PresentationADCHEM09
advertisement

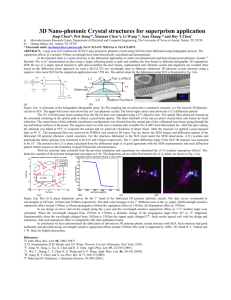
Robust Nonlinear Model Predictive Control using Volterra Models and the Structured Singular Value () Rosendo Díaz-Mendoza and Hector Budman ADCHEM 2009 July 12–15 2009 Background and Motivation Background and Motivation ► Chemical processes are nonlinear ► Nonlinear Model Predictive Control (NMPC) ► First principles or empirical models ► Robustness issues ► Robustness of NMPC ► Simulation studies for different parameter values ► Develop a Robust-NMPC methodology that considers parameter uncertainty Diaz-Mendoza R. and Budman H Robust NMPC using Volterra Models and the SSV Introduction Model Predictive Control Model Predictive Control MPC J min Y wrt U y1sp k yˆ1 k ynspy k yˆ n y k Y y sp k p yˆ k p 1 1 y sp k p yˆ k p ny ny Parameters: ► p, prediction horizon ► m, control horizon ► p≥m ► ny, number of outputs ► nu, number of inputs Diaz-Mendoza R. and Budman H u1 k unu k U u1 k m u k m nu A model is required to calculate ŷ Robust NMPC using Volterra Models and the SSV Introduction Volterra Models Volterra Models Why Volterra Models? ►Represent a wide variety of nonlinear behavior ►Model structure: nominal model + uncertain model M 1 u1 k0 n h x ,1 h x ,nu yˆ x k0 Mn 01 n 0 n n M 1 M 1 h u k0 i u1 k0 j i , j x ,1 1 i 0 j i M 1 M 1 unu k0 n hi , j x ,nu unu k0 i unu k0 j i 0 j i ►M, system memory ►nu, number of inputs ►x є [1,,ny]; ny, number of outputs Schetzen, M., The Volterra and Wiener theories of nonlinear systems; Robert E. Krieger, 1989 Diaz-Mendoza R. and Budman H Robust NMPC using Volterra Models and the SSV Introduction Volterra Models Volterra Models CA Comparison Real Process vs Nominal Model 0.4 CA+CB Real process Nominal Model 0.3 CSTR 0.2 A→B cooling fluid Control Variable cooling fluid 0.1 0 -0.1 -0.2 x2 dx1 x1 Da 1 x1 exp 1 dt 1 x2 dx2 x2 x2 B Da 1 x1 exp 1 dt 1 x2 Diaz-Mendoza R. and Budman H -0.3 -0.4 0 x2 xc 10 20 30 40 50 Sampling Instant ►Truncation error (M = 3) ►High order dynamics Robust NMPC using Volterra Models and the SSV 60 Introduction Volterra Models Volterra Models Identification ►Multilevel ►Nominal pseudo random binary sequence (PRBS) value = mean (parameters) ►Uncertainty = 2 (parameters) Nowak, R. D., and Van Veen, B. D. (1994). Random and pseudorandom inputs for Volterra filter identification, IEEE Transactions on Signal Processing, 42 (8), 2124–2135. Diaz-Mendoza R. and Budman H Robust NMPC using Volterra Models and the SSV Introduction Volterra Models Volterra Models Output equation with parameter uncertainty SISO System M 1 M 1 M 1 n 0 i 0 j i yˆ k0 hn hn u k0 n hi , j hi , j u k0 i u k0 j ►hn, hi,j, nominal value ►hn, hi,j, parameter uncertainty Diaz-Mendoza R. and Budman H Robust NMPC using Volterra Models and the SSV Introduction Volterra Models Volterra Models Comparison Real Process vs Nominal Model Comparison Real Process vs Nominal Model 0.4 0.4 Real process Nominal Model 0.3 0.3 Model + 2 Model - 2 0.2 Control Variable Control Variable 0.2 0.1 0 -0.1 0.1 0 -0.1 -0.2 -0.2 -0.3 -0.3 -0.4 Real process Nominal Model 0 10 20 30 Sampling Instant Diaz-Mendoza R. and Budman H 40 50 60 -0.4 0 10 20 30 40 Sampling Instant Robust NMPC using Volterra Models and the SSV 50 60 Introduction Nonlinear Model Predictive Control Nonlinear Model Predictive Control J min Y wrt U Worst Case Interpretation 6 wc(3) 4 SISO System wc(2) wc(1) y k yˆ k Y y sp k p yˆ k p sp Manipulated Variable 2 0 wc(5) -2 -4 wc(4) -6 0 1 2 3 4 Sampling Instant How to consider parameter uncertainty? Diaz-Mendoza R. and Budman H Robust NMPC using Volterra Models and the SSV 5 6 Introduction Nonlinear Model Predictive Control Nonlinear Model Predictive Control Worst Case Interpretation for the whole prediction horizon 6 wc( Y ) Manipulated Variable 5 y1sp k yˆ1 k max wrt hn ,hi , j ynspy k yˆ n y k 4 3 2 max Y wrt hn ,hi , j 1 0 0 1 2 3 4 5 6 Sampling Instant Diaz-Mendoza R. and Budman H Robust NMPC using Volterra Models and the SSV Introduction Nonlinear Model Predictive Control Nonlinear Model Predictive Control Structured Singular Value () Calculation of the worst ŷ(k) to ŷ(k+p) when parameter uncertainty is taken in consideration, i. e., for ŷ(k) Worst Case Interpretation 6 wc(3) 5 wc(4) Manipulated Variable 4 wc(2) 3 wc(1) 2 wc(5) 1 0 0 1 2 3 Sampling Instant 4 5 6 M 1 h h u k n n n n 0 M 1 M 1 max hi , j hi , j u k i u k j wrt hn ,hi , j i 0 j i wk d k Doyle, J., (1982). Analysis of feedback systems with structured uncertainties, IEE Proceedings D Control Theory & Applications, 129 (6), 242–250 Diaz-Mendoza R. and Budman H Robust NMPC using Volterra Models and the SSV Introduction Nonlinear Model Predictive Control Nonlinear Model Predictive Control Structured Singular Value (SSV) SSV Theorem max y1sp k yˆ1 k max Y max wrt hn ,hi , j wrt hn ,hi , j sp yn y k yˆ n y k wrt hn ,hi , j Y kssv M kssv Skew problem (convex) max wrt hn ,hi , j Y max wrt k ssv k ssv st M k ssv Braatz, R. D., Young, P. M., Doyle, J. C., and Morari, M. (1994). Computational complexity of calculation, IEEE Transactions on Automatic Control, 39 (5), 1000–10002. Diaz-Mendoza R. and Budman H Robust NMPC using Volterra Models and the SSV Introduction Nonlinear Model Predictive Control Nonlinear Model Predictive Control max wrt k ssv st M k ssv k ssv M M, interconnection matrix Δ, uncertainty block structure M11 M12 M M 21 M 22 M12 f k ssv , U M 21 f k ssv , Y Diaz-Mendoza R. and Budman H Robust NMPC using Volterra Models and the SSV Introduction Nonlinear Model Predictive Control Interconnection Matrix Example k ssv 0 k ssv 0 k ssvu 1 0 2 k ssvu 1 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 k ssv 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 c1 0 ic 1 0 h1 0 c2 0 ic 2 0 Feedback 0 0 k ssv 0 0 0 k ssv 0 0 0 h2 0 0 0 k ssv 0 0 0 0 0 h1,1 0 0 0 0 0 0 k ssv 0 k ssv 0 0 h2, 2 0 k ssv 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 h1 Nominal Diaz-Mendoza R. and Budman H 0 0 0 0 k ssv 0 0 0 0 0 h1,1 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 k ssv 0 h1, 2 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 h1 0 0 h1 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 h1,1 0 hy1 h1 0 h1,1 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 hy1 h1,1 h2 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 h2, 2 