PubMed - SDIS
advertisement

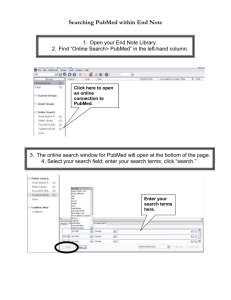
FORMATION ON : PubMed Prepared by Diane Sauvé, B. Sc., M. Bibl. Septembre 2014 PUBMED : SDIS To find the PubMed database: 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. 7. Write in the window of Google: sdis.inrs.ca Click on sdis.inrs.ca At the top left, under Ressources Select Bases de données In the box Titre, write Pubmed At the right, click on Go Finally, click on Pubmed PUBMED Started in 1996 is covering over 23.6 million citations . Oldest citations in PubMed date in 1809. 5 citations sources: free access to Medline, Pubmed, PubMed-in process, PubMed-as supplied by publisher and PubMed-OldMedline. Database of literature citations, primarily for articles from journals in the life sciences, but also for books and technical reports that are included in the NCBI bookshelf. Made 2.5 billion of searches for 2013 in Medline/Pubmed. Developed and maintained by the National Center for Biotechnology Information (NCBI), at the U.S. National Library of Medicine (NLM). PUBMED : MEDLINE Primary component of PubMed with more than 21 million citations. Subject scope of MEDLINE is medicine, nursing, dentistry, veterinary medicine, health care systems, and preclinical sciences. Since 2005, between 2,000-4,000 completed references with Medical Subject Headings are added each day since June 2, 2014. +735,000 citations indexed in 2013. Citations from 1946. PUBMED : MEDLINE Small number of newspapers, magazines, newsletters and 5,652 worldwide journal titles (November 2013). Journals in 39 languages (60 languages for older journals). Citations added from 2010-2012: about 93% are published in english about 84% have english abstracts written by authors of the articles PUBMED : ADVANCED RESEARCH PUBMED : SEARCH FIELDS PUBMED : SEARCH FIELDS PUBMED : DISPLAY FIELDS =80 PUBMED : DISPLAY FIELDS PUBMED : DISPLAY FIELDS PUBMED : DISPLAY FIELDS PUBMED : AUTHOR Enter the author’s last name followed by a space, plus the first 2 initials of the given name without punctuation followed by a space and all suffixes at the end (e.g. Vollmer Charles Jr). PubMed automatically truncates a search for an author's name, e.g., o'brien [au] = o'brien ma, o'brien kr, o'brien d o'brien j [au] = o'brien ja, o'brien jb, o'brien jc jr, o'brien j To turn off this automatic truncation : enclose the author’s name in double quotes and tag with [au] in brackets. PUBMED : AUTHOR PUBMED : AUTHOR Estimation of more than 2880 author names http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/24476258 J. Virol. 2012, 86 (8) : 4380-4393 PUBMED : AUTHOR 1 4 2 3 PUBMED : AUTHOR Select the different authors that you want by choosing in the online index and pressing CTRL together with the left mouse button. 1 4 2 3 PUBMED : AUTHOR Full author name may be searched for references published from 2002 forward if the full author name is available in the article. PUBMED : AUTHOR AFFILIATION Author, Corporate Author, and Collaborator Affiliation Display Changes 2013 December 24 Effective December 16, NLM now includes Author Affiliations for all Authors, Corporate Authors and Collaborators in PubMed if the data are supplied by publishers in their XML submissions for MEDLINE indexed journals. PUBMED : JOURNAL Enter the journal name or abbreviation J. Virol. 2012, 86 (8) : 4380-4393 J. Virol. 2012, 86 (8) : 4380-4393 PUBMED : SELECTED TERMS A Latent membrane protein 1 LMP 1 AND B Epstein-Barr virus AND C Apoptosis AND D B cells J. Virol. 