Payee
advertisement

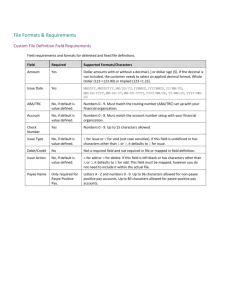
Transactions and Code Sets: Strategies in Implementing the 835 Transaction Brett Hacker, CIO Remettra, Inc. ©2003 Remettra, Inc. Page 1 Simple Concept Plans have been paying providers since providers started filing claims Providers need to know what was paid, rejected, or adjusted (remittance) HIPAA just wants to get that remittance standardized, and available electronically so providers can eventually auto-post receivables ©2003 Remettra, Inc. Page 2 Complex Issues Health care industry has little experience with banking beyond cutting a check and reconciling statements Banking industry as a whole has little experience with health care and is generally unaware of HIPAA ©2003 Remettra, Inc. Page 3 Driving Factors - Payers HIPAA Compliance - October Reduced print/mail costs - over time Increased efficiency – immediate Declined importance of float (although likely to rebound eventually) Reduced check fraud (if implementing EFT) ©2003 Remettra, Inc. Page 4 Driving Factors - Providers HIPAA Compliance - October Automatic receivables posting – eventually More timely payment receipt (if implementing EFT) ©2003 Remettra, Inc. Page 5 What’s The Problem? IG Scenarios/Prescribed Strategies: 2.1.2.1: ERA w/Payment by Check 2.1.2.2: ERA and EFT through DFI 2.1.2.3: ERA with Payment by Separate EFT 2.1.2.4: ERA and Payment Delivered Separately but Processed by a Value-Added Bank (VAB) 2.1.2.5: ERA with Debit EFT ©2003 Remettra, Inc. Page 6 ERA with Payment by Check 835 ERA Payer Payee Check Payer sends $ via check through the mail Payer sends ERA directly to the Payee Payee deposits the check and reconciles the ERA Requires reassociation “Gotchas”: Legacy Approach: keep same old process, tack on electronic delivery of ERA Payer (or Payer’s clearinghouse) responsible for ERA delivery, which becomes an additional process (still stuffing and mailing an envelope for the check) ©2003 Remettra, Inc. Page 7 ACH Primer Terms: DFI: Depository Financial Institution Electronic Funds Transfer (EFT): The electronic mechanism that payers use to instruct one DFI to move money from one account to another account at the same or at another DFI. Fund transfers may utilize ACH, FedWire, Swift, or other authorized electronic payment system. Originating DFI (ODFI): bank which initiates EFT instructions Receiving DFI (RDFI): bank which receives EFT instructions NACHA: NACHA is a not-for-profit trade association that develops operating rules and business practices for the Automated Clearinghouse (ACH) network and for other areas of electronic payments (http://www.nacha.org). ACH (Automated Clearinghouse): The most popular and widely used clearinghouse of electronic fund transfers (i.e. direct deposit of payroll, corporate payments, travel/expense reimbursements, state/federal, tax payments, consumer/business related transactions). Common ACH computer formats (NACHA formats) include CTX, CCD, and CCD+. Float: Refers to both the time delay related to exchange of funds (i.e. check, mail, processing) and the associated interest that may accrue during that delay. ©2003 Remettra, Inc. Page 8 ACH Primer, Continued More Terms: Financially EDI capable/Value Added bank (VAB): DFI that can successfully process and deliver incoming/outgoing EDI data, including translation, and store-and-forward mailboxing between bank customers and their trading partners. Lockbox-capable. Value added network (VAN): A third party service provider of secure networking services such as secure store-and forward mailbox delivery of EDI documents, EDI and proprietary in-network translation, and access to audit and reporting data on activity. Advance Notification of Funds: The receipt of payment related detailed information in advance of payment. Dollars and Data Together: When the payment and remittance are kept together through the entire data flow process, with the receiver also receiving the information together. Dollars and Data