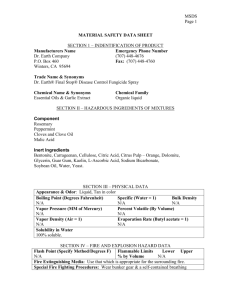
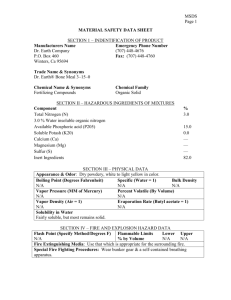
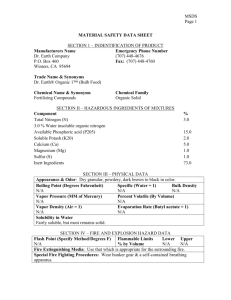
downloading
advertisement

A Trucker’s Guide to Washington Speak Translating Acronyms and Inside-the-Beltway Jargon for the Real World WWETT 2015 Indianapolis, Indiana February 23, 2015 John Conley ConleyComm LLC Chester MD Acronymonia FHWA DOE SAFER STP PHMSA USDOT# CPB CSA OOS CVSA RCRA TRB CDL MAP21 ANPRM PSP DQ DOT406 MC306 EOBR ASME MCSAP CT HME STEP ELD CFATS FMVSS SP ACC AAR NTSB NHTSA FAST CFR TWIC ERG MAWP Acronym Capitol/Capital of the World? D. C. of Course!!! Why learn to speak Gobbledgook? Gobbledegook -- “Pretentious and scarcely intelligible language, especially of the sort attributed to bureaucrats, sociologists, etc.” (Coined in 1944 by Texas Representative Maury Maverick.) Bureaucratese is the language of government and more specifically of regulations and regulators. It does, once understood, bring some consistency of meaning. Here are some reasons to have at least a struggling tourist familiarity with this strange language: 1. Regulatory Compliance -- Trucking company management wants to comply with the regulations coming at them from all levels of government. “They” know what they mean “ and so should you. 2. Enforcement Agency Actions – Who are they? What are they claiming we did wrong? What are my options? 3. Influencing Government – The regulated community does have the opportunity to comment on the development of regulations, enforcement and penalties. To do so, you must know the language and process. 4. Impress your spouse, teenagers, employees, and friends at cocktail parties. Let’s start at “THE DOT” Mission: The mission of the Department is to: Serve the United States by ensuring a fast, safe, efficient, accessible and convenient transportation system that meets our vital national interests and enhances the quality of life of the American people, today and into the future. Statutory Authority The Department of Transportation was established by an act of Congress on October 15, 1966. The Department’s first official day of operation was April 1, 1967. Pre-emption -- When legislation or regulations passed by states or local jurisdictions are in conflict with regulations of the U.S. Department of Transportation, the US DOT can pre-empt those rules. This is especially important to ensuring a consistent regulatory environment for HM transportation across the country. Office of the Secretary Current Secretary: Anthony Foxx Leadership of the DOT is provided by the Secretary of Transportation, who is the principal adviser to the President in all matters relating to federal transportation programs. The Secretary is assisted by the Deputy Secretary in this role. The Office of the Secretary (OST) oversees the formulation of national transportation policy and promotes intermodal transportation. Other responsibilities range from negotiation and implementation of international transportation agreements, assuring the fitness of US airlines, enforcing airline consumer protection regulations, issuance of regulations to prevent alcohol and illegal drug misuse in transportation systems and preparing transportation legislation. Federal Motor Carrier Safety Administration Acting Administrator: Scott Darling The Federal Motor Carrier Safety Administration was established within the Department of Transportation on January 1, 2000, pursuant to the Motor Carrier Safety Improvement Act of 1999 [Public Law No. 106-159, 113 Stat. 1748 (December 9, 1999)]. Formerly a part of the Federal Highway Administration, the Federal Motor Carrier Safety Administration's primary mission is to prevent commercial motor vehicle-related fatalities and injuries. It was once known as the Bureau of Motor Carrier Safety. Administration activities contribute to: •Ensuring safety in motor carrier operations through strong enforcement of safety regulations, targeting high-risk carriers and commercial motor vehicle drivers. •Improving safety information systems and commercial motor vehicle technologies; strengthening commercial motor vehicle equipment and operating standards •Increasing safety awareness. To accomplish these activities, the Administration works with Federal, state, and local enforcement agencies, the motor carrier industry, labor safety interest groups, and others. www.fmcsa.dot.gov Pipeline and Hazardous Materials Safety Administration Acting Administrator: Tim Butters The Pipeline and Hazardous Materials Safety Administration (PHMSA) oversees the safety of more than 800,000 daily shipments of hazardous materials in the United States and 64 percent of the nation's energy that is transported by pipelines. PHMSA is