2012, 86 (8) : 4380-4393 PUBMED : ADVANCED RESEARCH 1 2 Make selection of 3 desired expressions 4 Select the expressions that you want by selecting one line of the index (push the CTRL together with the left click of the mouse). PUBMED : HISTORY 1 Click the left button of the mouse 2 PUBMED : HISTORY PUBMED : HISTORY Latent membrane protein 1 Latent membrane proteins 1 Latent membrane protein1 Latent membrane proteins1 Latent membrane protein* AND 1 No result PUBMED : ADVANCED RESEARCH If you choose this strategy, you will not have the MeSH. Come from: Show index list PUBMED : MeSH - MAIN HEADINGS MeSH : Medical Subject Headings MeSH is the controlled vocabulary used for indexing articles for the MEDLINE® subset of PubMed. Published since 1954. MeSH terms are arranged hierarchically (tree structure) by subject categories with more specific terms arranged beneath broader terms. It is updated weekly and reviewed annually. MeSH in english-french, english-swedish and english-spanish-portuguese: HTTP://mesh.inserm.fr PUBMED : MeSH http://www.nlm.nih.gov/pubs/techbull/nd14/nd14_mesh.html PUBMED : MeSH http://www.nlm.nih.gov/pubs/techbull/nd14/nd14_medline_data_changes_2015.html PUBMED : MeSH PUBMED : MeSH PUBMED : MeSH HEADINGS Give more complete results because you have no more problem of spelling variations, synonyms and near-synonyms. Give greater accuracy using the major descriptor ( MeSH major topic). Permit to specify particular aspects of a descriptor in using subheadings. However, the references bearing the “PubMed-in process” and “PubMed- as supplied by publisher” or Pubmed status are not found because they have not yet or they will not received descriptors. However, if the research focuses on a new topic or subject very sharp, it could be that you don’t find a MeSH or you find a too generic MeSH. PUBMED : MeSH The 4 MeSH types included: Main Headings Subheadings Publication types Supplementary concept records PUBMED : MeSH - MAIN HEADINGS The MeSH 2014 included 27 149 MeSH Headings in 16 categories: PUBMED : MeSH - MAIN HEADINGS MeSH Heading : Subject analysts examine each article and assign the most specific MeSH terms applicable, with a related subheading; typically 10 to 12 headings per citation [mh] or [MeSH] 11 MeSH PUBMED : MeSH 1 2 3 PUBMED : MeSH PUBMED : MeSH PUBMED : MeSH - SUPPLEMENTARY CONCEPTS Formely called “Supplementary chemical records” 219,266 headings Used to index chemicals, drugs and other concepts such rare diseases for Medline Searched by “Substance name” [NM] No tree numbers Updated weekly PUBMED : HISTORY J. Virol. 2012, 86 (8) : 4380-4393 PUBMED : HISTORY #6 #5 #7 #4 #9 #8 PUBMED : HISTORY Try: Epstein Barr viruses PUBMED : MeSH 1 3 2 PUBMED : MeSH PUBMED : MeSH - SUBHEADINGS PUBMED : MeSH - SUBHEADINGS = 83 PUBMED : MeSH - SUBHEADINGS PUBMED : MeSH - SUBHEADINGS Subheadings : are used to help describe more completely a particular aspect of a subject. The subheadings logically paired with the main heading 2 letters may be used for subheadings. Subheadings PUBMED : RESEARCH STRATEGY Pathogenicity of Epstein-Barr virus= ( A AND B) OR C A Pathogen* B Epstein-Barr virus EBV … C Herpesvirus 4, Human/Pathogenicity PUBMED : HISTORY PUBMED : MeSH PUBMED : MeSH - MAJOR TOPICS Major Topics : used [majr] to restrict a search to citations where the term is the major topic or focus of the article, in the display reference , it’s represented by an asterisk. MAJR PUBMED : MeSH PUBMED : MeSH PUBMED : MeSH - EXPLOSION What you cannot see in “Search details”: The terms that are more specific under “Herpesviridae” in the MeSH: they are also searched. PUBMED : MeSH - ENTRY TERMS Many synonyms, near-synonyms, and closely related concepts are included as entry terms to help users find the most relevant MeSH descriptor for the concept they are seeking. J. Virol. 