Separate: The transfer and receipt of payment and related data separately (usually split to accommodate the advance notification of funds, requiring reassociation of both payment and remittance by receiver of information). ©2003 Remettra, Inc. Page 9 ACH Primer, Continued More Terms: ACH Operators Federal Reserve System, New York Clearing House Association, VisaNet ACH Services, and the American Clearing House Association ACH Formats CCD: “Cash Concentration and Disbursement” B2B EFT format 1 payment record, no addenda CCD+: “Cash Concentration and Disbursement with Addenda” 1 payment record, 1 addenda record of 80 bytes Suitable for transmission of payment order and 835 TRN segment CTX: “Corporate Trade eXchange” 1 payment record, up to 9,999 addenda records of 80 bytes each ©2003 Remettra, Inc. Page 10 CTX ©2003 Remettra, Inc. Page 11 CCD+ ©2003 Remettra, Inc. Page 12 ERA and EFT through DFI ERA Payer EFT Payer DFI ERA EFT Payee DFI ERA Payee FDN Payer sends $ and ERA in an 835 to the Payer’s DFI Payer’s DFI sends $ and ERA to Payee’s DFI Payee’s DFI notified Payee of the $ via FDN (Funds Deposit Notification) and delivers the ERA Reassociation not necessary ©2003 Remettra, Inc. Page 13 ERA and EFT through DFI ERA Payer EFT Payer DFI ERA EFT Payee DFI ERA Payee FDN “Gotchas”: Payer must maintain Account/Routing info for payees (information not available in 837) Since ODFI and RDFI will have access to PHI via the remittance portion of the 835, BA agreements will need to be in place (between Payer and ODFI, and Payee and RDFI) ©2003 Remettra, Inc. Page 14 ERA and EFT through DFI ERA Payer EFT Payer DFI ERA EFT Payee DFI ERA Payee FDN More “Gotchas”: 835 is “enveloped” into a NACHA CTX format by Originating bank (ODFI) – BAA required between Payer and ODFI CTX is transmitted to ACH (Federal Reserve, other CH) – in clear text over private connection CH forwards to Receiving bank (RDFI) – based on routing number (if correct: if not, NACK is sent back to ODFI) ©2003 Remettra, Inc. Page 15 ERA and EFT through DFI ERA Payer EFT Payer DFI ERA EFT Payee DFI ERA Payee FDN More “Gotchas”: RDFI extracts 835 from CTX and re-assembles – if RDFI is EDI-capable RDFI delivers 835 to Provider – if RDFI has electronic delivery mechanism ©2003 Remettra, Inc. Page 16 ERA and EFT through DFI ERA Payer EFT Payer DFI ERA EFT Payee DFI ERA Payee FDN NACHA ACH Rules (page OG99): “If the addenda record information will be provided in human-readable format, the RDFI must ensure that the addenda information is translated from ANSI ASC X12 syntax…and provided to the Receiver in human-readable text. If the addenda record information will be provided in machine-readable, electronic file format…the RDFI and Receiver will need to determine whether the information will be (1) transmitted to the Receiver as a pass-through of the electronic file format (i.e., …835), (2) translated into a proprietary format agreed to by the RDFI and Receiver, or (3) merged with the Receiver’s lockbox data.” ©2003 Remettra, Inc. Page 17 ERA and EFT through DFI ERA Payer EFT Payer DFI ERA EFT Payee DFI ERA Payee FDN More “Gotchas”: CTX format consists of (1) payment record (the “6” record in ACH format) and up to 9,999 “addenda” records (“7” records), each sequenced and related to the “6” record The ACH format allows 94-characters per line, and the addenda record allows an 80-character payload (plus 14 characters of ACH control information) The maximum “payload” or remittance data capable of being transmitted per payment record is just at 800k The data cannot be compressed, except to make “…one segment immediately follow(s) the preceding segment” ©2003 Remettra, Inc. Page 18 ERA with Payment by Separate EFT EFT Payer Payer DFI EFT Payee DFI FDN Payee ERA Payer sends $ via EFT instructions to the Payer’s DFI Payer sends ERA directly to Payee Payer’s DFI sends $ to Payee’s DFI Payee’s DFI notifies Payee of $ Payee reconciles ERA with $ ©2003 Remettra, Inc. Page 19 ERA with Payment by