Pre-A Chapter 3
advertisement

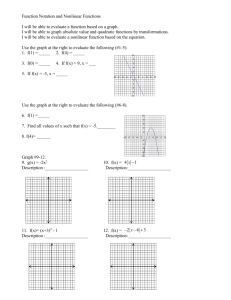
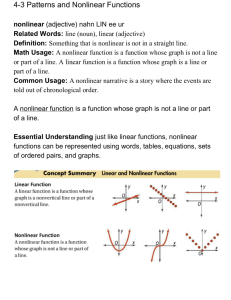
Pre-A Chapter 3 You are allowed 2 note-cards (front and back) for your Ch 3 Test. Items to review: 1. Your notes (math notebook, handouts) 2. Your homework 3. Concepts to Review section of these notes 4. Study guide portion of these notes 5. Vocab Review Concepts to review: 3-1: Relating Graphs to events. You should be able to interpret and sketch graphs that represent real-world situations. Example: the graph of the temperature during a 24-hr period. Vocab to understand: linear vs nonlinear 3-2: Functions. You should be able to evaluate functions and complete inputoutput tables. Example 1: use the function rule Z = 2X + 3. Find the output when the input X = 10. Example 2: Complete an input-output table for the function F = 3 + N. Vocab to understand: Function, Function rule A function is a rule that assigns to each input value exactly one output value. A function rule is an equation that describes a function. 3-3: Proportional Relationships. You should be able to determine if a relationship is proportional or not. Example : 2 for $1, 5 for $2, 8 for $3, and 12 for $4. Vocab to understand: proportional relationship 3-4:Linear Functions: You should be able to recognize linear functions and use tables and equations to graph them. You should understand the difference between discrete and continuous data. The function C = 15T represents the cost (in dollars) of T adult tickets to a museum. Make a table and graph the function. Is the function discrete or continuous? Vocab to understand: Linear functions, discrete data, continuous data 3-5: Nonlinear Functions. You should be able to identify nonlinear functions. If a function's greatest exponent is 2 or greater, or if it has a variable for an exponent, the function is nonlinear. If the ratios between the changes in variables in a table is not the same, the function is nonlinear. Vocab to understand: Nonlinear functions, quadratic functions, parabola Study Guide/Practice Use the graph for #1-#4 1. When during the hike is Rick’s altitude increasing? 2. When during the hike is Rick’s altitude decreasing? 3. When during the hike does Rick’s altitude appear linear? 4. When during the hike does Rick’s altitude appear nonlinear? 5. An athlete jogs for 30 min, sprints for 5 min, and walks for 10 min. Sketch a label a graph showing his speed. Use the function rule D = 3t – 1. Find each output. 6. T=2 7. T=8 8. T = -4 9. T = -5 10. A photocopy costs $0.08. Use the function rule c = 0.08n. Make a table of input/output pairs to show the cost for 5, 10, and 15 copies. Input N Output C 11. Suppose peaches cost $.99 per pound. The function c – 0.99p gives the cost c in dollars of p pounds of peaches. Find the output for the input p = 12. 12. Write a function rule for the following situation: Sam wants to sign up for a new phone plan. The cell phone company charges $45 a month and charges a $30 one-time set-up fee. Use T for the total cost of the plan for M months. Determine if the graph represents a function with a proportional relationship. Explain why or why not. 13. 14. Why? _________________________________ ________________________________________ Why? _______________________________ _______________________________ 15. Determine if the relationship is proportional. Explain why or why not? Korin’s Bike Trip Time t (min) 15 Distance d (mi) 4 30 8 45 12 60 16 Why or why not? ________________________________________________________________________ Determine for #16-#21 if the function represented by the table or graph is linear or nonlinear. 16. Why or why not? X 1 2 3 4 Y 1 8 27 64 17. X Y 9 1 7 10 18. 5 19 3 28 Why or why not? 19. Why or why not? 20. Y = 8 (x +1) Why or why not? 21. Y = 4x3 - 7 Determine whether the data for each function are discrete or continuous. Then make a table and graph for the function. 22. The function d = 40 -15x represents the amount of money d (in dollars) you have left after buying x CDs Input x (cds) Output d (money)