P6 Revision Quiz
advertisement

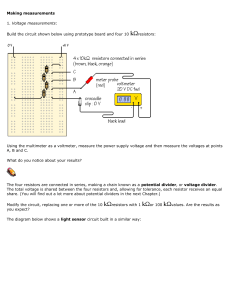
P6 – Revision Questions - Electricity for Gadgets Q1. Rheostat. 1. What is a Rheostat (Variable resistor) and what can it do in a electrical circuit? 2. (H) How does a Variable resistor work? 3. The graph to the right shows a changing voltage and current changes on a resistor. 1. How can you find the resistance from the 30 graph? 20 2. What is the relationship (equation) that 10 links Voltage, current and resistance? 3. (H) Calculate the resistance value from the 0 graph. 0 0.2 0.4 Voltage versus Current 4. (H) Use the V,I & R equation to fill in the table to the right. Voltage Q2. Non-ohmic. 5. Define the terms ‘Ohmic’ and ‘Non-ohmic’. Give examples for each. 6. (H) From the graph below explan what is happening to the resistance of each resistor (Separate line) as voltage increases. 240 0.6 0.8 Current Resistance 0.2 60 10 120 1000 Ohmic and Non-Ohmic Resistors 40 Voltage 30 20 A 10 B C 0 0 0.1 0.2 0.3 0.4 0.5 0.6 0.7 0.8 Current Q3. Potential Dividers 1. What is a potential divider? 2. Draw a simple potential divider circuit with R1 = 100 ohms and R2 = 200 ohms. 3. What is the benefit of replacing100 ohm resistor with a variable resistor? 4. (H) Explain how the variable resister works in this situation. 5. (H) If a 12 V supply is attached to the circuit in q2 what will the output be over R2? (Vout = Vin x R2 / (R1+R2)) Q4. LDR &Thermistors 1. LDR’s change resistance in different levels of light. Does the resistance increase/decrease with more light? 2. Themistors change resistance in different temperatures. Does the resistance increase/decrease with increased temperature? 3. (H) How can a Thermistor be used in a potential divider to make a temperature sensor (Thermostat). Explain how it works as temperature increases. Q5. Motor Effect. 1. Draw a diagram to show the shape of magnetic field around a wire with a current flowing through it. 2. What would happen to this wire if it was put near a magnet? 3. Looking at the diagram below, which way would the wire move? Q6. DC Motor 1. Draw a diagram of a simple motor with one loop of wire between two magnets. 2. Draw a current around the loop and the forces that will act on each side of the loop. 3. Explain why the motor turns. 4. (H) Explain the need for a split ring commutator. Q7. Generating. 1. Which of the following methods can generate a voltage in a wire. Explain each answer. ◦ A wire moving in a magnetic field. ◦ A magnet moving past a wire. ◦ A magnetic field changing strength. 2. One of the most common generators has a loop spinning in a magnetic field, explain how this produces a voltage. 3. Why is it common to spin a magnet in a coil instead? 4. How can the design or set up be changed to produce more voltage (4 main methods). 5. (H) Draw a diagram of a simple (1 loop) AC generator and how it is connected to produce AC. Q8. Transformers. 1. Draw a diagram to show the basic design of transformers. 2. Explain in simple terms how they work. 3. Explain the difference in design and output of ‘step up’ and ‘step down’ transformers. 4. Give 4 examples of where you would find transformers,. In each situation state, what type they are and why they are needed. 5. (H) use V1 x I1 = V2 x I2 & P = V x I to answer the following. 1. A 400 W transformer produces a current of 10 A what is the votage produces? 2. A primary current of 5A at 20 V produces a secondary current of 1A in a transformer, what is the voltage produced? 3. A transformer output is 240 V at 20 A, if the input (primary) voltage is 48000 V what was the primary coil current? Q9. Diodes 1. What is the function of a diode? 2. Explain what the graph below shows about diodes. 3. (H) Use the graph to explain forward and reverse resistance of a diode. 4. Explain what happens to AC when it is passed through a diode, use diagrams to help you explain it. 5. How can four diodes be arranged to produce full-wave rectification. 6. (H) Explain how a silicon diode functions (in terms of holes and electrons) Q10. Capacitors. 1. What is a capacitor? 2. Explain what happens when an uncharged capacitor is connected to a circuit and current. 3. Explain how the Voltage and Current in the circuit change as the capacitor is charged. 4. What is a smoothed out put? How does the capacitor help with this in Acto DC conversion? Q11. Logic. 1. What is the function (purpose) of a logic gate? 2. What are the possible outputs of a logic gate and what does it mean? 3. Draw diagrams of and explain the inputs and outputs (in a logic table) of the following gates, AND, OR, NAND and NOR. 4. Describe the use of logic gates as part of switching circuits using LDR’s and themistors in series. 5. (H) Explain the full function in terms of inputs and outputs and current flow for a LDR and logic switch circuit. 6. (H) How can a variable resistor improve the function of such circuits?