dedicated solely to safety by working toward the elimination of transportation-related deaths and injuries in hazardous materials and pipeline transportation, and by promoting transportation solutions that enhance communities and protect the natural environment. PHMSA writes the regulations that govern hazardous materials transportation by highway. It shares enforcement of those regulations with FMCSA. www.phmsa.dot.gov http://www.phmsa.dot.gov/resources/glossary Research & Innovative Technology Administration Administrator Greg Winfrey The Research & Innovative Technology Administration (RITA) is an agency whose mission is to identify and facilitate solutions to the challenges and opportunities facing America's transportation system. RITA's focus is to promote transportation research that will foster the use of innovative technology. RITA includes the Volpe National Transportation Systems Center, an organization dedicated to enhancing the effectiveness, efficiency, and responsiveness of other Federal organizations with critical transportation-related functions and missions. With responsibility for research policy and technology sharing, the agency partners with national and international organizations and universities. RITA also includes the Bureau of Transportation Statistics, the Transportation Safety Institute and the University Transportation Centers program. www.rita.dot.gov Federal Highway Administration Acting Administrator: Gregory Nadeau The Federal Highway Administration (FHWA) coordinates highway transportation programs in cooperation with states and other partners to enhance the country's safety, economic vitality, quality of life, and the environment. Major program areas include the Federal-Aid Highway Program, which provides federal financial assistance to the States to construct and improve the National Highway System, urban and rural roads, and bridges. This program provides funds for general improvements and development of safe highways and roads. The Federal Lands Highway Program provides access to and within national forests, national parks, Indian reservations and other public lands by preparing plans and contracts, supervising construction facilities, and conducting bridge inspections and surveys. The FHWA also manages a comprehensive research, development, and technology program. www.fhwa.dot.gov National Highway Traffic Safety Administration Acting Administrator: David Friedman The National Highway Traffic Safety Administration (NHTSA) is responsible for reducing deaths, injuries and economic losses resulting from motor vehicle crashes. NHTSA sets and enforces safety performance standards for motor vehicles and equipment, and through grants to state and local governments enables them to conduct effective local highway safety programs. NHTSA investigates safety defects in motor vehicles, sets and enforces fuel economy standards, helps states and local communities reduce the threat of drunk drivers, promotes the use of safety belts, child safety seats and air bags, investigates odometer fraud, establishes and enforces vehicle anti-theft regulations and provides consumer information on motor vehicle safety topics. Research on driver behavior and traffic safety is conducted by NHTSA to develop the most efficient and effective means of bringing about safety improvements. A toll-free Auto Safety Hotline, 1-888-DASH-2-DOT, furnishes consumers with a wide range of auto safety information. Surface Transportation Board Acting Board Chairman: Deb Miller The Surface Transportation Board (STB) is an independent, bipartisan, adjudicatory body organizationally housed within the DOT. It is responsible for the economic regulation of interstate surface transportation, primarily railroads, within the United States. The STB's mission is to ensure that competitive, efficient, and safe transportation services are provided to meet the needs of shippers, receivers, and consumers. The Board is charged with promoting, where appropriate, substantive and procedural regulatory reform in the economic regulation of surface transportation, and with providing an efficient and effective forum for the resolution of disputes. The STB performs in rail some of the regulatory functions once conducted by the Interstate Commerce Commission. The Rulemaking Process www.dot.gov/regulations/rulemaking-process What is rulemaking? Rulemaking is a process for developing and issuing rules (rules are also referred to as “regulations”). The process can lead to the issuance of a new rule, an amendment to an existing rule, or the repeal of an existing rule. The “public” has access to the rulemaking throughout the process. This access can as an individual