2012, 86 (8) : 4380-4393 PUBMED : HISTORY Do we have to add “cell death”? PUBMED : MeSH - ASSOCIATED TERMS J. Virol. 2012, 86 (8) : 4380-4393 PUBMED : HISTORY B cell B cells PUBMED : HISTORY The maximum number of searches available in History is 100. History will be lost after 8 hours of inactivity. PUBMED : HISTORY To obtain the final result of the 4 groups of terms, you have to select each group and click on ADD each time. In the builder, you need to have AND between each 4 groups. Final result Smallpox virus http://www.flickr.com/photos/sanofi-pasteur/5280407684/in/photostream/ PUBMED : AUTOMATIC TERM MAPPING Untagged terms that are entered in the search box are matched (in this order) against : MeSH translation table Journals translation table Full Author translation table Author index Full Investigator (Collaborator) translation table Investigator (Collaborator) index PUBMED : AUTOMATIC TERM MAPPING The MeSH Translation Table contains: o o o o o o MeSH Terms See-reference mappings (also known as entry terms) for MeSH terms MeSH Subheadings Publication Types Pharmacologic Actions Terms derived from the Unified Medical Language System (UMLS) that have equivalent synonyms or lexical variants in English o Supplementary Concepts (chemical, protocol or disease terms) and their synonyms PUBMED : PUBLICATION TYPES : 73 PUBMED : PUBLICATION TYPES PUBMED : AUTOMATIC TERM MAPPING When a match is found for a term or phrase in a translation table the mapping process is complete and does not continue on to the next translation table. When you enter your search terms as a phrase, PubMed will not perform automatic term mapping that includes the MeSH term and any specific terms indented under that term in the MeSH hierarchy. If no match is found, PubMed breaks apart the phrase and repeats the above automatic process untill a match is found. Pubmed ignores stopwords in searches. If there is no match, the individual terms will be combined with AND together and searched in all fields. PUBMED : STOPWORDS PUBMED : AUTOMATIC TERM MAPPING PUBMED : AUTOMATIC TERM MAPPING Terms enclosed in double quotes will be searched in all fields and not processed using automatic term mapping. "Herpesvirus 4, human" Herpesvirus 4, human Herpesvirus 4, human[MeSH Terms] PUBMED : AUTOMATIC TERM MAPPING Truncation, quotes, search tags turn off automatic term mapping and the process that includes the MeSH term and any specific terms indented under that term in the MeSH hierarchy. N.B. If a truncated term (e.g., tox* for toxic, toxicologic, toxicology, toxicological, toxicologist, toxicologists …) produces more than 600 variations, a warning message displays to lengthen the root word to search for all endings. PUBMED : AUTOMATIC TERM MAPPING Truncation turns off automatic term mapping and the process that includes the MeSH term and any specific terms indented under that term in the MeSH hierarchy. Herpesvirus* Herpesvirus Herpesviruses PUBMED : RECIPE FOR AN OPTIMAL RESEARCH 1. Put a word or phrase without quotes. 2. Make a second search with the plural of the word or the phrase without quotes. 3. Don’t forget to also search with abbreviations, the british and american languages. 4. Use the “Show search details” for points 1-3 to correct the terms or expressions displayed within the “Show search details”. 5. See if you can find a descriptor and if so, look in the MeSH database for additional information to modify the search. 