Early Mesoamerican Civilizations
advertisement

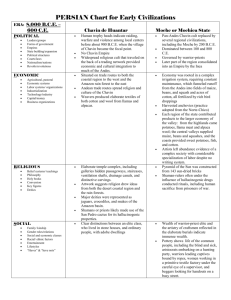
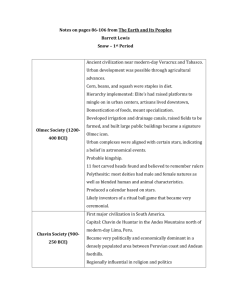
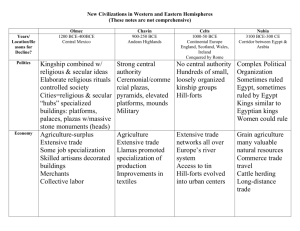
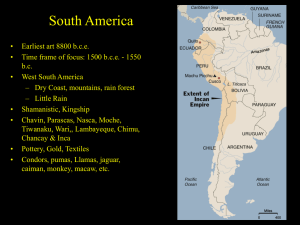
Early Mesoamerican Civilizations The Olmec and the Chavin The Isolated Americas Total and complete—all the ideas, technology, agriculture, writing, etc. flying around Eurasia was absent from here Environmental challenges: north-south axis, lots of mountains, changing terrain kept people separated and not alike Around 1000 BC the development of some trade, some domestication of plants led to urbanization and social stratification The Olmecs A cultural force —considered the mother of Mexican culture Flourished between 1200-400 BC Coincides with the Greeks, the Zhou, the Assyrians (western Asia), the Israelites in the Promised Land (Canaan); after the Hittites The Olmecs Famous for their 16 giant head sculptures probably “portraits” of important leaders Agriculture led to development of urban areas—corn, beans, and squash, maybe manioc As leaders emerged, they organized irrigation and public works projects Large-scale religious and civic buildings became the cultural draw The Olmecs Special buildings and large artificial platforms were sites of gatherings—people would visit from surrounding areas for these Cities laid out according to astronomical patterns like stars Produced high quality crafts like jade figurines, necklaces, etc. that distinguished their culture Ball game—rubber ball through a small stone hole in the wall, went on for days, players often died The Olmecs Rulers controlled People with aweInspiring religious Rituals; rulers were Associated with the gods through sacrifices and bloodletting Polytheistic, most gods dual natures (gender), the jaguar was important symbol/god Political center at San Lorenzo, then moved to La Venta The Chavin Located in Peru, in the Andes Mountains The coast of Peru had a dependable food supply (maize), which lends itself to urbanization Coastal populations traded textiles, food, ideas with those in the mountains and each other; Chavin de Huantar (capital) located at crossroads of trade Chavin is simply one group that dominated a long time and seems to have inherited culture from this area The Chavin Large labor projects indicate developed elite & maybe military control of neighbors to help construct buildings with very elaborate drainage system beneath them to resist floods Like Olmec, used religious rituals to attract “followers”/gain influence—jaguar again a major religious symbol Chavin de Huantar seems like a pilgrimage site The Chavin Social Classes: class of priests, main king and more local leaders existed, highly skilled artisans, must have been a large lower (slave?) class to build No evidence of destruction of society— increased warfare did occur at certain times, but when this group lost power is unknown Compare the Contemporaries Use of religion by elites to control some aspect of society Role of lowest class of people Geographical advantages/disadvantages Do this for: ◦ ◦ ◦ ◦ ◦ Chavin Olmec Egypt China Mesopotamia