but is more often done through an industry trade association like The American Trucking Associations or National Tank Truck Carriers. All Rulemaking steps are published in the Federal Register. The Federal Register Each step requires publication in the Federal Register, the Bible of Bureaucracy www.gpo.gov/fdsys/browse/collection.action?collectionCode=FR About Federal Register Published by the Office of the Federal Register, National Archives and Records Administration (NARA), the Federal Register is the official daily publication for rules, proposed rules, and notices of Federal agencies and organizations, as well as executive orders and other presidential documents. It is updated daily by 6 a.m. and is published Monday through Friday, except Federal holidays. FDsys contains Federal Register volumes from 59 (1994) to the present. Documents are available in Summary, PDF, ASCII text, or HTML format. HTML documents are available from 2000 forward and provide hypertext links to Web sites mentioned in the FR document. The active HTTP-link feature will be added to previous Federal Register databases in the near future. The HTML documents can be saved as text files with no loss or change in data. Not part of your daily reading or waiting for the movie? Trade publications like those published by Cole, trade associations, and commercial service companies like Labelmaster and JJ Keller, as well as industry consultants, can help keep you informed. How does an agency identify the need for a rulemaking? There are many reasons why an agency may decide to initiate the rulemaking process. The major reasons for DOT agencies fit mostly in the following categories: •Statutory mandate. Congress may specifically require a rule or at least the initiation of the rulemaking process – sometimes with a deadline. •Agency identification of a problem. It may identify a problem as a result of inspectors’ reports or general agency oversight. It may have difficulties enforcing existing rules, and this may provide evidence of a need to modify the rules. Requests for interpretations or exemptions may demonstrate that a rule needs to be clarified or modified. Changes in technology may justify a change to a rule. •Petition for rulemaking. The public has the right to petition an agency to issue, modify, or rescind a rule, and we may agree on the need for action. •NTSB, GAO, IG, or similar recommendations. Recommendations for rules may come from the National Transportation Safety Board (NTSB), the Government Accountability Office (GAO), the DOT Inspector General (IG), or special commissions or other bodies asked by Congress or the President to develop recommendations on particular issues. The Rulemaking Process • ANPRM – Advanced Notice of Proposed Rulemaking. This step is sometimes used to gather information and to ask questions such as if a rule is needed and what it should include. • NPRM– Notice of Proposed Rulemaking. This step is where the agency tells the public is it writing a rule and what it proposes that rule to include. Comments from the affected industry or public are especially important at this stage. • Final Rule – This is where the agency announces the new rule it has developed. It will provide details on how the final decisions were made and when the rule will be effective. • Interested parties can petition for reconsideration Selected terms and words with special meaning in the Bureaucratic world Request for Interpretation – Process through which public can ask DOT what it means by a certain rule. Interpretations can help in compliance but do not have force of law. Pre-emption -- Federal agency can over-rule a local or state agency that enacts a regulation that conflicts with a Federal rule or where the local agency does not have authority. Bulk package – A container that can hold 119 or more U.S. gallons. CVSA OOS -- The Commercial Vehicle Safety Alliance develops Out of Service Criteria which will prevent a vehicle from being moved until the violations are corrected. They have the force of regulations. EOBR v ELD - Electronic On-Board Recording device and Electronic logging device are not the same thing. Words Continued Negotiated rulemaking – Process where government and industry meet to develop the approach and language to be used in a rulemaking. Similar to the process used in Canada.. CSA – Compliance, Safety, Accountability – Process used by FMCSA to measure carrier safety and to determine what carriers need special enforcement attention. Carriers should check their scores on a regular basis as the information is available to the general public. csa.fmcsa.dot.gov/ and www.whatiscsa.com/glossary/ CSA BASIC-- BASICs (Behavioral Analysis and