Taking Good Notes - Teaching & Learning Centre
advertisement

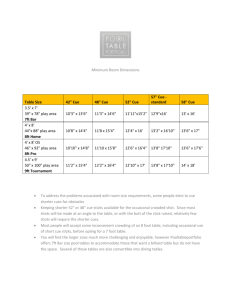
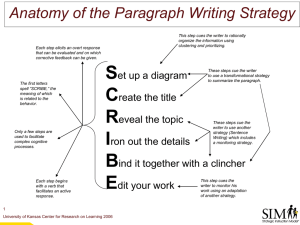
Taking Good Notes through the iStudyGuides Reading Skimming involves going over a text quickly to get the general idea of its contents and to gain a superficial understanding of its message. Scanning involves going quickly through a text to try to find particular information or to decide whether it is useful for the reader's purpose. Study Skills Scrutinising involves reading for detailed understanding of the writer's message. Study Skills THREE-STEP PROCESS 1) Understanding the content 2) Making summary notes 3) Internalising content Understanding the content Primary idea of the paragraph - It can be a proposed theory, argument, hypothesis, practice, concept, formula, proposition etc. It is typically written in the paragraph's introduction (first few sentences) or summary (last few sentences). Understanding the content Possible Secondary idea/s (Reason/s) - It is generally a development of the primary idea. It can possibly be written in the main body of paragraph or each of the latter paragraphs of the chapter/article. Understanding the content Possible Support information (Evidence) - It is emphasised to support each primary or secondary idea. It can be a research study, example, comparison, analogy, anecdote, set of statistical data etc Understanding the content Relate the primary idea, secondary ideas and support information. Understanding the content Determine if these relationships belong to: •Cause and effect •Categorization •Comparison and Contrast •Definitions •Problem and Solutions •Process or procedures •Sequence of events Understanding the content Routine activities theory was first coined by Lawrence Cohen and Marcus Felson. This theory states that a certain group of people is willing to commit crimes for revenge, greed, or some other self serving reasons. Such predatory crimes may usually involve an offender trying to steal an item directly and are usually influenced by some dynamic factors. Understanding the content The presence of suitable targets, such as places where items that are easily sold are kept or displayed, can be a good precursor for some people to commit such predatory crimes. And the absence of competent guardians, such as police, homeowners, neighbours and frequent passer-bys, can lead to predatory crimes too. At the same time, there must be the presence of potential predatory criminals, such as a large number of unemployed or restless youths. Understanding the content Cohen and Felson (1980) also found that predatory crime rates increased between 1960 and 1980 due to the reduction of homemakers as more females joined the workforce. They also discovered that burglary rates decreased as the cost of goods such as phones and cameras decreased. (Siegel, 2011, Criminology:The core, Pg 71) Understanding the content Cause and effect Understanding the content Categorization Understanding the content Comparison and Contrast Understanding the content Definitions Understanding the content Problem and Solutions Understanding the content Process or procedures Understanding the content Sequence of events Making summary notes 1)Paraphrasing 2)Using Cue Words 3)Setting Recall Questions 4)Setting Clarification / Probing Questions 5)Reflection Making summary notes: Paraphrasing • Do not copy word for word from the readings. • Paraphrase. • Paraphrasing is an important process in note- taking as it allows you to evaluate and internalise your understanding more effectively. Making summary notes: Paraphrasing •Include content that is relevant to the learning outcomes of the chapter. •Use a different word with the same meaning as the original one. •Use a different sentence structure. •Highlight the unique word or phrase you have borrowed from the paragraph while recording its source. •Check the meaning of your summary against the content to ensure that it is accurate. •Refer to SD103 Academic Integrity for paraphrasing exercises. Making summary notes: Using Cue Words • Reduce the ideas or facts to Cue Words for effective memorisation. Making summary notes: Using Cue Words Mnemonic Strategies Acronyms / Catchwords • Acrostics / Catchphrases • Imagery (Concept maps; method of loci) • Forming associations • Making summary notes: Using Cue Words • Acronyms / Catchwords For example, Routine Activities Theory = RAT Making summary notes: Using Cue Words • Imagery (Concept maps; Method of Loci) For example, the three conditions of Routine Activities Theory are represented in a concept map below. Making summary notes: Using Cue Words • Imagery (Concept maps; Method of Loci) The Method of Loci involves placing a piece of information along an imaginary but familiar journey to the learner. Making summary notes: Using Cue Words For example, to remember the conditions of RAT (Routine Activities Theory), one can imagine a short journey from his home to the bus stop: 1) opens home door and steps out (represents availability of suitable targets) —> 2) walks by an unmanned neighbourhood police centre (represents the absence of capable guardians) —> 3) reaches the bus-stop (represents the presence of predatory criminals). Making summary notes: Using Cue Words • Catchphrases For example, to remember that “Criminal,” “Target,” and “Guardian” are the three conditions of RAT, the catchphrase, “Clive (Criminal) talks (Target) to Gina (Guardian)” could be used. Making summary notes: Using Cue Words • Forming associations For example, to remember the three conditions of RAT, one may associate 1) the availability of suitable target with a man wearing a thick gold chain, 2) the presence of predatory criminals with a snatch thief lurking around, and 3) associate the presence of capable guardians with a policeman patrolling nearby. Making summary notes: Setting Recall Questions • Questions can be created by you to set trigger to recall the summary notes made. • These recall question can serve as practice test that help you to test your knowledge and more importantly internalise it. • Alternatively, attempt any questions set at the end of the chapter or complete the online formative quizzes. Making summary notes: Setting Clarification/Probing Questions Clarification questions are usually simple questions that aim to understand a certain concept, theory or paragraph in the content. Probing questions are questions that make you think more deeply about certain concept, theory or paragraph in the content. Making summary notes: Reflection Reflection is important in understanding the content in depth. 1) Reflect on the content through asking probing questions about the ideas and evidences. These questions can be: Making summary notes: Reflection What do you think are the purposes of the author in promoting this primary idea in the chapter? What are your thoughts about this? Do the secondary ideas sound sensible, logical and unprejudiced from your prior experiences and knowledge? If no, list down why you think so? Making summary notes: Reflection Are there any relationships between the secondary ideas? If yes, what are they? Are the evidences supporting each secondary idea valid, reliable, current, authoritative and objective? Are there any other contradictory evidences? Making summary notes: Reflection 2) Reflect on your practice in relation to the content. The ability to relate knowledge learnt in school to work is important. Making summary notes: Reflection It allows you to create meaning in the knowledge you have learnt to your work. It also enables you to use the acquired knowledge to solve real problems at your workplace. Making summary notes: Reflection As such, the knowledge you acquired while studying in UniSIM adds value to your work. Being able to reflect on the course content can significantly help you in the knowledge internalisation process. Internalising Content Forgetting what you remembered • • • • • Lack of understanding Cramming Insufficient cues Interference Test anxiety Internalising Content Memory Strategies Spaced practice • Repetition • Breaking into smaller tasks • Overlearning • THE END