Weight
advertisement

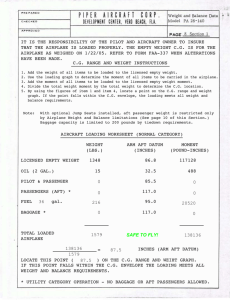
Commercial Pilot Ground School Stage 2 Module 2 Flight Computer Weight & Balance Flight Computer Reading Chapters 24 7 12 Finding True Airspeed Finding Heading and Ground speed Time en route and fuel calculations Wind components Unit conversions Find True Airspeed 20 deg. Celsius 4100 Pressure Altitude 96 KIAS Answers? Answer 104.1 KTS Find true heading and ground speed Wind 180 @ 10 TC 310 TAS 120 Answers? Answer TH = 306.3 deg. GS = 126.2 kts Calculate endurance Fuel 66 4 gal unusable 9.7 GPH @ 8000’ Answers? Answer: 06:23:30 62 gal. 6500 – (700 + 800) = 5000 to descend. 5000’ @ 500 FPM = 10 minutes. 107 Kts. GS +8 WCA WCA (+8) + Variation (+3) + Deviation (+2) = +13 TC 335 + 13 = 348 deg. CH 10 min. @ 8.5 gph = 1.4 gallons Using descent info, calculate time to descend. Calculate actual Ground speed and WCA Use variation, deviation and calculated WCA to find CH Use fuel burn and time, get fuel used Actual Winds Aloft TC 180 TH 160 GS 120 TAS 140 Start by setting TC under true index Place dot at -20 WCA with a 20 kt headwind TC 180 TH 160 GS 120 TAS 140 Rotate dot to top. Center at 100. TC 180 TH 160 GS 120 TAS 140 Answer: Winds 104 deg. At 50 Knots Off-course Correction Dist. Off / Miles Travelled Dist. Off / Miles To Go Pointer = Degrees to parallel Pointer = Degrees to intercept Total correction = Parallel + Intercept Off course corrections Off-Course Correction Dist Flown 150 NM Off Course 7 NM Dist Remaining 200 NM ( 7 * 60 ) \ 150 = 2.8 degrees to parallel 2.8 + 2.1 = 4.9 degrees ( 7 * 60 ) \ 200 = 2.1 degrees to go direct Conversions Find Statute miles 100 N.M. Find deg. Celsius 45 degrees F Weight Terminology Basic Empty weight = Standard empty weight + optional equipment. Standard empty weight = Weight of a standard airplane including unusable fuel, full operating fluids, and full oil. Licensed empty weight = Basic empty weight - undrainable oil (Older aircraft) Gross weight = Basic empty weight + every thing else that is loaded in the airplane. Useful load and Payload weight cont.. One gallon of AVGAS= 6 lbs. One gallon of oil = 7.5 lbs. Maximum weight- the airplane is limited to create enough lift for only a certain amount of weight( C-150=1600lbs). Maximum Ramp Weight Maximum Landing Weight Over weight If you load the aircraft over its max weight what can happen? higher stall speed higher takeoff speed and a longer takeoff run. Poor to no climb performance lower cruising level less maneuverability cont. higher fuel consumption, and less range and endurance reduced cruise speed for a given power setting higher landing speed and a longer landing distance and greater braking requirements when stopping Greater stress on structure of AC. Balance Center of gravity (CG) Pivotal point on the airplane where it would balance. Moment The force (turning effect) acting on the pivotal point (Datum) of the airplane. Weight x Arm = unit/units (pound/feet) Datum Reference plane from which all horizontal distances are measured. Completing a weight and balance Weight x CG = Moment Changes (deltas) Weight shifted x distance shifted = Gross weight X CG change CG Change = (Weight shifted x distance shifted) / Gross weight Center of Gravity Effects of movement of CG Forward CG Nose heavy, may not be able to rotate on takeoff or flare in the landing. More stable aircraft but will not perform as good Aft CG Tail heavy, will want to rotate sooner, will stall a lot quicker and stall characteristics will be quite different. More performance but will not be as stable.