Safety Improvement Categories) are the seven categories the Federal Motor Carrier Safety Administration (FMCSA) uses as part of the Safety Measurement System (SMS) to measure safety performance and create monthly CSA scores. CRASH BASIC – The most controversial element of CSA since FMCSA does not differentiate between preventable and non-preventable crashes in information available to the public. CDL Tank Endorsement – Required of any driver of a vehicle transporting liquids in a tanker OR in bulk containers that have aggregate 1,000 gallons or more. (If a vehicle has nine bulk containers or more, the driver needs a tank endorsement.) More words PPP – Public Private Partnership. An approach to building infrastructure such as roads by private parties who then charge for use of the road. (Indiana Turnpike) CR- Continuing Resolution is the way Congress continues to fund programs at the current funding level until a new Budget is enacted. USDOT# -- Companies that operate commercial vehicles hauling cargo in interstate commerce must be registered with the FMCSA and must have a USDOT Number. Intrastate carriers in most states also require a USDOT number which FMCSA uses to monitor safety performance. http://www.fmcsa.dot.gov/registration/do-i-need-usdot-number SPECIAL PROVISION – Notes in 172.102 to HM Table 172.101 that detail extra requirements for transporting certain HM in various packages. SPECIAL PERMIT -- Issued by PHMSA to allow a deviation from its rules as long as safety is not lessened. SAFETY PERMIT – Required by FMCSA for certain HM considered High Hazard. www.fmcsa.dot.gov/sites/fmcsa.dot.gov/files/docs/Hazardous_Materials_Safety_Permit_Progra m_Brochure.pdf Acronymonia Revisited FHWA DOE SAFER STP PHMSA USDOT# CPB CSA OOS CVSA RCRA TRB CDL MAP21 ANPRM PSP DQ DOT406 MC306 EOBR ASME MCSAP CT HME STEP ELD CFATS FMVSS SP ACC AAR NTSB NHTSA FAST CFR TWIC ERG MAWP Acronymonia Revisited John Conley, ConleyComm LLC concomm@atlantaaicbb.net FHWA- Federal Highway Administration) “provides stewardship” over the construction, maintenance and preservation of the Nation’s highways, bridges and tunnels. FHWA also conducts research and provides technical assistance to state and local agencies in an effort to improve safety, mobility, and livability, and to encourage innovation. www.fhwa.gov. DOE- Department of Energy. Agency can have its own rules for picking up some materials such as low level nuclear waste as well as unique driver identification requirements. SAFER -- The FMCSA Safety and Fitness Electronic Records (SAFER) System offers company safety data and related services to industry and the public over the Internet. Users can search FMCSA databases, register for a USDOT number, pay fines online, order company safety profiles, challenge FMCSA data using the DataQs system, access the Hazardous Material Route registry, obtain National Crash and Out of Service rates for Hazmat Permit Registration, get printable registration forms and find information about other FMCSA Information Systems. https://safer.fmcsa.dot.gov/ STP – Surface Transportation Program is one of the main sources of flexible funding available for transit or highway purposes. STP provides the greatest flexibility in the use of funds. These funds may be used (as capital funding) for public transportation capital improvements, car and vanpool projects, fringe and corridor parking facilities, bicycle and pedestrian facilities, and intercity or intracity bus terminals and bus facilities. PHMSA – Pipeline and Hazardous Materials Safety Administration—Writes regulations covering the transportation of hazardous materials. www.phmsa.dot USDOT# -- Companies that operate commercial vehicles transporting passengers or hauling cargo in interstate commerce must be registered with the FMCSA and must have a USDOT Number. Also, commercial intrastate hazardous materials carriers who haul quantities requiring a safety permit must register for a USDOT Number. http://www.fmcsa.dot.gov/registration/do-i-need-usdot-number. CPB -- U S Customs and Border Patrol is one of the world's largest law enforcement organizations and is charged with keeping terrorists and their weapons out of the U.S. while facilitating lawful international travel and trade. http://www.cbp.gov/about CSA -- – Compliance, Safety, Accountability – Process used by FMCSA to measure carrier safety and to determine what carriers need special enforcement attention. Carriers should check their scores on a regular basis as the information is available to the general public. csa.fmcsa.dot.gov/ and www.whatiscsa.com/glossary/ OOS – Out of Service criteria are developed by the Commercial Vehicle Safety Alliance (CVSA). www.cvsa.org. RCRA -- Resource Conservation and Recovery Act — commonly referred to as RCRA — is the primary law governing the disposal of solid and hazardous waste. Congress passed RCRA on October 21, 1976 to address the increasing problems the nation faced from our growing volume of municipal and industrial waste. http://www.epa.gov/osw/laws-regs/rcrahistory.htm TRB – Transportation Research Board receives government funds to conduct studies in a variety of fields, including trucking and hazardous materials transportation safety. www.trb.org CDL – Commercial Driver’s License is issued by the driver’s states of residence for to operate any type of vehicle: Weighing 26,001 pounds, or 10,001 pounds with any type of trailer towed Transports quantities of hazardous materials that require warning placards That is designed to transport 16 or more passengers (including driver) or more than 8 passengers (including the driver), for compensation. (Consult individual states.) MAP21 --, The Moving Ahead for Progress in the 21st Century Act (MAP-21). MAP-21 was signed on July 6, 2012, by President Obama. It was name given to law P.L. 112-141 which provided transportation funds for surface transportation programs at over $105 billion for fiscal years (FY) 2013 and 2014 (Note: We are now planning fiscal year 2016 and highway funding is still being done under a CR (Continuing Resolution.) ANPRM – Advance Notice of Public Rulemaking. First step through which a Federal government agency announces that it will write a regulation and solicits input. PSP -- The Pre-Employment Screening Program (PSP) allows carriers, individual drivers, and industry service providers access to commercial drivers' safety records from the Federal Motor Carrier Safety Administration's (FMCSA) Motor Carrier Management Information System (MCMIS.) Account holders may request PSP records solely for the purpose of conducting pre-employment screening and only with the driver's consent. Please remember that all account holders must use this language on every consent form. https://www.psp.fmcsa.dot.gov/psp/default.aspx. DQ – DataQs DataQs allows you to request and track a review of Federal and State data issued by FMCSA that you feel may be incomplete or incorrect. The system automatically forwards your Request for Data Review (RDR) to the appropriate office for resolution and collects updates and responses for current Requests. https://dataqs.fmcsa.dot.gov/Default.aspx?enc=4orUr4VSakAlYsjxOmHrCeQ158IknHedB2 0QvqZJtcw= DOT406 – Department of Transportation Specification for a cargo tank designed to haul petroleum and other hazardous materials built after August 31, 1995. See 178.345. MC306 – Department of Transportation Specification for a cargo tank designed to haul petroleum and other hazardous materials after December 1, 1967. Note: If a cargo tank is not maintained to the specification to which it was constructed, remove or mark out the specification plate or it will continue to be considered a specification cargo tank by DOT. EOBR or ELD -- Electric Onboard Recorder or Electronic Logging Device is an electronic device designed to record a driver's driving hours and duty status automatically. FMCSA has an open rulemaking which will eventually require ELDs for any driver required to keep logs. ASME – American Society of Mechanical Engineers is an independent organization which writes standards, some of which are adopted by government. Certain tank trailers must be built to meet the ASME Code and any manufacturer which builds specification cargo tanks must hold an ASME U-Stamp. MCSAP – The Motor Carrier Safety Assistance Program is authorized by Congress as a process for the Federal Department of Transportation to provide fund grants to states for improving commercial vehicle highway safety. Each state has a lead MCSAP agency and must meet certain Federal requirements to receive the tax money. CT Number -- The Cargo Tank (CT) number is assigned to facilities and/or individuals that manufacture, assemble, inspect, test, certify or perform welded repairs on cargo tanks or a cargo tank motor vehicles manufactured in accordance with a DOT specification or under the terms of an exemption. Make sure any shop that performs Part 180 Tests and Inspections on your cargo tanks holds a current CT number. http://www.fmcsa.dot.gov/registration/cargo-tank-facilities HME Hazardous Materials Endorsement is one of several endorsements to the CDL. The TSA Hazardous Materials Endorsement Threat Assessment Program conducts a security threat assessment for any driver seeking to obtain, renew, or transfer a hazardous materials endorsement (HME) on a state-issued commercial driver’s license (CDL). The