Fruits Power Point
advertisement

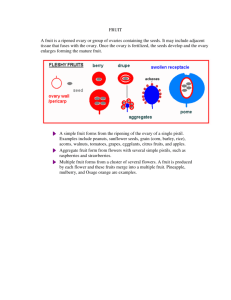
Fruits Foods I: Fundamentals Definition Fruit: The ripened ovary, seeds and surrounding tissue of a flowering plant Fruit Classifications Simple Fruits: develop from one flower (=one fruit) DRUPES – fruits with a hard pit POMES – fruits with seeds and a central core Ex. Grapefruit, oranges, lemons Aggregate Fruits: develop from several fruits in one flower Ex. Apples, pears CITRUS Ex. Peaches, plums, apricots Ex. Raspberries, Strawberries, Blueberries Multiple Fruits: develop from a cluster of several flowers Ex. Pineapples. figs Nutrients in Fruit Fruits are composed of: Water Carbohydrates Main source of calories in fruit Starts out in form of starch but as it ripens, it is converted to sugar Fiber – found in skinnn! Vitamins 70-95% Ascorbic acid, Vitamin A, B vitamins Minerals Potassium, calcium, phosphorous, magnesium, iron, zinc, selenium Nutrients in Fruits Skin = Nutrients Try to peel as thinly as possible to retain nutrients or leave skin on altogether Skin also contains tons of fiber Colors in Fruits Fruits get their color from chemicals in them Carotenoids Yellow-Orange Includes beta-carotene from vitamin A (which is good for EYESIGHT) Anthocyanins Red-Blue Forms of Fruit Fresh Fruit Selection: Fruit should feel heavy for its size If purchased during off season, it is MORE expensive. Besides for bananas, apples and pears, GREEN fruits should be avoided because they do not ripen well. Mature fruit has reached its full size and color Preparation: Once cut, should be served ASAP. Storage: This can be indicated by a slight tenderness when pressed Will also have a pleasant aroma Can be stored in refrigerator for up to a week. Refrigeration slows ripening. Benefits: MOST nutritious form of fruit. The least processing the better! Forms of Fruit Frozen Fruit Serving: Should be served slightly frozen Benefits: Lasts longer than fresh fruit Is considered a “convenience food” Forms of Fruit Canned Benefits: Is considered a “convenience food” Usually least expensive form of fruit Forms: Heavy syrup – most sugar Medium syrup – medium amt. of sugar Light syrup – lighter amt. of sugar Juice – least amount of sugar Forms of Fruit Dried Benefits: Is considered a “convenience food” Perfect for snacks because it is an excellent source of concentrated nutrients Fruit Preparation Enzymatic Browning The discoloration that comes when fruits interact too long with the oxygen in the air. Ex. Bananas & Apples that turn brown when they are cut and sit out too long Prevention Add an acid like orange or lemon juice Fruit Preparation Remember to ALWAYS wash fresh fruit in cool water before consumption and/or preparation This removes dirt & pesticides Cooking Mediums: Use water when sauce is expected as the end product Cinnamon sticks can be added to enhance flavor Use sugar to help fruits retain their shape Fruit Preparation Cooking Methods: Poaching Baking Firm fruits bake best Boiling Method of turning fruit in hot liquid so that it retains its shape Should be done until fruit is tender Fruit Sauces: during preparation, the texture of fruits is broken down Microwaving Fruit should be microwaved with little liquid Piercing fruit before microwaving prevents bursting