6. Put the phrase in double quotes or use the truncation. PUBMED : Pseudomonas aeruginosa http://phil.cdc.gov/phil/home.asp PUBMED : TERM SUGGESTED PUBMED : AUTHOR KEYWORDS Author Keywords in PubMed (2013 February 07) PubMed now displays author keywords when supplied by publishers. NLM will not review author keywords for accuracy or add them to non-publisher supplied citations. Author keywords can be searched untagged or using the Other Term [OT] or Text Words [TW] tags. PUBMED : DISPLAY SETTINGS PUBMED : DISPLAY SETTINGS - SUMMARY PUBMED : DISPLAY SETTINGS - SUMMARY PUBMED : DISPLAY SETTINGS - SUMMARY - TEXT PUBMED : DISPLAY SETTINGS - SUMMARY - TEXT PUBMED : DISPLAY SETTINGS - ABSTRACT Social media icons: since 2014 July PUBMED : DISPLAY SETTINGS - ABSTRACT PUBMED : DISPLAY SETTINGS - ABSTRACT Structured abstract PUBMED : DISPLAY SETTINGS - STRUCTURED ABSTRACT Formats were developed in the late 1980s and early 1990s. To assist health professionals in selecting clinically relevant and methodologically valid journal articles. To guide authors in summarizing the content of their article. To facilitate the peer-review process. To enhance computerized literature searching. Standardized formats for structured abstracts have been defined for original research studies, review articles and clinical practice guidelines. PUBMED : DISPLAY SETTINGS - ABSTRACT PUBMED : DISPLAY SETTINGS - ABSTRACT - TEXT PUBMED : DISPLAY SETTINGS - ABSTRACT - TEXT PUBMED : DISPLAY SETTINGS - ABSTRACT - TEXT PUBMED : DISPLAY SETTINGS - MEDLINE Pubmed unique identifier Status tag Completion date ISSN Volume Date Date created created Organization that supplied citation data Modification date Issue Publication date Pagination Title Pii or doi that serves the role of pagination Abstract Full author name Author Affiliation Language Grant number PUBMED : DISPLAY SETTINGS - MEDLINE Publication type Place of publication Full journal title Enzyme Commission or Registry number of CAS Date of electronic publication Journal title abbreviation NLM unique ID Subset MeSH terms Other identification numbers MeSH date Publication history status date Publication status Date the citation was added to PubMed Create date Article identifier Source PUBMED : DISPLAY SETTINGS - XML Xml (ExTENSIBLE Markup Language) is generally used for displaying and manipulating data in software applications. PUBMED : Bacillus anthracis http://phil.cdc.gov/phil/home.asp PUBMED : STATUS TAGS PUBMED : STATUS TAG - PUBMED - AS SUPPLIED BY PUBLISHER PUBMED : STATUS TAG - PUBMED - IN PROCESS Citations bibliographic data will be reviewed and indexed. PUBMED : STATUS TAG - PUBMED - INDEXED FOR MEDLINE Citations have been indexed with MeSH terms, Publication Type, Substance Names, etc. Bibliographic data has been reviewed. PUBMED : STATUS TAG - PUBMED - OLDMEDLINE Over 2 million OLDMEDLINE citations, most without abstracts. Citations originally printed in hardcopy indexes published from 1946 throught 1965 that have not yet had all of their original subject terms mapped to current MeSH. Partially MeSH indexed Bibliographic data has been reviewed. Bibliographic data has been reviewed. PUBMED : STATUS TAG - PUBMED PUBMED : STATUS TAG - PUBMED-BOOKS & DOCUMENTS PUBMED : STATUS TAG - PUBMED PUBMED : SAVE SEARCH PUBMED : SAVE SEARCH PUBMED : PASSWORD PASSWORD Most common passwords of 2013 http://splashdata.com/press/worstpasswords2013.htm PASSWORD How to select your password? by Burçin Gerçek Take care of the lenght A good password must have at least 8 characters. Choose well your words Avoid words that can be found in a dictionary, the names of dogs, cats of fish or dates birth, to use the same code for your login or password. No note on your keyboard Avoid putting your password on a post-it and attach it to the keyboard or on the screen, or worse to store it in a computer file. Translation of : http://www.symantec.com/region/fr/resources/mots_passe.html PUBMED : PASSWORD PASSWORD How to select your password? by Burçin Gerçek Use exotic characters It must be composed of at least 3 differents types of characters among the 4 existing types of characters (uppercase, lowercase, numbers and special characters) .