program was implemented to meet the requirements of the USA PATRIOT Act which prohibits states from issuing a license to transport hazardous materials in commerce unless a determination has been made that the driver does not pose a security risk. The Act further requires that the risk assessment include checks of criminal history records, legal status, and relevant international databases. The driver must pass a fingerprint background check. http://www.tsa.gov/stakeholders/hazmat-endorsement-threat-assessment-program STEP -- Surface Transportation Environment and Planning Cooperative Research Program is a Federal program to provide money to improve understanding of the complex relationship between surface transportation, planning and the environment. CFATS – Chemical Facility Anti-Terrorism Standards were developed by the Department of Homeland Security. They establish risk-based performance standards for the security of chemical facilities. It requires covered chemical facilities to prepare Security Vulnerability Assessments, which identify facility security vulnerabilities, and to develop and implement Site Security Plans, which include measures that satisfy the identified risk-based performance standards. http://www.dhs.gov/chemical-facility-anti-terrorism-standards FMVSS – Federal Motor Vehicle Safety Standards. The National Highway Traffic Safety Administration issues Federal Motor Vehicle Safety Standards (FMVSS) and Regulations to which manufacturers of motor vehicle and equipment items must conform and certify compliance SP - Special Permit Safety Permit Special Provision. A Special Permit is issued by PHMSA and can allow a variation to regulation as long as safety is not lessened. A Safety Permit is issued by FMCSA to carriers of certain “high hazard” hazardous materials. A Special Provision is a note in the HM Table 172.100 which details extra requirements or restrictions for certain ACC American Chemistry Council represents chemical companies and has safety information available. It also manages the CHEMTREC hazardous materials emergency information program. www.americanchemistry.com. AAR – Association of American Railroads. Is active in developing new regulations for the rail transportation of crude oil. www.aar.org. NTSB – National Transportation Safety Board. Federal agency that investigates transportation crashes or incidents of any mode. NTSB makes recommendations to the public and private sectors, but does not have regulatory authority. www.ntsb.org. NHTSA – National Highway Traffic Safety Administration. NHTSA was established by the Highway Safety Act of 1970 and is dedicated to achieving the highest standards of excellence in motor vehicle and highway safety. www.nhtsa.gov FAST - Free and Secure Trade is a program through which truck drivers can apply for a FAST card which will reduce the time they spend at border crossings between the US and Canada and the US and Mexico. http://usa.immigrationvisaforms.com/travel/fast-pass-faqs CFR Code of Federal Regulations. The CFR contain all of the regulations of the Federal Government. They are available on-line. U S Department of Transportation regulations are in Title 49. http://www.archives.gov/federal-register/cfr/subject-title-49.html TWIC – Transportation Workers Identification Credential is a common identification credential for all personnel requiring unescorted access to secure areas of Maritime Transportation Security Act ( MTSA) -regulated facilities and vessels, and all mariners holding Coast Guard-issued credentials. Individuals who meet TWIC eligibility requirements will be issued a tamper-resistant credential containing the worker's biometric (fingerprint template) to (eventually) allow for a positive link between the card and the individual. ERG – Emergency Response Guide. Response Guidebook (ERG) provides first responders with a go-to manual to help deal with hazmat accidents during the critical first 30 minutes. The ERG contains an indexed list of dangerous goods and the associated ID number, the general hazards they pose and recommended safety precautions. The 2012 ERG is available for downloading from PHMSA and from commercial suppliers. http://www.phmsa.dot.gov/hazmat/library/erg MAWP – Maximum Allowable Working Pressure. means the maximum pressure allowed at the top of the cargo tank in its normal operating position. The MAWP must be calculated as prescribed in Section VIII of the ASME Code. In use, the MAWP must be greater than or equal to the maximum lading pressure conditions prescribed in § 173.33 of Title 49 for each material transported. Thank You! John Conley ConleyComm LLC 142 Evelyne St. Chester MD 216719 703/216-0449 concomm@atlanticbb.net