Surgical Site Infections a hidden Hospital
advertisement

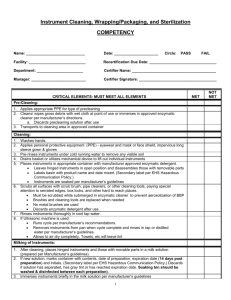
Leslie Teachout MT(ASCP), CIC Infection Prevention Riverton and Lander Hospitals Discuss the five steps in Sterilization Process Learn what processes in the OR the Infection Prevention should review and/or understand. Learn the five steps to monitor sterilization Behind closed doors Special clothing-only scrubs Red lines to cross Very busy Sterile! Patient privacy very important A very specialized team Sterilize instruments Remove bio-burden!!! Proper type of sterilization Proper instruments in each tray/wrap Monitor autoclaves/sterilization equipment Maintain autoclaves/sterilization equipment Immediate use sterilization Association for the Advancement of Medical Instruments Standards Association of Operating Room Nurses 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. Clean/Disinfect Prep/pack Sterilize Store Issue/use Open hinged instruments to remove bioburden Must clean before sterilization! Rust and/or pitting are the enemy! Instruments design and material Don’t reprocess single use instruments FOLLOW MANUFACTURE RECOMMENDATIONS!! Enzymatic cleaner immediately Washer sterilizer can be used Monitor process with indicator Load size? Maintenance Hospital specific trays or sets All surfaces of the instruments must be contacted by sterilant Wet packs mean water can contaminate instruments Weight limits of trays Best way to sterilize steam (see below for types) ETO Sterrad (plasma) Types of steam cycles Gravity Pre-vacuum SFPP (Steam Flash Pressure Pulse) Regular Cleaning Lint trap Maintenance 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. Equipment Control Load Control Pack Control Exposure Control Record keeping How to determine if your sterilizer is doing it’s job. When using dynamic-air removal (i.e. vacuumassisted steam cycles or pre-vac) Begin each day with a Bowie-Dick test to detect air leaks. Air leaks, poor steam quality, inadequate vacuum and air pockets can lead to poor steam penetration. Monitor the rest of the day by watching physical monitors Foundation of successful sterilization process monitoring: Biological Indicator or BI Only way to detect actual killing of microbial spores Most reliable test Rapid read outs reduces risk of recalls and is less expensive Required with implantable devices Use of chemical indicators (CI) for internal monitoring of packs Verifies the sterilant has penetrated the pack/peel pouch Chemical indicators are designed to react to two or more of the critical variables required for steam sterilization: Time Temperature Presence of steam CI have classes (not hierarchical!) Staff aware and understand importance!! CI Classes To know at a glance if the packs have been exposed to the sterilization process. These are CI class 1 process indicators So packs don’t have to be opened Provides documentation that items have been processed along with evidence of their monitoring results. Extremely important in a recall investigation Required for accrediation How long is the wrap good for/shelf life? Inventory control Look for wet packs Are “flashed packs” being usedpreferred Instruments cleaned prior to IU? Types of cycles Monitor for frequency of IU as this may indicate an instrument need Is all the OR staff educated and aware of the whole process? Gown up or bunny suit up and go to the OR! Ask questions! Ask questions! Watch processes! Get educated by staff as well as know the standards! Who cleans the OR rooms/how often Check for cleanliness-white glove test Review logs for monitoring and maintenance! Watch processes in the OR! (i.e. medication administration) Open doors! Check carts be NOSEY! Look at storage areas especially sterile storage Look for storage in “hidden sterile storage areas”(i.e. ED, PT and OB) Remember and remind we are all on the same team! Find out who does and owns the processes Open doors on cupboards! Check drawer in carts for open skin preps or medication! We all have the patients’ safety in mind! Monitor Surgical Site Infections for trends: OR staff OR Room Surgeon Was the immediate use autoclave used for instruments Customize for your hospital Share findings with OR Staff! Share findings with Surgeons Share findings with Anesthesia Keeping patients’ is everyone's responsibility Who process the instruments at your hospital? Are the individuals employed by your organization! Check packages – have a process just like checking outdates Initials Date Condition of package Indicator on peal pack Is SPD cleaning instruments well before sterilization? Watch process Are any instruments being used in your facility coming form outside (vendors, dentists, etc.) Is washer used? Then how is it monitored? Are all autoclave cycles and autoclaves monitored? Know what class of monitors are being used Frequency and documentation of Biological Indicators (BI) Assure all implants are being monitored with a BI What is your recall process when there is a failure? (make sure your on the list) How are autoclaves cleaned (how and frequency)? Monitor room cleaning All patient rooms (ATP or Diazo) White glove the tops of high surfaces/high dusting and vents? Frequency of terminal cleaning and difference between daily cleaning Who does the cleaning? Cleaned prior? Walk through process; same a SPD Cycles used for what and when Are logs complete? Who owns this process? Is OR staff knowledgeable and handles instruments appropriately? Discuss the five steps in Sterilization Process Learn what processes in the OR the Infection Prevention should review and/or understand. Learn the five steps to monitor sterilization Be aware of the hidden hospital in your hospital Stop the spread of the undiagnosed cancer! Bring the process into the light!