* Choose a sentence, a poem or the title of a movie that you know and take the first letters to form the password, for example:: « Gone with the Wind" = GwtW26#? Change your passwords regularly Translation of : http://www.symantec.com/region/fr/resources/mots_passe.html * Translation of : http://www.cnil.fr/linstitution/actualite/article/article/securite-comment-construire-un-mot-de-passe-sur-et-gerer-laliste-de-ses-codes-dacces/ PUBMED : SIGN IN TO NCBI If you have an account If you need an account PUBMED : NEW ACCOUNT TO NCBI PUBMED : SAVE SEARCH PUBMED : SAVE SEARCH PUBMED : Influenza virus http://www.flickr.com/photos/sanofi-pasteur/5280410308/in/photostream/ PUBMED : SEND TO FILE (ENDNOTE) 1 2 3 4 PUBMED : SEND TO FILE (ENDNOTE) With Internet Explorer (test version: 11) PUBMED : SEND TO FILE (ENDNOTE) With Chrome (test version: 34.0.1847.116 m) PUBMED : SEND TO FILE (ENDNOTE) With Internet Explorer (test version: 11) With Chrome (test version: 34.0.1847.116 m) PUBMED : SEND TO FILE (ENDNOTE) With Internet Explorer (test version: 11) With Chrome (test version: 34.0.1847.116 m) PUBMED : SEND TO FILE (ENDNOTE) With Internet Explorer (test version: 11) With Chrome (test version: 34.0.1847.116 m) PUBMED : SEND TO FILE (ENDNOTE) With Internet Explorer (test version: 11) With Chrome (test version: 34.0.1847.116 m) 1 2 3 PUBMED : SEND TO FILE (ENDNOTE) With Firefox (test version : 19.0) 1 2 PUBMED : SEND TO FILE (ENDNOTE) With Firefox (test version : 19.0) 1 2 PUBMED : SEND TO FILE (ENDNOTE) PUBMED : SEND TO COLLECTIONS PUBMED : SEND TO COLLECTIONS 1 2 PUBMED : SEND TO COLLECTIONS Limit of 1,000 references 1 Limit of 100 alphanumeric characters 2 3 Note that accounts that do not register any activity in 2 years will be deleted. PUBMED : SEND TO CITATION MANAGER (ENDNOTE) 1 2 3 PUBMED : SEND TO CITATION MANAGER (ENDNOTE) With Internet Explorer (test version: 11): see the slides 129, 132-133 With Chrome (test version: 34.0.1847.116 m): see the slides 130, 132-133 With Firefox (test version 19.0): see slides 131-133 PUBMED : SEND TO CITATION MANAGER (ENDNOTE) With Internet Explorer (test version: 11) PUBMED : SEND TO CITATION MANAGER (ENDNOTE) With Chrome (test version: 34.0.1847.116 m) PUBMED : SEND TO CITATION MANAGER (ENDNOTE) With Firefox (test version : 19.0) 1 2 PUBMED : SEND TO CITATION MANAGER (ENDNOTE) With Internet Explorer (test version: 11 With Chrome (test version: 34.0.1847.116 m) With Firefox (test version 19.0) 2 1 PUBMED : SEND TO CITATION MANAGER (ENDNOTE) PUBMED : SEND TO CLIPBOARD To save references temporarily to selected citations from one or several searches. It will be lost after 8 hours of inactivity on PubMed or other NCBI databases. 1 2 3 PUBMED : SEND TO CLIPBOARD The maximum number of 500 references PUBMED : SEND TO CLIPBOARD References in the clipboard are representes by the search number #0 PUBMED : SEND TO CLIPBOARD To remove all references 1 To remove selected references 2 PUBMED : SEND BY E-MAIL 1 2 3 4 5 6 PUBMED : SEND BY E-MAIL PUBMED : SEND BY E-MAIL PUBMED : SEND BY E-MAIL PUBMED : SEND TO MY BIBLIOGRAPHY PUBMED : SEND TO MY BIBLIOGRAPHY 1 2 3 4 PUBMED : SEND TO MY BIBLIOGRAPHY Limit: 500 references download in one time PUBMED : SEND TO MY BIBLIOGRAPHY PUBMED : SEND TO MY BIBLIOGRAPHY 2 1 PUBMED : SEND TO MY BIBLIOGRAPHY PUBMED : SEND TO MY BIBLIOGRAPHY PUBMED : SEND TO MY BIBLIOGRAPHY PUBMED : SEND TO MY