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 h1, 2 Uncertain Robust NMPC using Volterra Models and the SSV 0 k ssv 0 k ssv 0 k ssvu 1 0 2 k ssvu 1 k ssvu 2 2 k ssvu 2 k ssvu 1u 2 0 Introduction Nonlinear Model Predictive Control Nonlinear Model Predictive Control NMPC Cost Function max wrt hn ,hi , j Y u ulimits tc max wrt k ssv st M k ssv Diaz-Mendoza R. and Budman H k ssv M11 M12 M M M 22 21 M12 f k ssv , U M 21 f k ssv , Y, u, ulimits , tc Robust NMPC using Volterra Models and the SSV Introduction Nonlinear Model Predictive Control Nonlinear Model Predictive Control Additional terms Manipulated variables movement penalization W u k u k 1 u Wmu u k m u k m 1 u 1 u max W1 u k u k 1 k ssv max W u u k m u k m 1 k m ssv Diaz-Mendoza R. and Budman H Robust NMPC using Volterra Models and the SSV Introduction Nonlinear Model Predictive Control Nonlinear Model Predictive Control Additional terms Manipulated variables constraints ulimits u k k ssv u k bound u k m k ssv ubound k m u k k ssv max k ssv max u k ubound k ubound k u k m k ssv max u k m ubound k m max k ssv ubound k m Diaz-Mendoza R. and Budman H Robust NMPC using Volterra Models and the SSV Introduction Nonlinear Model Predictive Control Nonlinear Model Predictive Control Additional terms Terminal Condition Terminal Condition Representation 1.4 1.2 1 Control Variable 0.8 0.6 0.4 0.2 0 -0.2 -0.4 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 Sampling Instant max M M M sp y k hi hi u k m hi , j hi , j u 2 k m wk d k i 1 i 1 j i Diaz-Mendoza R. and Budman H Robust NMPC using Volterra Models and the SSV Introduction Nonlinear Model Predictive Control Nonlinear Model Predictive Control NMPC Cost Function max wrt hn ,hi , j Y u ulimits tc max wrt k ssv st M k ssv k ssv M11 M12 M M M 22 21 M12 f k ssv , U M 21 f k ssv , Y, u, ulimits , tc NMPC Algorithm at each sampling instant min max wrt U wrt hn ,hi , j Diaz-Mendoza R. and Budman H u max k ssv min wrt U ulimits wrt k ssv st M k ssv tc Y Robust NMPC using Volterra Models and the SSV Case Studies SISO Case Study SISO System CSTR with first order exothermic reaction Control Specifications CA CA+CB cooling fluid CSTR A→B ► ► cooling fluid ► x2 dx1 x1 Da 1 x1 exp 1 dt 1 x2 dx2 x2 x2 B Da 1 x1 exp 1 dt 1 x2 x2 xc CV: x1 (dimensionless reactant concentration) MV: xc (cooling jacket dimensionless temperature) β: process disturbance Parameter Calculation ► Multilevel PRBS ► Parameter uncertainty Doyle III, F. J., Packard, A., and Morari, M. (1989). Robust controller design of a nonlinear CSTR, Chemical Engineering Science, 44 (9), 1929–1947. Diaz-Mendoza R. and Budman H Robust NMPC using Volterra Models and the SSV Case Studies SISO Disturbance Characteristics Disturbance Value dimensionless cooling rate 0.32 0.3 0.28 0.26 0.24 0.22 0.2 0 5 10 15 20 25 Sampling Instant Diaz-Mendoza R. and Budman H Robust NMPC using Volterra Models and the SSV Case Studies SISO Control Variable p=10 , m=2 0.05 0 Control Variable -0.05 -0.1 -0.15 -0.2 Wi u = 2.5 -0.25 Wi u = 1.5 Wi u = 2.0 Wi u = 1.0 -0.3 0 5 10 15 20 Manipulated Variable p=10 , m=2 25 0.7 Sampling Instant Manipulated Variable 0.6 0.5 0.4 0.3 0.2 Wi u = 2.5 0.1 Wi u = 1.5 Wi u = 2.0 Wi u = 1.0 0 0 5 10 15 Sampling Instant Diaz-Mendoza R. and Budman H Robust NMPC using Volterra Models and the SSV 20 25 Case Studies SISO Controlled Variable Case with constraints, p=10 , m=2 , W u = 0.5 i 0.05 Controlled Variable 0 -0.05 -0.1 -0.15 -0.2 -0.25 Manipulated Variable Case with constraints, p=10 , m=2 , W u = 0.5 0 5 10 15 20 25 30 35 40 45 i 50 0.25 Sampling Instant Constraint set at 0.2 Manipulated Variable 0.2 0.15 0.1 0.05 0 0 5 10 15 20 25 30 35 Sampling Instant Diaz-Mendoza R. and Budman H Robust NMPC using Volterra Models and the SSV 40 45 50 Case Studies SISO Control Variable p=10 , m=2 , Wu = 2.5 i 0.05 0 Control Variable -0.05 Sum absolute error Robust = 1.46 Sum absolute error Non-Robust = 1.55 6% improvement -0.1 -0.15 -0.2 -0.25 -0.3 Robust Controller Non-Robust Controller 0 5 10 15 20 Manipulated Variable p=10 , m=2 , Wu = 2.5 i 25 0.7 Sampling Instant Manipulated Variable 0.6 0.5 0.4 0.3 0.2 0.1 0 Robust Controller Non-Robust Controller 0 5 10 15 Sampling Instant Diaz-Mendoza R. and Budman H Robust NMPC using Volterra Models and the SSV 20 25 Case Studies WiΔu SISO 1.5 Robust Controller is better than Non-Robust 37% 1 41% 0.75 50% 0.50 66% 25 different disturbances for each weight Diaz-Mendoza R. and Budman H Robust NMPC using Volterra Models and the SSV Case Studies MIMO Case Study MIMO System D Sf ► X S P Fermenter ► ► ► ► X, biomass concentration S, substrate concentration P, product concentration D, dilution rate Sf, feed substrate concentration dX dX k X dt dS 1 D S f S k X dt YX / S Control Specifications ► CV: X and P ► MV: D and Sf ► YX/S: process disturbance dP DP k X dt m 1 P / Pm S k K m S S 2 / Ki Parameter calculation ► Multilevel PRBS ► Parameter uncertainty Saha, P., Hu, Q., and Rangaiah, G., P. (1999). Multi-input multi-output control of a continuous fermenter using nonlinear model based controllers, Bioprocess Engineering, 21, 533–542. Diaz-Mendoza R. and Budman H Robust NMPC using Volterra Models and the SSV Case Studies MIMO Manipulated Variable (Dilution Rate) u u p=10 , m=2 , W = 0.2 , W = 0.5 1 2 0.14 0.12 0.1 Manipulated Variable 0.08 Control Variables p=10 , m=2 , Wu = 0.2 , Wu = 0.5 1 2 0.06 Control Variables 0.04 0.06 0.04 0.02 0 0.02 -0.02 0 -0.04 -0.06 -0.02 0 5 10 15 20 25 20 25 Sampling Instant -0.04 Subustrate Feed Concentration u u p=10 , m=2 , W = 0.2 , W = 0.5 1 -0.06 2 0.4 -0.08 0.35 -0.1 -0.12 -0.14 0 5 10 15 Sampling Instant 20 25 Manipulated Variable 0.3 Biomass Product 0.25 0.2 0.15 0.1 0.05 0 0 5 10 15 Sampling Instant Diaz-Mendoza R. and Budman H Robust NMPC using Volterra Models and the SSV Preliminary Conclusions Preliminary Conclusions Conclusions ► A Robust-NMPC algorithm was developed ► The algorithm considers all the features of previous NMPC formulations ► In average the robust controller results in better performance as the input weight is decreased Diaz-Mendoza R. and Budman H Robust NMPC using Volterra Models and the SSV Preliminary Conclusions Challenges Current challenges ► Computational demand ► Multivariable control Diaz-Mendoza R. and Budman H Robust NMPC using Volterra Models and the SSV