Digestive Enzymes - Warren County Schools
advertisement

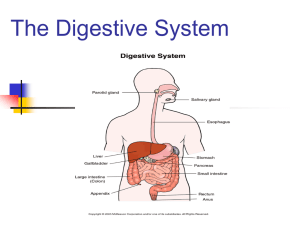
Enzymes………. Digestive Enzymes assist the body in the breakdown of food. Different enzymes with different functions are produced in particular areas of the digestive tract . • Incomplete digestion may be a contributing factor in the development of many ailments including flatulence, bloating, belching, food allergies, nausea, bad breath, bowel problems and stomach disorders. • Digestive enzymes are primarily responsible for the chemical breakdown of food and constitute a large portion of digestive secretions. The human body makes approximately 22 different enzymes that are involved in digestion. Mouth • Saliva contains the enzyme salivary amylase. This enzymes breaks starch into smaller sugars and is stimulated by chewing. It is important to chew food thoroughly as this is the first stage of the digestive process. Stomach • The stomach is responsible for the digestion of protein and ionisation of minerals. The parietal cells of the stomach secrete hydrochloric acid (gastric acid). Hydrochloric acid, along with pepsin, breaks down proteins to their individual amino acids. • Deficient hydrochloric acid secretion (hypochlorhydria) causes malabsorption and may result in a number of signs and symptoms. These include bloating, belching, flatulence, nausea, a sense of fullness immediately after meals, indigestion, diarrhoea, constipation, food allergies, anaemia (Folic acid, vitamin B12 and iron will not be absorbed if there is too little acid), undigested food in stool, chronic intestinal parasites, abnormal flora and weak, peeling and cracked fingernails. • A number of diseases have been associated with low gastric acidity. They include asthma, coeliac disease, eczema, osteoporosis and pernicious anaemia. An excess of hydrochloric acid (hyperchlorhydria) can cause heartburn, gas and may lead to ulcers. Small Intestine • The small intestine is divided into three segments and secretes a variety of digestive substances. The small intestine also receives secretions and enzymes from the pancreas, liver and the gallbladder. The first section, the duodenum, is primarily responsible for the absorption of minerals. The second section, the jejunum, absorbs water-soluble vitamins, protein and carbohydrates. The ileum is the final section of the small intestine and absorbs fat-soluble vitamins, fat, cholesterol and bile salts. Pancreas • The pancreas produces digestive enzymes that act in the small intestine. These enzymes play a major role in digestion. The pancreas secretes about one and a half litres of pancreatic juice a day. The enzymes produced by the pancreas include; - Lipases - Lipases function in the digestion of fats, oils and fat-soluble vitamins. - Amylases - These break down starch molecules into smaller sugars. Amylases also break down carbohydrates into maltose. - Proteases - are responsible for breaking down protein into smaller amino acids. Proteases include trypsin, chromotrypsin and carboxypeptidase. Proteases are also responsible for keeping the small intestine free from parasites (intestinal worms, yeast overgrowth and bacteria). A lack of proteases can cause incomplete digestion that can lead to allergies and the formation of toxins. Liver and Gall Bladder • The liver produces bile that is either stored by the gallbladder or secreted into the small intestine. Bile emulsifies fats and fatsoluble vitamins. It also helps keep the small intestine free from parasites. The liver metabolises proteins, carbohydrates and cholesterol and is responsible for the detoxification of toxins, drugs and hormones. PLANT ENZYMES • Plant enzymes also act in the stomach. They occur naturally in food or are taken as a supplement. They are essential for predigesting food and work with the body's own enzymes. Common plant enzymes are• Bromelain - a protein-digesting enzyme found in pineapples, primarily the core. Bromelain is called a proteolytic enzyme. This means it can prevent and help tissue damage, inflammation and swelling. - Papain- a protein-digesting enzyme extracted from pawpaw fruit (pawpaw). Papain can also decrease inflammation and tissue damage.