Columbia, Puerto Rico, and the U.S. Virgin Islands. Its mission is “to promote uniformity in the law among the several States on subjects as to which uniformity is desirable and practicable.”2 In the 117 years of its existence, the ULC has produced hundreds of uniform laws and forwarded them to the legislatures of its member jurisdictions for enactment, often with striking and sometimes with universal success. National Governors Same as Uniform act XO/Courts Executive Orders Supreme Court Rulings Consult the States/DC Best of both worlds • Opt in clause • Best answers are • Race to the bottom • Lack of uniformity • Probabilistic Solvency Privates Text: The United States federal government should offer tax credits to any firms willing to ______ in the United States. Private funding can fill in and is popular Reinhardt ‘11 William Reinhardt, His authoritative publication is read monthly in 15 countries by 3,600 senior executives in the infrastructure project development/construction, finance and facility operations markets, “The Role of Private Investment in Meeting U.S. Transportation Infrastructure Needs,” May 2011 In September 1990, the ARTBA Board of Directors voted unanimously to authorize the formation of a Public- Private Partnerships Division as part of the association’s membership structure. The division’s mission since its inception has been two-fold. First, to develop and help the association move legislative and regulatory recommendations that will help advance P3s in the marketplace as a means to augment, or supplement, traditional public financing mechanisms. And the second, to help educate the association’s members, public-sector officials, legislators and the public-at-large about the value of public-private partnerships in transportation. With the U.S. Congress now developing legislation to reauthorize the federal highway and transit programs, ARTBA believed it was an ideal time to take an objective look at where the P3 market stands today after almost two decades of active promotion and assistance at the federal level. This is particularly important as leaders from both political parties increasingly suggest that private investment must take on a much larger role in replacing public funding for needed transportation projects now and in the years ahead. For example, for the past half-dozen years, many advocates of P3s have claimed that anywhere from “$100 billion to $400 billion in private investment” is available for such use.