BIBLIOGRAPHY PUBMED : SEND TO MY BIBLIOGRAPHY PUBMED : SEND TO MY BIBLIOGRAPHY PUBMED : SEND TO MY BIBLIOGRAPHY PUBMED : SEND TO MY BIBLIOGRAPHY PUBMED : Rabies virus http://www.flickr.com/photos/sanofi-pasteur/5279807113/in/photostream/ PUBMED : NCBI ACCOUNT SETTINGS PUBMED : NCBI ACCOUNT SETTINGS PUBMED : MY NCBI - CUSTOMIZE HOMEPAGE 1 2 PUBMED : MY NCBI - CUSTOMIZE HOMEPAGE PUBMED : MY NCBI - SITE PREFERENCES PUBMED : MY NCBI - SITE PREFERENCES PUBMED : MY NCBI - SITE PREFERENCES PUBMED : MY NCBI - SAVE SEARCH Send to references Edit the strategy PUBMED : MY NCBI - MY BIBLIOGRAPHY PUBMED : MY NCBI - RECENT ACTIVITY Recent Activity is tracking your searches and records viewed for the last 6 months. PUBMED : MY NCBI - COLLECTIONS PUBMED : MY NCBI - COLLECTIONS - FAVORITES The Favorites collection which helps you keep a list of your preferred NCBI database records. PUBMED : MY NCBI - COLLECTIONS - FAVORITES PUBMED : MY NCBI - COLLECTIONS PUBMED : MY NCBI - COLLECTIONS 2 1 3 4 PUBMED : MY NCBI - COLLECTIONS 1 2 3 PUBMED : MY NCBI - COLLECTIONS PUBMED : MY NCBI - COLLECTIONS 2 1 3 PUBMED : MY NCBI - COLLECTIONS PUBMED : MY NCBI - FILTERS You can have up to 15 active filters using My NCBI. PUBMED : FILTERS Links to Web accessible full text articles (all available free of charge). Links to Web accessible full text articles (some may require subscription). PUBMED : FILTERS PUBMED : FILTERS P The "in process" and "supplied by publisher" citations may be excluded for some filter selections (article types, species, sex and ages) because they have not yet completed the MEDLINE indexing process. PUBMED : MY NCBI - FILTERS 1 2 3 4 5 PUBMED : MY NCBI - FILTERS PUBMED : MY NCBI - FILTERS The "Popular" category lists the most commonly requested filters according to each NCBI database. PUBMED : MY NCBI - FILTERS The "LinkOut" category groups records that have links to resources provided by outside organizations, such as full-text publications, biological databases, consumer health information, library holdings and research tools. These links provide supplemental information related to records in NCBI databases. PUBMED : MY NCBI - FILTRES The "Properties" category groups records according to specific criteria for each database. PUBMED : MY NCBI - FILTERS The "Links" category groups records that have links to other NCBI databases. PUBMED : Mycobacterium tuberculosis http://phil.cdc.gov/phil/home.asp PUBMED : FIND RELATED DATA PUBMED : FIND RELATED DATA PUBMED : SINGLE CITATION MATCHER The Single Citation Matcher searchs for a citation when you have some bibliographic information. PUBMED : SINGLE CITATION MATCHER To find a specific reference PUBMED : SINGLE CITATION MATCHER PUBMED : RELATED CITATIONS The Related citations See all…link will retrieve a pre-calculated set of PubMed citations that are closely related to the selected article. The related citations will be displayed in ranked order from most to least relevant, with the “linked from” citation displayed first. PUBMED : RRS PUBMED: RSS RSS (Really Simple Syndication) is an XML-based format used to send new items or information to recipients who use RSS feed readers. PUBMED : RSS PUBMED : RSS 2 Click 1 Drag and drop the XML icon onto the feed reader interface. PUBMED : RSS PUBMED : SIGN OUT Most of the information in coming from the sites : http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK3827/ Web address to see again this presentation: HTTP://SDIS.INRS.CA/ Under the heading : Formations/Autoformations/Pubmed/Formation PowerPoint IAF : Anglais EndNote formation Michel Courcelles # 4275 michel.courcelles @iaf.inrs.ca For comments: Diane Sauvé # 4340 diane.sauve@iaf.inrs.ca