Separate EFT Payer EFT Payer DFI EFT Payee DFI FDN Payee ERA “Gotchas”: Payer must maintain account/routing numbers and payment preferences for payees Payer must generate CCD+ file for ODFI, or establish BA with ODFI before sending 835; ODFI must generate CCD+ from 835 Payee must set up account/routing number and payment preferences with each payer he transacts with ©2003 Remettra, Inc. Page 20 ERA and Payment Delivered Separately but Processed by a Value-Added Bank (VAB) Funds Payer Payer DFI Funds Payee DFI (VAB) FDN Payee ERA Payer sends $ as appropriate for EFT or check to Payee’s DFI. Payer sends ERA to Payee’s DFI Payee’s DFI reconciles ERA and $ and notifies Payee Reassociation performed by VAB ©2003 Remettra, Inc. Page 21 ERA and Payment Delivered Separately but Processed by a Value-Added Bank (VAB) Funds Payer Payer DFI Funds Payee DFI (VAB) FDN Payee ERA “Gotchas”: This is HHS legalese for “lockbox operations”. Provider’s bank (RDFI) receives payment and remittance, either electronically or via paper, and processes the information for consolidated delivery to provider. Inherently involves reformatting if received as a standard transaction and consolidated to paper, or if received as paper and delivered as 835: RDFI would be a covered entity. ©2003 Remettra, Inc. Page 22 ERA and Payment Delivered Separately but Processed by a Value-Added Bank (VAB) Funds Payer Payer DFI Funds Payee DFI (VAB) FDN Payee ERA More “Gotchas”: Payer separates dollars and data then delivers ERA to RDFI (VAB) Payer must have mechanism to communicate with each RDFI directly. With mailed remittance, this is not a problem, but for ERA either the payer or the payer’s clearinghouse would have to electronically transmit the ERA to the receiving bank. The reassociation trace number (TRN segment) would still have to be transmitted through the ACH from ODFI to RDFI. ©2003 Remettra, Inc. Page 23 ERA with Debit EFT Debit Request 835 Payer Payee EFT/FDN Debit Request Payee DFI Funds Payer DFI Debit Notice Payer sends 835 with ERA and debit authorization to Payee Payee instructs DFI to take funds from the Payer’s DFI Payee’s DFI gets funds from Payer’s DFI and notifies Payee Reassociation is necessary ©2003 Remettra, Inc. Page 24 ERA with Debit EFT Debit Request Payer 835 Payee EFT/FDN Debit Request Payee DFI Funds Payer DFI Debit Notice “Gotchas”: More risk for payer (operating account authorized for debits) More complexity and effort for provider (provider must set up with his RDFI as a debit originator) Payer (or clearinghouse) must still deliver 835 directly to payee ©2003 Remettra, Inc. Page 25 Other DFI Issues NACHA/ABA believe they should be exempt from HIPAA rules due to privacy mandates of Graham/Leach/Bliley, and exemptions outlined in Section 1179. GLB requires bank to restrict outside entities from access to collected data: no restrictions for internal use. HIPAA Privacy requires entities with access to PHI to have measures in place to restrict access internally. Section 1179 refers to exemption for “payment” activities; remittance is not exempted. ©2003 Remettra, Inc. Page 26 Still a Problem? Alternate Strategies ERA Delivered by Payer, Payment Delivered by 3rd-party payment processor ERA Delivered by a Healthcare Clearinghouse, Payment Delivered by 3rd-party payment processor ERA and Payment Delivered Separately but Processed by a Healthcare Clearinghouse ©2003 Remettra, Inc. Page 27 ERA Delivered by Payer, Payment Delivered by 3rd-party payment processor ERA Payer Payment Processor EFT Or ERA Payee FDN EFT Order (CCD+) Payer DFI Funds Payee DFI Funds Payer sends $ via EFT instructions (via CCD+ ERA) to the Payer’s DFI Payer sends ERA directly to Payee Payer’s DFI sends $ to Payee’s DFI Payee’s DFI notifies Payee of $ Payee reconciles ERA with $ ©2003 Remettra, Inc. Page 28 ERA Delivered by Payer, Payment Delivered by 3rd-party payment processor ERA Payer EFT Or ERA Payment Processor Payee FDN EFT Order (CCD+) Payer DFI Funds Payee DFI Funds “Gotchas”: Payer still responsible for ensuring delivery of the ERA to the Payee Depending on the policies of the 3rd-party processor, Payer may need to maintain payee account/routing numbers and payment prefs If Payer maintains prefs, Payee must set up prefs with each payer he does business with (using a payment processor of this type) Due to state banking regulations, Payer must maintain control of funds before release to Payee (or keep equal amount on hand); CH must access Payer account or a new account must be established by Payer for funds access by CH. ©2003 Remettra, Inc. Page 29 ERA Delivered by a Healthcare Clearinghouse, Payment Delivered by 3rd-party payment processor ERA CH ERA Payee Payer FDN EFT Or ERA Payment Processor EFT Order (CCD+) Payer DFI Funds Payee DFI Funds Payer sends $ via EFT instructions (via CCD+ ERA) to the Payer’s DFI Payer sends ERA to Clearinghouse; Clearinghouse delivers ERA to Payee Payer’s DFI sends $ to Payee’s DFI Payee’s DFI notifies Payee of $ Payee reconciles ERA with $ ©2003 Remettra, Inc. Page 30 ERA Delivered by a Healthcare Clearinghouse, Payment Delivered by 3rd-party payment processor ERA ERA CH Payee Payer FDN EFT Or ERA Payment Processor EFT Order (CCD+) Payer DFI Funds Payee DFI Funds “Gotchas”: Payer manages multiple relationships (CH, payment processor) Depending on the policies of the 3rd-party processor, Payer may need to maintain payee account/routing numbers and payment prefs If Payer maintains prefs, Payee must set up prefs with each payer he does business with (using a payment processor of this type) Due to state banking regulations, Payer must maintain control of funds before release to Payee (or keep equal amount on hand); CH must access Payer account or a new account must be established by Payer for funds access by CH. ©2003 Remettra, Inc. Page 31 ERA and Payment Delivered Separately but Processed by a Healthcare Clearinghouse ERA Payer FDN CH ERA EFT Order (CCD+) Funds Payee Payer DFI Funds Payee DFI Funds Payer Sends 835 to CH Payer Sends $ to ODFI CH creates CCD+ from 835 and transmits to ODFI ODFI initiates funds transfer to RDFI via CCD+ instructions CH sends Funds Deposit Notification to Payee Payee retrieves ERA from CH ©2003 Remettra, Inc. Page 32 ERA and Payment Delivered Separately but Processed by a Healthcare Clearinghouse ERA Payer CH Payee ERA Funds FDN EFT Order (CCD+) Payer DFI Funds Payee DFI Funds “Gotchas”: Due to state banking regulations (in most states), Payer must maintain control of funds before releasing to Payee or keep equal amount on hand, so CH must have access to Payer account or a separate account must be established for payer to put funds into for access by CH. Many traditional clearinghouses have indicated they do not want to handle the EFT transaction. ©2003 Remettra, Inc. Page 33 Summary There are many issues, both unresolved and under debate, regarding utilizing the ACH network for ERA delivery. Payers must carefully evaluate both strategy and partners when deciding on a remittance and EFT delivery method. To fully realize HIPAA cost savings in the remittance process, both payment and remittance must be delivered electronically or outsourced to a partner. ©2003 Remettra, Inc. Page 34 Thank You! Remettra, Inc. (reh-‘meh-truh) is a specialized healthcare clearinghouse providing remittance advices (electronic or paper) and payments (electronic or paper) to healthcare providers for claims previously adjudicated. Unlike most clearinghouses that provide an array of services, Remettra has focused on services specifically tailored to meet payers' accounts payable objectives. Remettra fills the role of a one-stop outsourcing solution for converting our clients' paper-based accounts payable processes to fully automated electronic systems. We do this through our core products, MedRemit and MedRing. Brett Hacker, CIO Remettra, Inc. 400 Hardin Rd., Ste. 140 Little Rock, AR 72211 (866) 226-9641 http://www.remettra.com ©2003 Remettra, Inc. Page 35